Intro
High troponin levels can be a concerning sign for many individuals, as it can indicate potential damage to the heart muscle. Troponin is a protein found in cardiac muscle cells, and when these cells are damaged, troponin is released into the bloodstream. Elevated troponin levels can be a sign of a heart attack, cardiac injury, or other cardiac conditions.
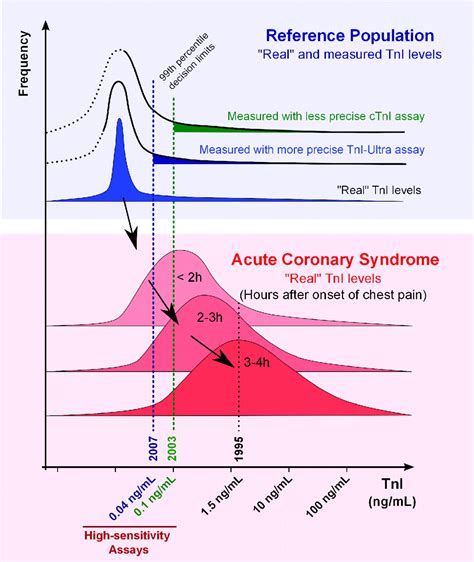
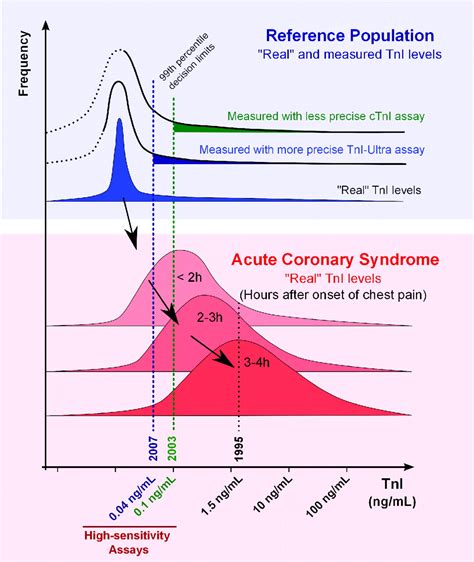
In this article, we will delve into the world of troponin levels, exploring what they mean, how they are measured, and what high levels might indicate. We will also discuss the potential causes and symptoms of elevated troponin levels and provide guidance on what to do if you or a loved one is experiencing high troponin levels.
Understanding Troponin Levels
Troponin is a protein found in cardiac muscle cells, and it plays a crucial role in the contraction and relaxation of these cells. When cardiac muscle cells are damaged, troponin is released into the bloodstream, where it can be measured. There are three types of troponin: troponin T, troponin I, and troponin C. Troponin T and troponin I are the most commonly measured types.
Troponin Level Measurement
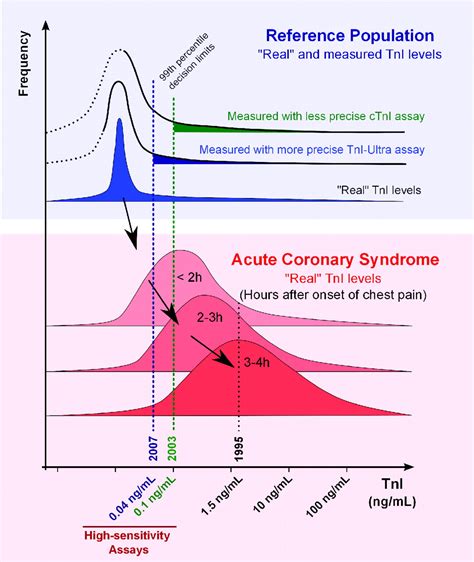
Troponin levels are typically measured using a blood test. The test involves taking a sample of blood from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results are usually reported in units of nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL) or picograms per milliliter (pg/mL).
A normal troponin level is usually considered to be less than 0.01 ng/mL. However, the exact normal range may vary depending on the laboratory and the specific test used.
Causes of High Troponin Levels
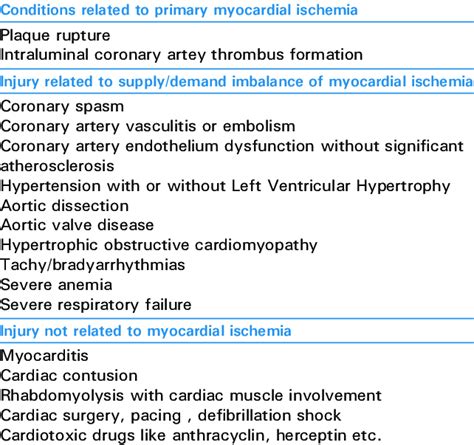
High troponin levels can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Heart attack (myocardial infarction): A heart attack occurs when the blood flow to the heart is blocked, causing damage to the cardiac muscle cells.
- Cardiac injury: Cardiac injury can occur due to trauma, surgery, or other medical procedures.
- Cardiac arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms, such as atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia, can cause cardiac muscle cell damage.
- Cardiomyopathy: Cardiomyopathy is a condition in which the heart muscle becomes weakened or damaged.
- Heart failure: Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs.
Symptoms of High Troponin Levels
The symptoms of high troponin levels can vary depending on the underlying cause. However, common symptoms may include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Nausea or vomiting
Potential Complications of High Troponin Levels
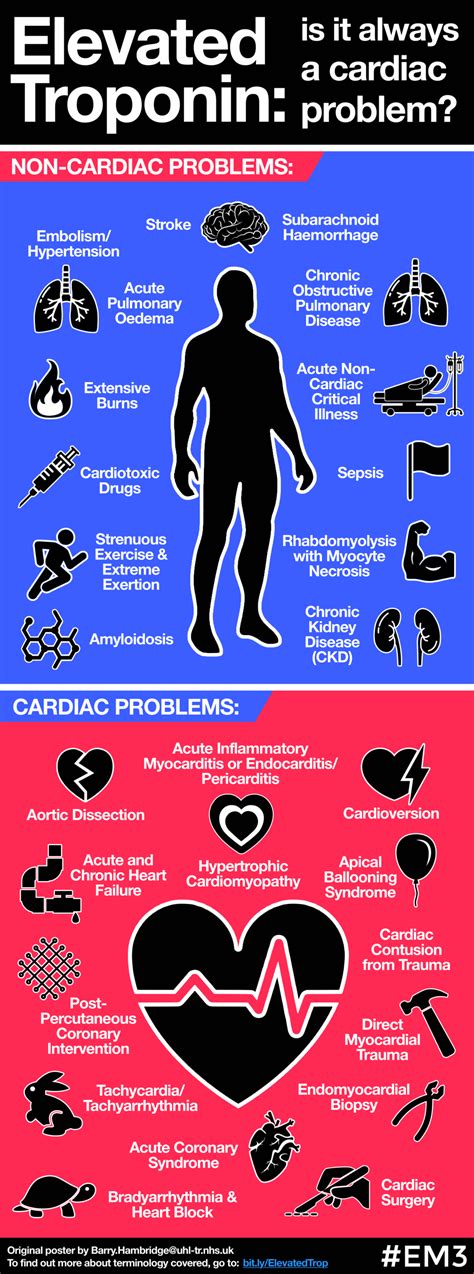
High troponin levels can lead to several potential complications, including:
- Cardiac arrest: Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart stops beating.
- Heart failure: Heart failure can occur if the cardiac muscle cells are severely damaged.
- Cardiac arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms can occur due to cardiac muscle cell damage.
- Cardiogenic shock: Cardiogenic shock occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs.
Diagnosis and Treatment of High Troponin Levels
Diagnosis of high troponin levels typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the high troponin levels.
- Heart attack: Treatment for heart attack typically involves emergency medical care, including oxygen therapy, pain management, and cardiac catheterization.
- Cardiac injury: Treatment for cardiac injury may involve surgery, medication, or other medical interventions.
- Cardiomyopathy: Treatment for cardiomyopathy may involve medication, lifestyle modifications, or surgery.
Prevention of High Troponin Levels
Prevention of high troponin levels involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including:
- Regular exercise
- Healthy diet
- Stress management
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Managing underlying medical conditions, such as high blood pressure or diabetes
Conclusion
High troponin levels can be a concerning sign, but with prompt medical attention and proper treatment, it is possible to manage and prevent potential complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for high troponin levels, individuals can take steps to maintain a healthy heart and reduce their risk of cardiac complications.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable information about high troponin levels. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.
What is the normal range for troponin levels?
+A normal troponin level is usually considered to be less than 0.01 ng/mL. However, the exact normal range may vary depending on the laboratory and the specific test used.
What are the common symptoms of high troponin levels?
+The symptoms of high troponin levels can vary depending on the underlying cause. However, common symptoms may include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, fatigue, dizziness or lightheadedness, and nausea or vomiting.
How can I prevent high troponin levels?
+Prevention of high troponin levels involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, healthy diet, stress management, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and managing underlying medical conditions.
