Intro
Master the California Board of Behavioral Sciences (BBS) with our expert guide. Discover 5 essential ways to navigate BBS requirements, including licensure, certification, and continuing education. Learn how to avoid common pitfalls and ensure compliance with BBS regulations, covering topics like MFT, LPCC, and LCSW licensure, to advance your behavioral science career in California.
Navigating the California Board of Behavioral Sciences (BBS) can be a daunting task, especially for those who are new to the field of behavioral sciences or are unfamiliar with the regulatory landscape. The BBS is responsible for regulating and overseeing the practices of licensed therapists, counselors, and social workers in California, and it plays a critical role in ensuring that these professionals provide high-quality services to their clients. In this article, we will explore five ways to navigate the California Board of Behavioral Sciences, including understanding the licensing process, staying up-to-date with continuing education requirements, and knowing how to file a complaint.
Understanding the Licensing Process
One of the most important aspects of navigating the BBS is understanding the licensing process. The BBS offers several types of licenses, including the Licensed Marriage and Family Therapist (LMFT), Licensed Professional Clinical Counselor (LPCC), and Licensed Clinical Social Worker (LCSW). Each of these licenses has its own set of requirements, including education, training, and experience.
To become licensed, applicants must submit an application to the BBS, which includes providing transcripts, training hours, and other documentation. The BBS also requires applicants to pass a written exam and a clinical exam, which assesses their knowledge and skills in areas such as diagnosis, treatment planning, and therapy techniques.
Staying Up-to-Date with Continuing Education Requirements
Continuing Education Requirements

In addition to obtaining a license, therapists, counselors, and social workers must also complete continuing education (CE) requirements to maintain their licenses. The BBS requires licensees to complete a certain number of CE hours every two years, which can include courses, workshops, and conferences.
Staying up-to-date with CE requirements is essential for navigating the BBS, as failure to complete the required hours can result in disciplinary action. Licensees can find approved CE providers on the BBS website, and they can also track their CE hours using the BBS's online system.
Knowing How to File a Complaint
Filing a Complaint

If a client or colleague has concerns about a therapist, counselor, or social worker, they may want to file a complaint with the BBS. The BBS has a formal complaint process, which involves submitting a written complaint and providing documentation to support the allegations.
Complaints can be filed online or by mail, and they must include specific information, such as the name of the licensee, the nature of the complaint, and the dates of the alleged misconduct. The BBS will then investigate the complaint and take disciplinary action if necessary.
Understanding the BBS's Enforcement Process
Enforcement Process
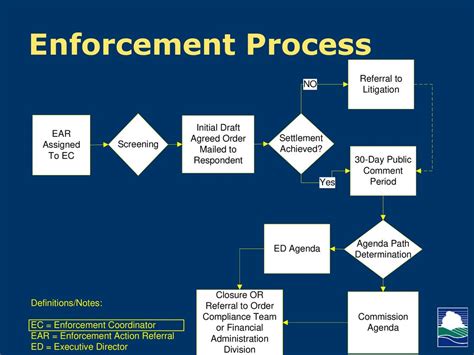
The BBS has the authority to take disciplinary action against licensees who violate the laws and regulations governing their professions. The BBS's enforcement process involves investigating complaints, conducting audits, and imposing discipline, such as fines, suspension, or revocation of a license.
Licensees who are subject to disciplinary action have the right to appeal the decision, and they can also request a hearing to contest the allegations. Understanding the BBS's enforcement process is essential for navigating the regulatory landscape and avoiding disciplinary action.
Seeking Support from Professional Organizations
Professional Organizations

Finally, navigating the BBS can be challenging, and licensees may need support from professional organizations, such as the California Association of Marriage and Family Therapists (CAMFT) or the California Association of Licensed Professional Clinical Counselors (CALPCC). These organizations provide resources, such as continuing education courses, advocacy, and support, to help licensees navigate the regulatory landscape.
Professional organizations can also provide guidance on licensing requirements, CE hours, and disciplinary action, and they can advocate for licensees' rights and interests. Joining a professional organization is an essential step in navigating the BBS and staying up-to-date with the latest developments in the field.
In conclusion, navigating the California Board of Behavioral Sciences requires a deep understanding of the licensing process, continuing education requirements, and the enforcement process. By staying informed and seeking support from professional organizations, therapists, counselors, and social workers can avoid disciplinary action and provide high-quality services to their clients.
We encourage you to share your experiences and thoughts on navigating the BBS in the comments below. How have you navigated the licensing process or stayed up-to-date with CE requirements? What challenges have you faced, and how have you overcome them?
What is the California Board of Behavioral Sciences?
+The California Board of Behavioral Sciences (BBS) is a state agency responsible for regulating and overseeing the practices of licensed therapists, counselors, and social workers in California.
What types of licenses does the BBS offer?
+The BBS offers several types of licenses, including the Licensed Marriage and Family Therapist (LMFT), Licensed Professional Clinical Counselor (LPCC), and Licensed Clinical Social Worker (LCSW).
How do I file a complaint with the BBS?
+Complaints can be filed online or by mail, and they must include specific information, such as the name of the licensee, the nature of the complaint, and the dates of the alleged misconduct.
What is the purpose of continuing education requirements?
+The purpose of continuing education requirements is to ensure that licensees stay up-to-date with the latest developments in their field and maintain their competence to practice.
What are the consequences of failing to complete continuing education requirements?
+Failing to complete continuing education requirements can result in disciplinary action, including fines, suspension, or revocation of a license.
