Intro
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) interpretation is a crucial skill for healthcare professionals, particularly those working in cardiology, emergency medicine, and critical care. An ECG is a non-invasive test that measures the electrical activity of the heart, providing valuable information about heart rate, rhythm, and function. However, interpreting ECGs can be challenging, even for experienced healthcare professionals. In this article, we will provide a step-by-step guide to mastering ECG interpretation.
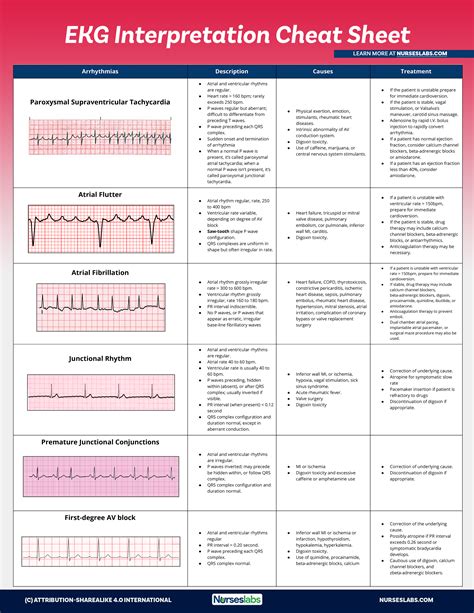
Understanding the Basics of ECG Interpretation
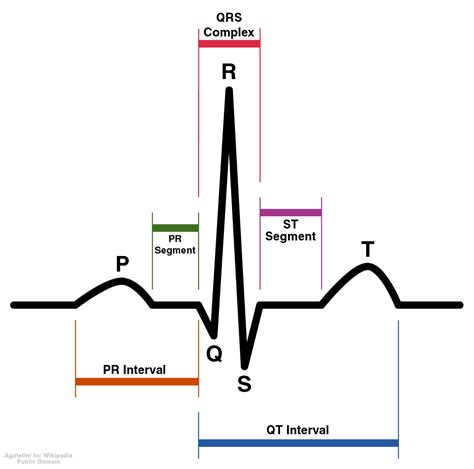
Before diving into the step-by-step guide, it's essential to understand the basics of ECG interpretation. An ECG tracing consists of several components, including:
- P wave: represents atrial depolarization
- QRS complex: represents ventricular depolarization
- T wave: represents ventricular repolarization
- PR interval: measures the time between atrial and ventricular depolarization
- QT interval: measures the time between ventricular depolarization and repolarization
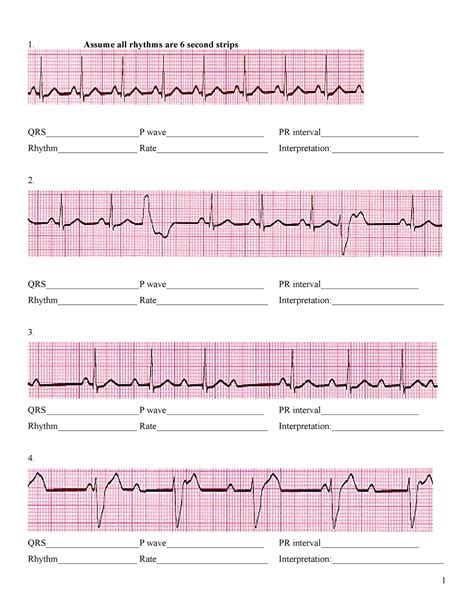
Step 1: Determine the Heart Rate and Rhythm
The first step in ECG interpretation is to determine the heart rate and rhythm. To do this, measure the distance between two consecutive R waves (R-R interval) and calculate the heart rate. A normal heart rate is between 60-100 beats per minute.
Step 2: Identify the P Wave and PR Interval
The P wave represents atrial depolarization, and the PR interval measures the time between atrial and ventricular depolarization. A normal PR interval is between 120-200 milliseconds.
Step 3: Analyze the QRS Complex
The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization. A normal QRS complex is less than 120 milliseconds. Abnormalities in the QRS complex can indicate ventricular arrhythmias or conduction disorders.
Step 4: Evaluate the T Wave and QT Interval
The T wave represents ventricular repolarization, and the QT interval measures the time between ventricular depolarization and repolarization. A normal QT interval is between 300-440 milliseconds.
Step 5: Look for Arrhythmias and Conduction Disorders
Finally, look for arrhythmias and conduction disorders, such as atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, or bundle branch blocks.
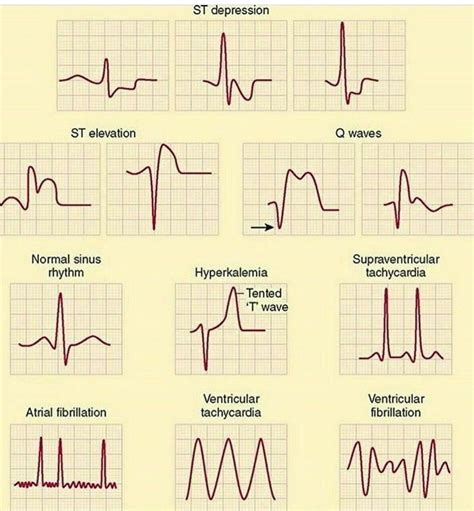
Common ECG Patterns and Their Meanings
Here are some common ECG patterns and their meanings:
- Normal sinus rhythm: a normal heart rate and rhythm
- Atrial fibrillation: an irregular heart rhythm with no discernible P waves
- Ventricular tachycardia: a rapid heart rhythm with a wide QRS complex
- Bundle branch block: a delay in ventricular depolarization due to a block in the bundle branches
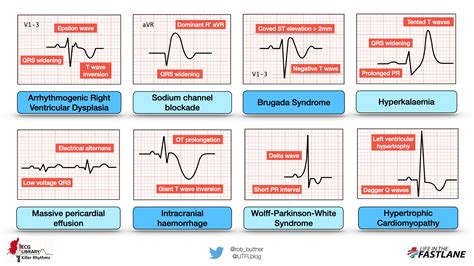
Tips for Mastering ECG Interpretation
Here are some tips for mastering ECG interpretation:
- Practice, practice, practice: the more ECGs you interpret, the more comfortable you will become with different patterns and rhythms.
- Use online resources: there are many online resources available to help you learn ECG interpretation, including tutorials, videos, and practice quizzes.
- Seek feedback: ask a colleague or mentor to review your ECG interpretations and provide feedback.
Conclusion
Mastering ECG interpretation takes time and practice, but with a step-by-step approach and a thorough understanding of the basics, you can become proficient in no time. Remember to practice regularly, use online resources, and seek feedback from colleagues or mentors.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive guide to mastering ECG interpretation. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
What is the normal heart rate range?
+A normal heart rate is between 60-100 beats per minute.
What does the P wave represent?
+The P wave represents atrial depolarization.
What is the normal QT interval range?
+A normal QT interval is between 300-440 milliseconds.

