Intro
Discover the complexities of Closed Head Injury, a type of traumatic brain injury that occurs when the head is struck or shaken, causing damage to the brain without penetrating the skull. Learn about symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and rehabilitation strategies for this often-misdiagnosed condition, also known as non-penetrating TBI.
Traumatic brain injuries (TBI) are a leading cause of death and disability worldwide, with closed head injuries being one of the most common types. A closed head injury occurs when the brain is damaged due to a blow to the head or a sudden deceleration, without any visible signs of trauma. This type of injury can be devastating, affecting not only the individual but also their loved ones. In this article, we will delve into the world of closed head injuries, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and the importance of seeking medical attention.
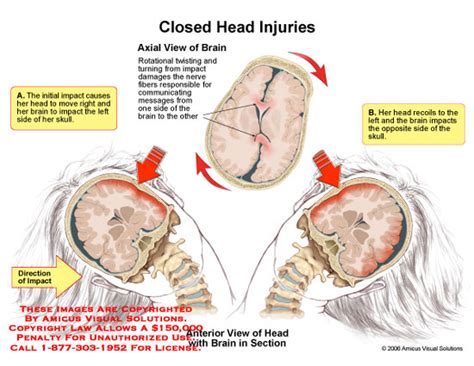
Causes of Closed Head Injuries
Closed head injuries can occur due to various reasons, including:
- Falls: Falls are a leading cause of closed head injuries, especially among older adults and young children.
- Motor vehicle accidents: Car accidents can result in closed head injuries, especially if the individual is not wearing a seatbelt or is ejected from the vehicle.
- Sports injuries: Contact sports, such as football, hockey, and soccer, can increase the risk of closed head injuries.
- Assaults: Physical assaults can result in closed head injuries, especially if the individual is hit on the head or face.
Symptoms of Closed Head Injuries
The symptoms of closed head injuries can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Common symptoms include:
- Headache: A headache is one of the most common symptoms of a closed head injury.
- Dizziness: Dizziness or loss of balance can occur due to a closed head injury.
- Nausea and vomiting: Some individuals may experience nausea and vomiting after a closed head injury.
- Confusion: Confusion, disorientation, or difficulty concentrating can be symptoms of a closed head injury.
- Memory loss: Memory loss or difficulty remembering events before or after the injury can occur.
Diagnosing Closed Head Injuries
Diagnosing closed head injuries can be challenging, as the symptoms may not be immediately apparent. A healthcare professional will typically perform a physical examination and take a detailed medical history to diagnose a closed head injury. Imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRI scans, may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Closed Head Injuries
The treatment options for closed head injuries depend on the severity of the injury. Mild closed head injuries may require:
- Rest: Rest and relaxation can help alleviate symptoms.
- Pain management: Over-the-counter pain medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help manage headaches and other symptoms.
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring by a healthcare professional is essential to ensure the individual is recovering properly.
Moderate to severe closed head injuries may require:
- Hospitalization: Hospitalization may be necessary to monitor the individual's condition and provide treatment.
- Surgery: Surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the brain or repair damaged blood vessels.
- Rehabilitation: Rehabilitation, including physical, occupational, and speech therapy, may be necessary to help the individual recover.
Importance of Seeking Medical Attention
Seeking medical attention immediately after a closed head injury is crucial. Delaying medical attention can lead to further complications, including:
- Brain damage: Untreated closed head injuries can lead to permanent brain damage.
- Increased risk of seizures: Untreated closed head injuries can increase the risk of seizures.
- Increased risk of dementia: Untreated closed head injuries can increase the risk of dementia.
Preventing Closed Head Injuries
While some closed head injuries are unavoidable, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk:
- Wearing protective gear: Wearing protective gear, such as helmets, can reduce the risk of closed head injuries.
- Following safety guidelines: Following safety guidelines, such as wearing seatbelts, can reduce the risk of closed head injuries.
- Being aware of surroundings: Being aware of surroundings can reduce the risk of falls and other accidents.

Recovering from a Closed Head Injury
Recovering from a closed head injury can be a long and challenging process. It's essential to:
- Follow medical advice: Following medical advice and treatment plans is crucial for recovery.
- Get plenty of rest: Getting plenty of rest and relaxation can help alleviate symptoms.
- Seek support: Seeking support from family, friends, and support groups can help individuals cope with the emotional and psychological aspects of recovery.
Conclusion
Closed head injuries can be devastating, affecting not only the individual but also their loved ones. Seeking medical attention immediately after a closed head injury is crucial to prevent further complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and importance of seeking medical attention, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk of closed head injuries and ensure proper recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a closed head injury?
+A closed head injury occurs when the brain is damaged due to a blow to the head or a sudden deceleration, without any visible signs of trauma.
What are the symptoms of a closed head injury?
+The symptoms of a closed head injury can vary depending on the severity of the injury, but common symptoms include headache, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, confusion, and memory loss.
How is a closed head injury diagnosed?
+A healthcare professional will typically perform a physical examination and take a detailed medical history to diagnose a closed head injury. Imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRI scans, may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis.
