Intro
Discover the hidden link between dehydration and diarrhea. Learn how dehydration triggers diarrhea through 5 key mechanisms, including electrolyte imbalance, gut motility, and intestinal permeability. Stay hydrated and prevent diarrhea with our expert insights, exploring the intersection of dehydration, gut health, and digestive wellness.
Dehydration and diarrhea are two closely linked health issues that can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life. While it may seem counterintuitive, dehydration can actually trigger diarrhea, creating a vicious cycle that can be challenging to break. In this article, we will explore the five ways dehydration triggers diarrhea, and what you can do to prevent and manage these issues.
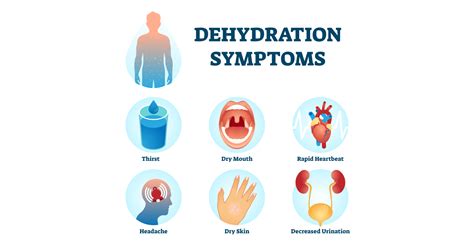
Understanding Dehydration and Diarrhea
Before we dive into the ways dehydration triggers diarrhea, it's essential to understand these two health issues. Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, causing an imbalance in the body's water and electrolyte levels. Diarrhea, on the other hand, is a condition characterized by loose, watery stools that can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, food poisoning, and certain medications.
The Link Between Dehydration and Diarrhea
Dehydration and diarrhea are closely linked, as diarrhea can cause dehydration, and dehydration can trigger diarrhea. When the body loses fluids and electrolytes due to diarrhea, it can disrupt the balance of fluids in the body, leading to dehydration. Conversely, dehydration can cause the body to pull water from the colon, making stools looser and more watery, which can trigger diarrhea.
5 Ways Dehydration Triggers Diarrhea
Now that we understand the link between dehydration and diarrhea, let's explore the five ways dehydration triggers diarrhea.
1. Electrolyte Imbalance
Dehydration can cause an electrolyte imbalance in the body, which can disrupt the functioning of the digestive system. Electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and chloride, play a crucial role in regulating the balance of fluids in the body. When the body loses electrolytes due to dehydration, it can cause the muscles in the digestive tract to contract, leading to diarrhea.

2. Reduced Blood Flow to the Gut
Dehydration can cause a decrease in blood flow to the gut, which can lead to a reduction in the absorption of nutrients and electrolytes. This can cause the body to pull water from the colon, making stools looser and more watery, which can trigger diarrhea.
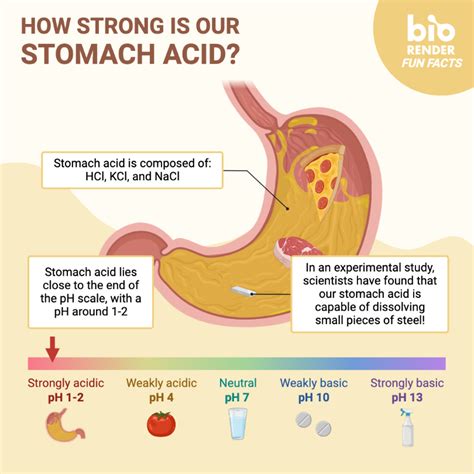
3. Increased Production of Gastric Acid
Dehydration can cause an increase in the production of gastric acid in the stomach, which can irritate the digestive tract and trigger diarrhea. Gastric acid is essential for breaking down food, but excessive production can cause inflammation and irritation in the digestive tract.
4. Disruption of Gut Motility
Dehydration can disrupt the normal functioning of the gut, causing a slowdown in gut motility. Gut motility refers to the movement of food through the digestive tract. When gut motility is disrupted, it can cause food to sit in the digestive tract for longer periods, leading to fermentation and the production of gas, which can trigger diarrhea.
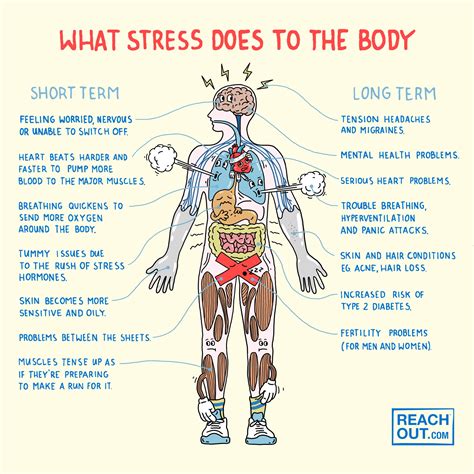
5. Increased Stress on the Body
Dehydration can cause increased stress on the body, which can trigger the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones can cause the digestive system to slow down, leading to a buildup of toxins in the body, which can trigger diarrhea.
Preventing and Managing Dehydration and Diarrhea
Preventing and managing dehydration and diarrhea requires a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and medical treatment. Here are some tips to help you prevent and manage dehydration and diarrhea:
- Drink plenty of fluids, including water, clear broths, and electrolyte-rich beverages like sports drinks.
- Avoid caffeinated and carbonated beverages, which can exacerbate dehydration.
- Eat a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Avoid spicy, fatty, and high-fiber foods, which can irritate the digestive tract.
- Practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands regularly, to prevent the spread of infections.
- Seek medical attention if you experience severe diarrhea, vomiting, or signs of dehydration, such as excessive thirst, dark urine, or dizziness.

Conclusion
Dehydration and diarrhea are two closely linked health issues that can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life. By understanding the five ways dehydration triggers diarrhea, you can take steps to prevent and manage these issues. Remember to drink plenty of fluids, eat a balanced diet, and practice good hygiene to prevent dehydration and diarrhea. If you experience severe symptoms, seek medical attention to prevent complications.
What are the symptoms of dehydration?
+The symptoms of dehydration include excessive thirst, dark urine, dizziness, headache, and fatigue.
How can I prevent dehydration?
+You can prevent dehydration by drinking plenty of fluids, including water, clear broths, and electrolyte-rich beverages like sports drinks. Avoid caffeinated and carbonated beverages, which can exacerbate dehydration.
What are the complications of dehydration?
+The complications of dehydration include kidney damage, heat stroke, and seizures. In severe cases, dehydration can be life-threatening.
