Intro
Unlock the power of descriptive statistics in Excel with our 5-step guide. Master the art of summarizing and analyzing data with ease, using tools like mean, median, mode, and standard deviation. Improve data visualization and interpretation skills with Excels built-in functions, and make informed decisions with confidence.
Descriptive statistics is a crucial aspect of data analysis, providing a comprehensive summary of a dataset's characteristics. Microsoft Excel, a widely used spreadsheet software, offers a range of tools and functions to help users master descriptive statistics. In this article, we will explore the 5 easy steps to master descriptive statistics in Excel.
Understanding Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics is a branch of statistics that deals with summarizing and describing the main features of a dataset. It involves calculating various measures such as mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and variance to understand the distribution of data. Descriptive statistics is essential in data analysis, as it helps to identify patterns, trends, and correlations within the data.
Step 1: Preparing Your Data
Before diving into descriptive statistics, it's essential to prepare your data in Excel. This involves organizing your data into a clean and structured format. Here are a few tips to help you prepare your data:
- Ensure that your data is in a single column or row.
- Remove any duplicate or missing values.
- Check for errors and inconsistencies in the data.
- Use headers to label your data columns.
Step 2: Calculating Mean and Median
The mean and median are two of the most commonly used measures of central tendency in descriptive statistics. The mean is the average value of a dataset, while the median is the middle value when the data is arranged in ascending order.
To calculate the mean in Excel, use the AVERAGE function. For example, if your data is in cells A1:A10, the formula would be:
=AVERAGE(A1:A10)
To calculate the median, use the MEDIAN function:
=MEDIAN(A1:A10)
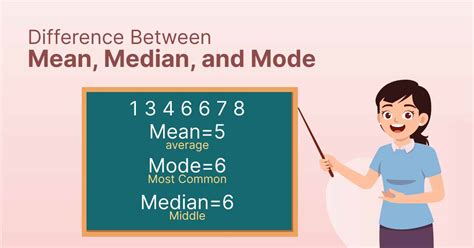
Step 3: Calculating Mode and Standard Deviation
The mode is the most frequently occurring value in a dataset, while the standard deviation measures the amount of variation or dispersion in the data.
To calculate the mode in Excel, use the MODE function:
=MODE(A1:A10)
To calculate the standard deviation, use the STDEV function:
=STDEV(A1:A10)

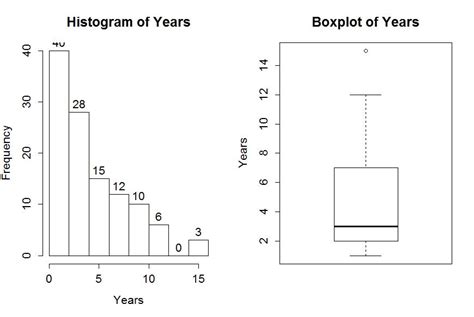
Step 4: Creating Histograms and Box Plots
Histograms and box plots are visual representations of data that help to understand the distribution of values.
To create a histogram in Excel, go to the "Insert" tab, click on "Bar Chart," and then select "Histogram." To create a box plot, go to the "Insert" tab, click on "Other Charts," and then select "Box and Whisker."
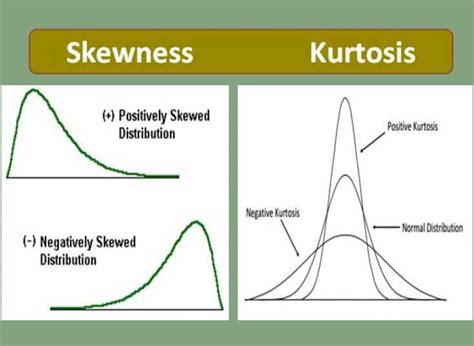
Step 5: Analyzing Skewness and Kurtosis
Skewness and kurtosis are measures of the shape of a distribution. Skewness measures the asymmetry of the distribution, while kurtosis measures the "tailedness" or "peakedness" of the distribution.
To calculate skewness and kurtosis in Excel, use the SKEW and KURT functions respectively:
=SKEW(A1:A10) =KURT(A1:A10)
Putting it All Together
Mastering descriptive statistics in Excel requires practice and patience. By following these 5 easy steps, you can become proficient in calculating various measures of central tendency, dispersion, and shape. Remember to always prepare your data, calculate mean and median, mode and standard deviation, create histograms and box plots, and analyze skewness and kurtosis.
What is descriptive statistics?
+Descriptive statistics is a branch of statistics that deals with summarizing and describing the main features of a dataset.
How do I calculate mean in Excel?
+To calculate mean in Excel, use the AVERAGE function. For example, if your data is in cells A1:A10, the formula would be: =AVERAGE(A1:A10)
What is the difference between skewness and kurtosis?
+Skewness measures the asymmetry of the distribution, while kurtosis measures the "tailedness" or "peakedness" of the distribution.
We hope this article has helped you master descriptive statistics in Excel. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences, please leave a comment below. Don't forget to share this article with your friends and colleagues who may find it useful.
