Intro
Identify gestational diabetes symptoms early to ensure a healthy pregnancy. Learn to recognize warning signs such as increased thirst, frequent urination, and blurred vision. Understand the risks and complications associated with gestational diabetes, and discover the importance of prenatal care and glucose testing for a safe and successful pregnancy.
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy, usually in the second or third trimester. It affects millions of women worldwide, and if left untreated, can pose serious health risks to both the mother and the baby. Recognizing gestational diabetes symptoms early on is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications. In this article, we will delve into the importance of early detection, the common symptoms of gestational diabetes, and what to expect if you are diagnosed with this condition.
Why Early Detection Matters
Gestational diabetes can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. Some of the potential risks include:
- High birth weight: Babies born to mothers with uncontrolled gestational diabetes may experience high birth weight, which can increase the risk of cesarean delivery and other complications.
- Preterm labor: Women with gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of preterm labor, which can lead to respiratory problems and other health issues in the baby.
- Hypoglycemia: Newborns of mothers with gestational diabetes may experience hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) after birth, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
- Increased risk of type 2 diabetes: Women who develop gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes
Certain women are at a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes. These risk factors include:
- Age: Women over 35 years old are at a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes.
- Obesity: Women with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher are at a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes.
- Family history: Women with a family history of diabetes are at a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes.
- Previous history of gestational diabetes: Women who have had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy are at a higher risk of developing it again.
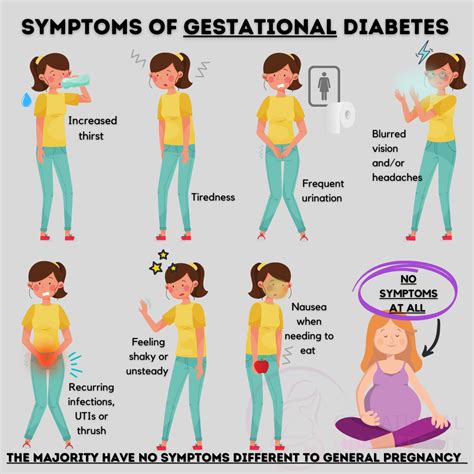
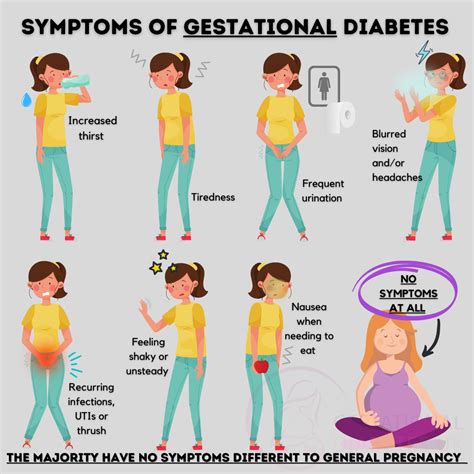
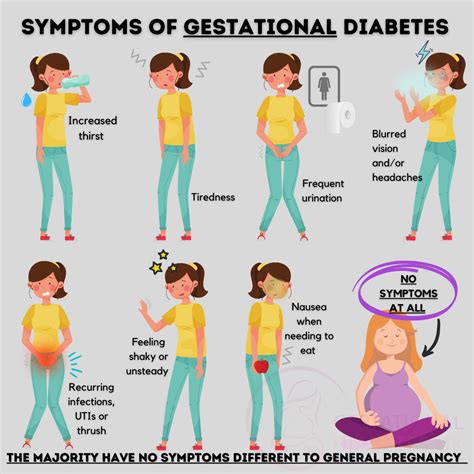
Common Symptoms of Gestational Diabetes
While some women may not experience any noticeable symptoms, others may exhibit the following:
- Increased thirst and urination: High blood sugar levels can cause the kidneys to produce more urine, leading to increased thirst and urination.
- Fatigue: High blood sugar levels can cause fatigue, which can be mistaken for normal pregnancy exhaustion.
- Blurred vision: High blood sugar levels can cause blurred vision, which can be a symptom of gestational diabetes.
- Cuts or wounds that are slow to heal: High blood sugar levels can affect the body's ability to heal wounds.
How Gestational Diabetes is Diagnosed
Gestational diabetes is typically diagnosed between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy using a glucose screening test. This test involves drinking a sugary drink and then having a blood test to measure blood sugar levels. If the results are high, a follow-up glucose tolerance test may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Managing Gestational Diabetes
If you are diagnosed with gestational diabetes, your healthcare provider will work with you to develop a management plan. This may include:
- Dietary changes: Eating a healthy, balanced diet that is low in sugar and refined carbohydrates can help manage blood sugar levels.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Monitoring blood sugar levels: Regularly checking blood sugar levels can help you understand how different foods and activities affect your levels.
- Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage blood sugar levels.

Reducing the Risk of Complications
While gestational diabetes can pose serious health risks, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of complications:
- Attend prenatal appointments: Regular prenatal appointments can help your healthcare provider monitor your condition and make any necessary adjustments to your management plan.
- Take medication as prescribed: If medication is prescribed, it is essential to take it as directed to help manage blood sugar levels.
- Monitor blood sugar levels: Regularly checking blood sugar levels can help you understand how different foods and activities affect your levels.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Recognizing gestational diabetes symptoms early on is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications. If you are diagnosed with gestational diabetes, it is essential to work with your healthcare provider to develop a management plan. By making dietary changes, exercising regularly, and monitoring blood sugar levels, you can reduce the risk of complications and have a healthy pregnancy.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with gestational diabetes in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider.
What is gestational diabetes?
+Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy, usually in the second or third trimester.
What are the risk factors for gestational diabetes?
+Risk factors for gestational diabetes include age, obesity, family history, and previous history of gestational diabetes.
How is gestational diabetes diagnosed?
+Gestational diabetes is typically diagnosed between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy using a glucose screening test.
