Intro
Navigate the healthcare maze with our expert guide to HMO vs PPO plans. Discover the 5 key differences between these popular health insurance options, including network coverage, out-of-pocket costs, and provider flexibility. Make informed decisions with our in-depth comparison, covering managed care, healthcare networks, and insurance premiums.
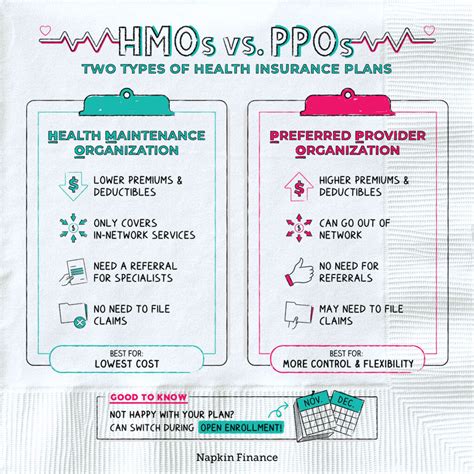
Choosing the right health insurance plan can be overwhelming, especially with the numerous options available. Two popular types of health insurance plans are Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) and Preferred Provider Organization (PPO). While both plans have their advantages and disadvantages, there are key differences between them. In this article, we will explore the 5 key differences between HMO and PPO plans to help you make an informed decision.
1. Network of Providers
One of the primary differences between HMO and PPO plans is the network of providers. HMO plans have a narrower network of providers, which means that you can only see doctors and hospitals that are part of the HMO's network. If you see a doctor outside of the network, you may not be covered or may have to pay a higher out-of-pocket cost. On the other hand, PPO plans have a broader network of providers, which gives you more flexibility when choosing a doctor or hospital.
How it Works
In an HMO plan, you typically need to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates your care and refers you to specialists within the network. If you see a specialist outside of the network, you may need to get a referral from your PCP first. In a PPO plan, you can see any doctor or hospital within the network without a referral. However, if you see a doctor outside of the network, you may have to pay a higher copayment or coinsurance.
2. Out-of-Network Care
Another significant difference between HMO and PPO plans is the out-of-network care. HMO plans typically do not cover out-of-network care, except in emergency situations. If you see a doctor outside of the network, you may have to pay the entire bill yourself. PPO plans, on the other hand, do cover out-of-network care, but you may have to pay a higher copayment or coinsurance.

Example
Let's say you have an HMO plan and you see a doctor outside of the network. You may have to pay the entire bill yourself, which could be hundreds or even thousands of dollars. On the other hand, if you have a PPO plan, you may have to pay a higher copayment or coinsurance, but you will still have some coverage.
3. Referrals
HMO plans typically require referrals from your primary care physician (PCP) before seeing a specialist. This is because HMO plans want to ensure that you receive coordinated care and that your PCP is involved in your care decisions. PPO plans, on the other hand, do not require referrals to see a specialist.
How it Works
In an HMO plan, your PCP will typically refer you to a specialist within the network. You may need to get a referral before seeing a specialist, which can take some time. In a PPO plan, you can see a specialist without a referral, which can be more convenient.
4. Premium Costs
The premium costs of HMO and PPO plans can vary significantly. HMO plans are typically less expensive than PPO plans, especially for individuals and families who do not need to see specialists frequently. However, PPO plans can be more cost-effective for those who need to see specialists regularly.
Example
Let's say you have a family of four and you choose an HMO plan. Your monthly premium may be $500, but you may have to pay more out-of-pocket costs if you see a doctor outside of the network. On the other hand, if you choose a PPO plan, your monthly premium may be $700, but you may have more flexibility when choosing a doctor or hospital.
5. Flexibility
Finally, PPO plans offer more flexibility than HMO plans. With a PPO plan, you can see any doctor or hospital within the network without a referral, and you can also see doctors outside of the network, albeit at a higher cost. HMO plans, on the other hand, have more restrictions on seeing specialists and out-of-network care.
How it Works
In a PPO plan, you can see any doctor or hospital within the network without a referral. You can also see doctors outside of the network, but you may have to pay a higher copayment or coinsurance. In an HMO plan, you typically need to see a primary care physician (PCP) first, who will refer you to a specialist within the network.
In conclusion, while both HMO and PPO plans have their advantages and disadvantages, there are key differences between them. HMO plans have a narrower network of providers, require referrals to see specialists, and typically do not cover out-of-network care. PPO plans, on the other hand, have a broader network of providers, do not require referrals to see specialists, and cover out-of-network care, albeit at a higher cost. When choosing between an HMO and PPO plan, consider your healthcare needs, budget, and preferences to make an informed decision.
What is the main difference between HMO and PPO plans?
+The main difference between HMO and PPO plans is the network of providers. HMO plans have a narrower network of providers, while PPO plans have a broader network of providers.
Do HMO plans cover out-of-network care?
+HMO plans typically do not cover out-of-network care, except in emergency situations.
Do PPO plans require referrals to see specialists?
+No, PPO plans do not require referrals to see specialists.
We hope this article has helped you understand the key differences between HMO and PPO plans. Remember to consider your healthcare needs, budget, and preferences when choosing between these two types of health insurance plans.
