Intro
Discover the importance of monitoring your blood sugar levels after meals. Learn how to measure and interpret your postprandial glucose levels, and understand the impact of food choices on your blood sugar spikes. Get expert insights on managing blood sugar levels, insulin sensitivity, and preventing diabetes complications.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for our overall well-being. When we eat, our body breaks down the carbohydrates in our food into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. This causes our blood sugar levels to rise. But have you ever wondered what your blood sugar level should be after a meal? In this article, we will delve into the world of blood sugar levels, exploring what's considered normal, how to measure it, and what factors can influence it.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
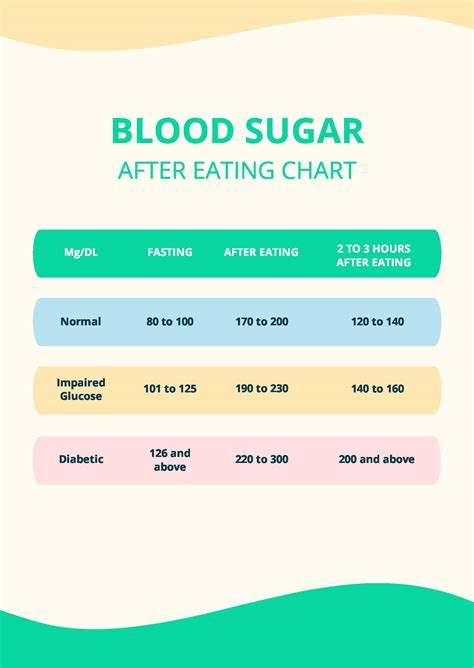
Blood sugar levels are measured in millimoles per liter (mmol/L) or milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). The American Diabetes Association recommends the following blood sugar levels:
- Fasting blood sugar (before eating): Less than 100 mg/dL
- Before meals: 70-130 mg/dL
- After meals (1-2 hours): Less than 180 mg/dL
However, these are general guidelines, and your target blood sugar levels may vary depending on your individual needs and health status.
Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels After a Meal
Several factors can influence your blood sugar levels after a meal, including:
- Type and amount of carbohydrates consumed
- Presence of fiber, protein, and healthy fats
- Physical activity level
- Medications or supplements
- Underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or insulin resistance
For example, consuming a meal high in simple carbohydrates, such as white bread or sugary snacks, can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, eating a balanced meal with protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Measuring Blood Sugar Levels
There are several ways to measure blood sugar levels, including:
- Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test: Measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast
- Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT): Measures blood sugar levels after consuming a sugary drink
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): Tracks blood sugar levels throughout the day
- Self-monitoring blood glucose (SMBG): Uses a glucometer to measure blood sugar levels at home
What to Do if Your Blood Sugar Levels Are High
If your blood sugar levels are consistently high after meals, there are several steps you can take:
- Consult with your healthcare provider to adjust your diet or medication
- Incorporate physical activity, such as walking or exercise, into your daily routine
- Choose complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables
- Include protein and healthy fats in your meals to slow down carbohydrate digestion
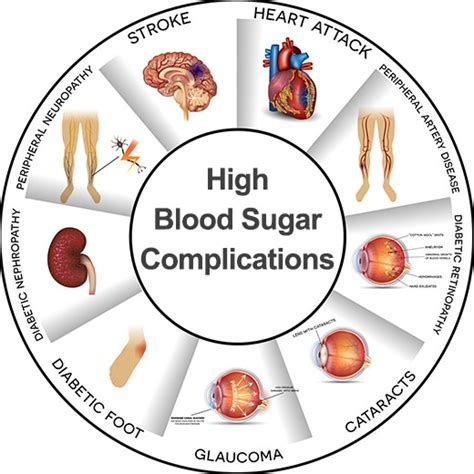
Complications of High Blood Sugar Levels
Consistently high blood sugar levels can lead to serious health complications, including:
- Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
- Cardiovascular disease and stroke
- Kidney damage and nephropathy
- Nerve damage and neuropathy
Prevention and Management
Preventing and managing high blood sugar levels requires a comprehensive approach, including:
- Healthy eating habits
- Regular physical activity
- Stress management
- Adequate sleep
- Regular health check-ups
By understanding what your blood sugar level should be after a meal and taking proactive steps to manage it, you can reduce your risk of developing serious health complications and maintain optimal well-being.
What is a normal blood sugar level after a meal?
+A normal blood sugar level after a meal is typically less than 180 mg/dL. However, this can vary depending on individual factors, such as age, health status, and medication.
How can I lower my blood sugar levels after a meal?
+To lower your blood sugar levels after a meal, try incorporating physical activity, choosing complex carbohydrates, and including protein and healthy fats in your meals.
What are the complications of high blood sugar levels?
+Consistently high blood sugar levels can lead to serious health complications, including insulin resistance, cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights into understanding your blood sugar levels after a meal. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider if you have any concerns or questions. Don't forget to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below!
