Intro
Atrial fibrillation, commonly referred to as Afib, is a type of irregular heartbeat that can significantly impact a person's quality of life. It occurs when the upper chambers of the heart, known as the atria, beat chaotically and irregularly, leading to symptoms such as palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue. While there are various treatment options available for Afib, cardioversion is a popular choice for many patients. In this article, we will explore six ways to treat Afib with cardioversion.
What is Cardioversion?
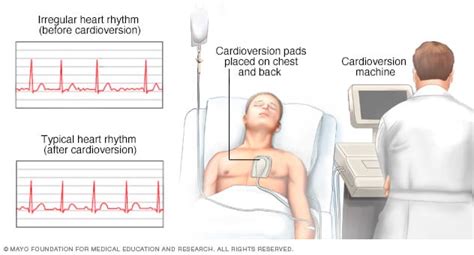
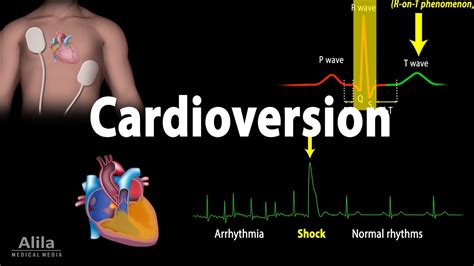
Cardioversion is a medical procedure that uses electrical shocks to restore a normal heartbeat in patients with Afib. During the procedure, a doctor will use a defibrillator to deliver a controlled electrical shock to the heart, which helps to reset the heart's rhythm and restore a normal sinus rhythm. Cardioversion is often performed in a hospital setting, and the procedure typically takes about 30 minutes to an hour to complete.
6 Ways to Treat Afib with Cardioversion
1. Electrical Cardioversion
How it Works
Electrical cardioversion is the most common type of cardioversion used to treat Afib. During the procedure, a doctor will use a defibrillator to deliver a controlled electrical shock to the heart. The shock is usually administered through patches placed on the chest, and the patient is typically under sedation to minimize discomfort.
Benefits of Electrical Cardioversion
- Highly effective in restoring a normal heartbeat
- Can be performed in a hospital setting
- Quick procedure time (about 30 minutes to an hour)
2. Pharmacological Cardioversion
How it Works
Pharmacological cardioversion uses medications to restore a normal heartbeat in patients with Afib. These medications, known as anti-arrhythmics, work by slowing down the heart rate and restoring a normal sinus rhythm.
Benefits of Pharmacological Cardioversion
- Can be performed in a hospital setting or at home
- May be more suitable for patients who are not good candidates for electrical cardioversion
- Can be used in combination with electrical cardioversion
3. External Cardioversion
How it Works
External cardioversion uses a defibrillator to deliver a controlled electrical shock to the heart from outside the body. This type of cardioversion is often used in emergency situations where a patient's Afib is causing severe symptoms.
Benefits of External Cardioversion
- Quick and effective in restoring a normal heartbeat
- Can be performed in a hospital setting or emergency room
- May be more suitable for patients who are in critical condition
4. Internal Cardioversion
How it Works
Internal cardioversion uses a device implanted in the chest to deliver a controlled electrical shock to the heart. This type of cardioversion is often used in patients who have a history of recurrent Afib.
Benefits of Internal Cardioversion
- Can be used to treat recurrent Afib
- May be more suitable for patients who are not good candidates for external cardioversion
- Can be used in combination with medications to prevent Afib episodes
5. Biphasic Cardioversion
How it Works
Biphasic cardioversion uses a defibrillator that delivers two electrical shocks to the heart in rapid succession. This type of cardioversion is often used in patients who have a history of failed cardioversion attempts.
Benefits of Biphasic Cardioversion
- Highly effective in restoring a normal heartbeat
- May be more suitable for patients who have a history of failed cardioversion attempts
- Can be used in combination with medications to prevent Afib episodes
6. Catheter Ablation with Cardioversion
How it Works
Catheter ablation with cardioversion uses a minimally invasive procedure to destroy the abnormal electrical pathways in the heart that are causing Afib. During the procedure, a doctor will use a catheter to deliver energy to the heart, which helps to restore a normal sinus rhythm.
Benefits of Catheter Ablation with Cardioversion
- Highly effective in restoring a normal heartbeat
- Minimally invasive procedure
- May be more suitable for patients who are not good candidates for other types of cardioversion
Conclusion
Cardioversion is a highly effective treatment option for patients with Afib. By understanding the different types of cardioversion available, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment options. Whether it's electrical cardioversion, pharmacological cardioversion, or catheter ablation with cardioversion, there are many ways to treat Afib with cardioversion. If you're experiencing symptoms of Afib, talk to your doctor about the best treatment option for you.
FAQs
What is the success rate of cardioversion?
+The success rate of cardioversion varies depending on the type of procedure used and the individual patient. However, studies have shown that cardioversion can be effective in restoring a normal heartbeat in up to 90% of patients.
What are the risks associated with cardioversion?
+While cardioversion is generally a safe procedure, there are some risks associated with it. These include bleeding, infection, and stroke. However, these risks are rare and can be minimized by following the doctor's instructions and taking medications as prescribed.
How long does it take to recover from cardioversion?
+The recovery time for cardioversion varies depending on the type of procedure used and the individual patient. However, most patients can return to their normal activities within a few days of the procedure.
