Intro
Discover the significance of the Anion Gap Blood Test with our in-depth guide. Learn about the 5 crucial facts surrounding this vital medical test, including its purpose, calculation, and interpretation. Understand how it helps diagnose conditions like metabolic acidosis, kidney disease, and more. Get informed about your health with our expert insights.
The anion gap blood test is a crucial diagnostic tool used by healthcare professionals to identify and manage various medical conditions. While it may seem like a complex topic, understanding the basics of the anion gap blood test can empower individuals to take a more active role in their healthcare.
In this article, we will delve into the world of anion gap blood tests, exploring what they are, why they are performed, and what the results can reveal about a person's health.
What is an Anion Gap Blood Test?
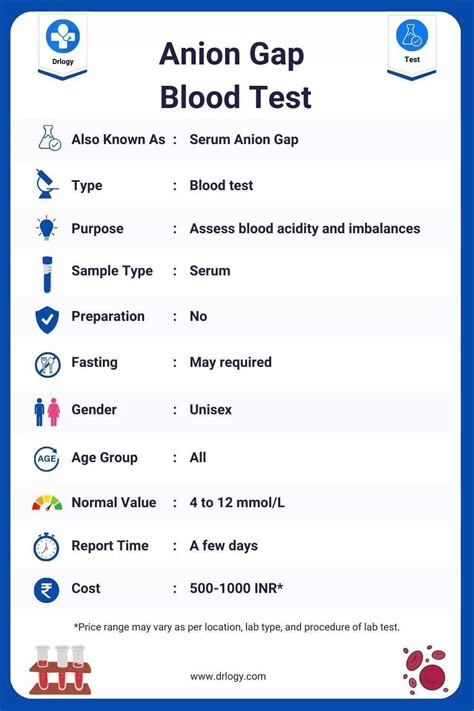
An anion gap blood test is a diagnostic tool used to measure the difference between the levels of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions) in the blood. The test is usually performed as part of a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) or an electrolyte panel.
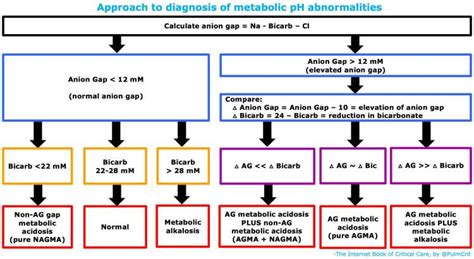
The anion gap is calculated by subtracting the sum of chloride and bicarbonate levels from the sum of sodium levels. The normal range for the anion gap is typically between 8-12 mmol/L. A high anion gap can indicate the presence of an underlying medical condition.
Why is an Anion Gap Blood Test Performed?
An anion gap blood test is performed for several reasons:
- To diagnose and monitor metabolic acidosis, a condition characterized by an excessive amount of acid in the blood
- To identify the presence of kidney disease or kidney failure
- To monitor the effectiveness of treatment for conditions such as diabetes and kidney disease
- To detect the presence of certain toxins or poisons in the blood
How is an Anion Gap Blood Test Performed?
The anion gap blood test is performed by drawing a blood sample from a vein in the arm. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
The test is usually performed as part of a routine check-up or when symptoms suggest the presence of an underlying medical condition. In some cases, the test may be performed on an emergency basis, such as when a person is experiencing severe symptoms or is suspected of having ingested a toxic substance.
What do the Results of an Anion Gap Blood Test Mean?
The results of an anion gap blood test can provide valuable information about a person's health. Here are some possible interpretations of the results:
- A normal anion gap: This suggests that the levels of cations and anions in the blood are balanced.
- A high anion gap: This can indicate the presence of metabolic acidosis, kidney disease, or other underlying medical conditions.
- A low anion gap: This is less common and may indicate the presence of certain medical conditions, such as hypoproteinemia or hyperchloremia.
What are the Causes of a High Anion Gap?
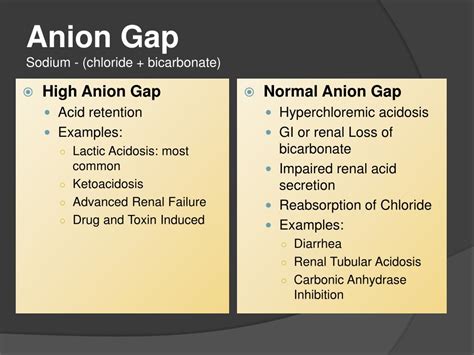
A high anion gap can be caused by several factors, including:
- Metabolic acidosis: This is a condition characterized by an excessive amount of acid in the blood.
- Kidney disease: Kidney disease can cause a high anion gap by impairing the kidneys' ability to filter waste products from the blood.
- Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can cause a high anion gap by leading to the production of ketones, which are acidic compounds.
- Poisoning: Ingestion of certain toxins, such as methanol or ethylene glycol, can cause a high anion gap.
- Lactic acidosis: This is a condition characterized by the accumulation of lactic acid in the blood.
What are the Symptoms of a High Anion Gap?
The symptoms of a high anion gap can vary depending on the underlying cause. Here are some possible symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Confusion
- Seizures
- Coma
How is a High Anion Gap Treated?
The treatment of a high anion gap depends on the underlying cause. Here are some possible treatments:
- Fluid replacement: Administering fluids to help restore balance to the blood.
- Medications: Using medications to treat underlying conditions, such as diabetes or kidney disease.
- Dialysis: Performing dialysis to remove waste products from the blood.
- Supportive care: Providing supportive care, such as oxygen therapy and pain management.
Can a High Anion Gap be Prevented?
While some causes of a high anion gap cannot be prevented, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk:
- Maintaining good blood sugar control if you have diabetes
- Following a healthy diet and lifestyle
- Avoiding toxins and poisons
- Getting regular check-ups with your healthcare provider
We hope this article has provided you with a better understanding of the anion gap blood test and its importance in diagnosing and managing various medical conditions. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider.
What is the normal range for the anion gap?
+The normal range for the anion gap is typically between 8-12 mmol/L.
What is the anion gap blood test used for?
+The anion gap blood test is used to diagnose and monitor metabolic acidosis, kidney disease, and other underlying medical conditions.
What are the symptoms of a high anion gap?
+The symptoms of a high anion gap can vary depending on the underlying cause, but may include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, confusion, seizures, and coma.
