Intro
Acute pain is a common issue in nursing care, affecting millions of patients worldwide. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including surgery, injury, illness, or medical procedures. As a nurse, managing acute pain effectively is crucial to ensure patient comfort, prevent complications, and promote optimal recovery. In this article, we will explore five ways to manage acute pain in nursing care.
Effective pain management requires a comprehensive approach that involves assessing the patient's pain, developing an individualized pain management plan, and continuously monitoring and adjusting the plan as needed. Here are five ways to manage acute pain in nursing care:
1. Assessing Pain
Assessing pain is the first step in managing acute pain. Nurses should use a standardized pain assessment tool, such as the Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) or the Faces Pain Scale (FPS), to evaluate the patient's pain intensity, location, and characteristics. This information will help nurses to develop an individualized pain management plan that addresses the patient's specific needs.
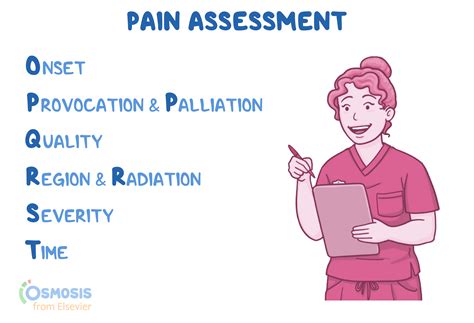
Pain Assessment Tools
- Numeric Rating Scale (NRS): A 0-10 scale that asks patients to rate their pain intensity.
- Faces Pain Scale (FPS): A scale that uses facial expressions to rate pain intensity.
- McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ): A questionnaire that evaluates pain intensity, location, and characteristics.
2. Pharmacological Interventions
Pharmacological interventions are a common approach to managing acute pain. Nurses should be familiar with various pain medications, including opioids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and acetaminophen. The choice of medication depends on the patient's pain intensity, medical history, and other health conditions.
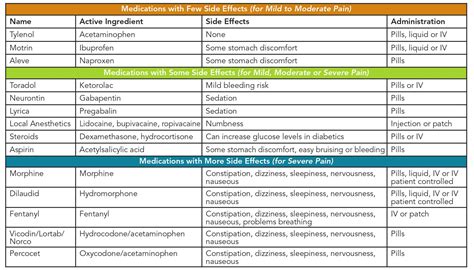
Common Pain Medications
- Opioids: Morphine, fentanyl, and oxycodone.
- NSAIDs: Ibuprofen, naproxen, and celecoxib.
- Acetaminophen: Tylenol.
3. Non-Pharmacological Interventions
Non-pharmacological interventions are an essential part of acute pain management. These interventions can reduce pain intensity, promote relaxation, and improve sleep quality. Nurses should consider the following non-pharmacological interventions:
Non-Pharmacological Interventions
- Deep breathing exercises
- Progressive muscle relaxation
- Guided imagery
- Music therapy
- Massage therapy
4. Alternative Therapies
Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), can be effective in managing acute pain. Nurses should consider these therapies as part of a comprehensive pain management plan.
Alternative Therapies
- Acupuncture
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)
- Heat and cold therapy
- Massage therapy
5. Patient Education
Patient education is a critical component of acute pain management. Nurses should educate patients about their pain management plan, including the use of pain medications, non-pharmacological interventions, and alternative therapies. Patients should also be encouraged to report any changes in their pain intensity or characteristics.

Key Points to Educate Patients
- Pain management plan
- Use of pain medications
- Non-pharmacological interventions
- Alternative therapies
- Reporting changes in pain intensity or characteristics
In conclusion, managing acute pain in nursing care requires a comprehensive approach that involves assessing pain, developing an individualized pain management plan, and continuously monitoring and adjusting the plan as needed. By using the five ways to manage acute pain outlined in this article, nurses can provide effective pain management and promote optimal recovery for their patients.
What is acute pain?
+Acute pain is a type of pain that is caused by a specific injury or illness and is typically short-term.
What are the common causes of acute pain?
+Common causes of acute pain include surgery, injury, illness, and medical procedures.
What are the benefits of non-pharmacological interventions for acute pain management?
+Non-pharmacological interventions, such as deep breathing exercises and progressive muscle relaxation, can reduce pain intensity, promote relaxation, and improve sleep quality.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights into managing acute pain in nursing care. Share your thoughts and experiences on this topic in the comments section below.
