Intro
Understanding applicable federal interest rates is crucial for individuals and businesses to make informed decisions about borrowing, investing, and managing debt. The federal interest rate, also known as the federal funds rate, is set by the Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States. It has a significant impact on the overall economy, as it influences the interest rates that banks charge their customers.
In this article, we will explore five ways to understand applicable federal interest rates, including their history, calculation, impact on the economy, and how they affect different types of loans and investments.
What Are Federal Interest Rates?
Federal interest rates are the interest rates at which banks and other depository institutions lend and borrow money from each other. These rates are set by the Federal Reserve, which uses them as a tool to promote economic growth, full employment, and low inflation. The federal funds rate is the interest rate at which banks lend and borrow money from each other overnight.
History of Federal Interest Rates
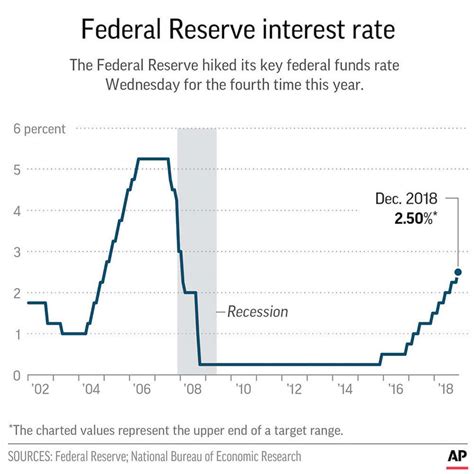
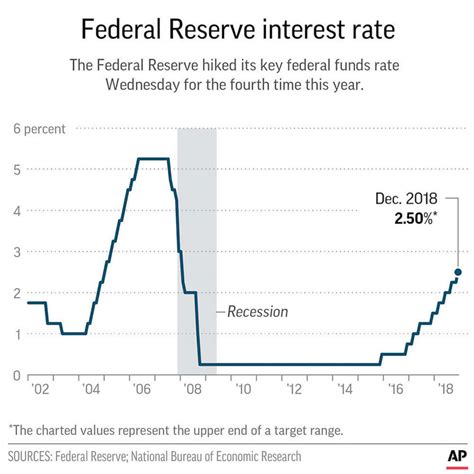
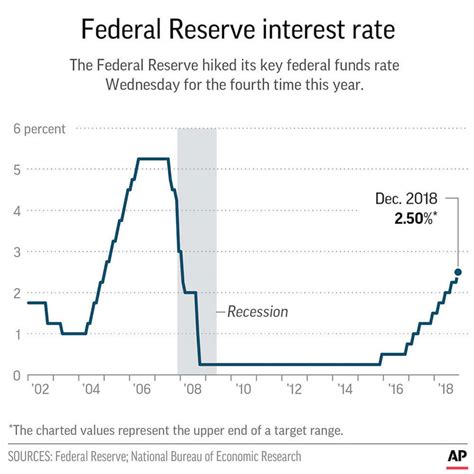
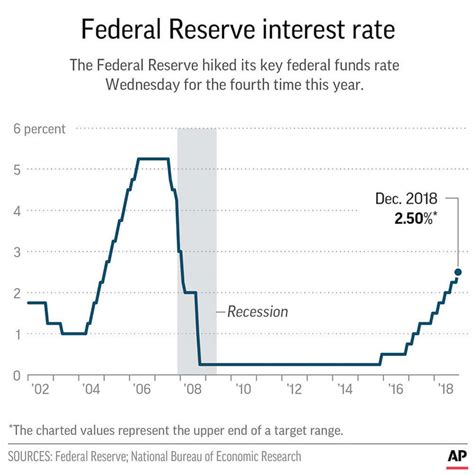
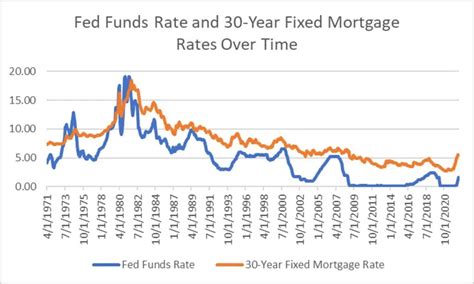
The history of federal interest rates dates back to the early 20th century, when the Federal Reserve was established. Since then, the federal funds rate has fluctuated significantly, influenced by various economic factors such as inflation, recession, and monetary policy.
In the 1970s and 1980s, the federal funds rate was relatively high, reaching as high as 20% in 1981. This was due to high inflation rates and the Federal Reserve's efforts to combat it. In the 1990s and 2000s, the federal funds rate declined, reaching as low as 1% in 2003.
During the 2008 financial crisis, the federal funds rate was lowered to near zero, where it remained until 2015. Since then, the rate has gradually increased, reaching 2.5% in 2019.
How Are Federal Interest Rates Calculated?
The federal funds rate is calculated based on the supply and demand of money in the economy. When banks have excess reserves, they lend them to other banks overnight at the federal funds rate. This rate is determined by the market forces of supply and demand.
The Federal Reserve also uses monetary policy tools, such as open market operations and reserve requirements, to influence the federal funds rate. For example, when the Federal Reserve buys government securities from banks, it increases the money supply and reduces the federal funds rate.
Impact of Federal Interest Rates on the Economy
Federal interest rates have a significant impact on the economy, influencing borrowing costs, spending, and investment. When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes cheaper, and consumers and businesses are more likely to take out loans and invest in new projects.
On the other hand, high interest rates make borrowing more expensive, which can slow down economic growth. However, high interest rates can also attract foreign investors, strengthen the currency, and reduce inflation.
How Do Federal Interest Rates Affect Different Types of Loans and Investments?
Federal interest rates affect different types of loans and investments in various ways. For example:
- Mortgages: When federal interest rates rise, mortgage rates also tend to increase, making it more expensive for homebuyers to borrow money.
- Credit cards: Higher federal interest rates can lead to higher credit card interest rates, making it more expensive for consumers to carry credit card debt.
- Savings accounts: Higher federal interest rates can lead to higher interest rates on savings accounts, making it more attractive for consumers to save money.
- Bonds: When federal interest rates rise, bond prices tend to fall, making it more attractive for investors to buy bonds.
Key Takeaways
- Federal interest rates are set by the Federal Reserve and have a significant impact on the economy.
- The federal funds rate is the interest rate at which banks lend and borrow money from each other overnight.
- Federal interest rates are calculated based on the supply and demand of money in the economy.
- Federal interest rates affect different types of loans and investments, such as mortgages, credit cards, savings accounts, and bonds.
What is the current federal interest rate?
+The current federal interest rate is 2.5% (as of 2023). However, interest rates are subject to change, and you should check the Federal Reserve's website for the most up-to-date information.
How do federal interest rates affect the stock market?
+Federal interest rates can affect the stock market in various ways. When interest rates rise, it can make borrowing more expensive, which can slow down economic growth and negatively impact the stock market. On the other hand, low interest rates can make borrowing cheaper, which can boost economic growth and positively impact the stock market.
Can I predict changes in federal interest rates?
+While it's possible to make educated guesses about changes in federal interest rates, it's challenging to predict them with certainty. The Federal Reserve considers various economic factors when setting interest rates, and unexpected events can influence their decisions.
In conclusion, understanding applicable federal interest rates is crucial for making informed decisions about borrowing, investing, and managing debt. By understanding the history, calculation, and impact of federal interest rates, you can better navigate the complex world of finance and make more informed decisions about your financial future.
