Intro
Discover the importance of the Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT) in detecting gastrointestinal disorders. Learn how this non-invasive screening test helps identify hidden blood in stool, a potential indicator of colon cancer, ulcers, and other gut health issues. Understand the procedure, preparation, and results interpretation to take control of your digestive health.
The importance of early detection and prevention of diseases cannot be overstated. One of the most effective ways to achieve this is through regular health screenings. Among the various tests available, the Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT) has proven to be a valuable tool in identifying potential health issues, particularly in the detection of colorectal cancer. In this article, we will delve into the world of FOBT, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and steps involved in the testing process.
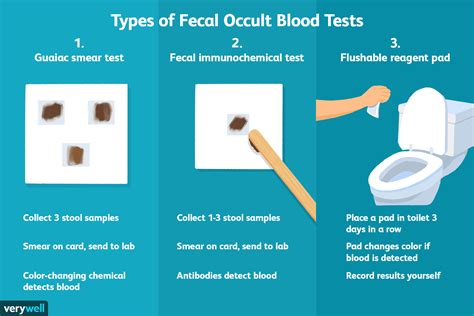
What is a Fecal Occult Blood Test?
A Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT) is a non-invasive screening test used to detect the presence of hidden (occult) blood in stool samples. The test is designed to identify bleeding in the digestive tract, which can be a sign of various health issues, including colorectal cancer, ulcers, and inflammatory bowel disease.
How Does FOBT Work?
The FOBT works by detecting the presence of hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells, in stool samples. When bleeding occurs in the digestive tract, the blood is broken down into smaller components, including hemoglobin, which is then excreted in the stool. The FOBT uses a chemical reaction to detect the presence of hemoglobin, which indicates the presence of blood in the stool.
Benefits of FOBT
The FOBT offers several benefits, including:
- Early detection of colorectal cancer: FOBT has been shown to be effective in detecting colorectal cancer in its early stages, when it is more treatable.
- Non-invasive: The test is non-invasive, requiring only a stool sample, making it a more comfortable option for patients.
- Cost-effective: FOBT is a relatively inexpensive test compared to other diagnostic tests, such as colonoscopy.
- Simple to perform: The test is easy to perform, requiring only a few minutes to complete.
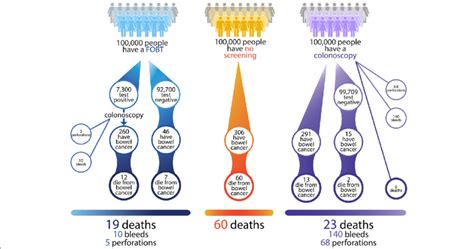
Steps Involved in FOBT
The FOBT involves the following steps:
- Collection of stool sample: A stool sample is collected from the patient, usually in a special container.
- Preparation of the sample: The stool sample is prepared for testing by adding a chemical solution that helps to detect the presence of hemoglobin.
- Testing: The prepared sample is then tested for the presence of hemoglobin using a chemical reaction.
- Interpretation of results: The results of the test are interpreted by a healthcare professional, who will determine if further testing is required.
What to Expect During FOBT
During the FOBT, patients can expect the following:
- A healthcare professional will provide instructions on how to collect the stool sample.
- The patient will collect the stool sample in a special container.
- The sample will be sent to a laboratory for testing.
- The results of the test will be interpreted by a healthcare professional.
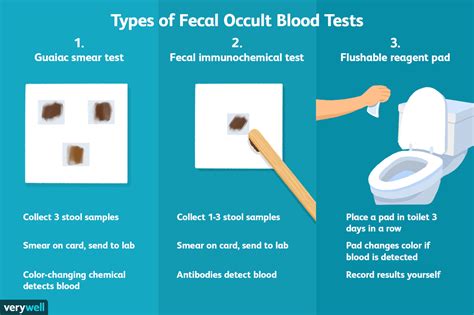
FOBT Results
The results of the FOBT can be either positive or negative.
- Positive result: A positive result indicates the presence of blood in the stool, which may require further testing to determine the cause of the bleeding.
- Negative result: A negative result indicates that no blood was detected in the stool.
What to Do if FOBT Results are Positive
If the FOBT results are positive, patients should:
- Follow up with their healthcare professional to discuss the results.
- Undergo further testing, such as a colonoscopy, to determine the cause of the bleeding.
- Follow any recommended treatment plans.
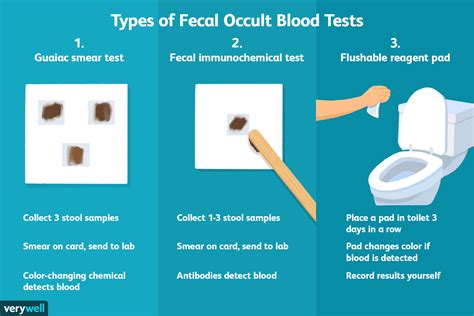
Limitations of FOBT
While the FOBT is a valuable tool in detecting colorectal cancer, it has some limitations, including:
- False positive results: The test may detect bleeding from other sources, such as ulcers or inflammatory bowel disease.
- False negative results: The test may not detect bleeding in all cases, particularly if the bleeding is intermittent.
- Limited sensitivity: The test may not detect small amounts of bleeding.
Improving FOBT Accuracy
To improve the accuracy of the FOBT, patients can:
- Follow the instructions provided by their healthcare professional for collecting the stool sample.
- Avoid eating certain foods, such as red meat, before collecting the sample.
- Avoid taking certain medications, such as aspirin, before collecting the sample.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the Fecal Occult Blood Test is a valuable tool in detecting colorectal cancer and other health issues. While it has some limitations, the benefits of early detection and prevention make it an important screening test for patients. By understanding the benefits, working mechanisms, and steps involved in the testing process, patients can make informed decisions about their health.
What is the purpose of a Fecal Occult Blood Test?
+The purpose of a Fecal Occult Blood Test is to detect the presence of hidden (occult) blood in stool samples, which can be a sign of various health issues, including colorectal cancer, ulcers, and inflammatory bowel disease.
How does FOBT work?
+FOBT works by detecting the presence of hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells, in stool samples. When bleeding occurs in the digestive tract, the blood is broken down into smaller components, including hemoglobin, which is then excreted in the stool.
What are the benefits of FOBT?
+The benefits of FOBT include early detection of colorectal cancer, non-invasive testing, cost-effectiveness, and simplicity of performance.
