Intro
As the global population ages, the prevalence of impaired mobility is becoming an increasingly significant concern. Impaired mobility, also known as limited mobility or mobility impairment, refers to the inability to move freely and easily, which can be caused by various factors such as injury, illness, or disability. This condition can have a profound impact on an individual's quality of life, affecting their physical and emotional well-being, social interactions, and overall independence. As a result, it is essential for nurses to develop effective care strategies to address impaired mobility and promote optimal recovery.
Impaired mobility can manifest in different ways, including difficulty walking, standing, or transferring from one position to another. It can also lead to secondary complications, such as pressure ulcers, contractures, and respiratory problems. Therefore, early identification and intervention are critical to prevent these complications and promote optimal outcomes. In this article, we will discuss the nursing diagnosis and care strategies for impaired mobility, highlighting the importance of a comprehensive and individualized approach to care.
Assessment and Diagnosis
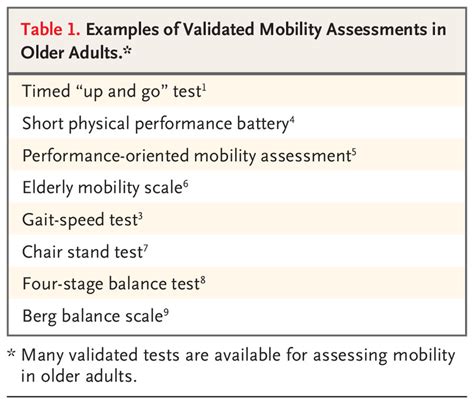
A thorough assessment is essential to diagnose impaired mobility accurately. Nurses should evaluate the patient's medical history, physical condition, and functional abilities to identify potential mobility issues. The assessment should include:
- Medical history: Review the patient's medical history to identify any underlying conditions that may contribute to impaired mobility, such as arthritis, stroke, or spinal cord injury.
- Physical examination: Perform a physical examination to assess the patient's muscle strength, range of motion, and flexibility.
- Functional assessment: Evaluate the patient's ability to perform daily activities, such as walking, standing, and transferring.
- Mobility assessment tools: Use standardized mobility assessment tools, such as the Timed Up and Go (TUG) test or the Berg Balance Scale, to quantify the patient's mobility.
Based on the assessment findings, the nurse can diagnose impaired mobility using the NANDA-I taxonomy. The diagnosis may include:
- Impaired physical mobility
- Limited mobility
- Difficulty walking
- Difficulty standing
- Difficulty transferring
Care Strategies

Effective care strategies for impaired mobility involve a comprehensive and individualized approach that addresses the patient's physical, emotional, and social needs. The following care strategies can be implemented:
- Mobility exercises: Encourage the patient to perform regular mobility exercises, such as range-of-motion exercises, strengthening exercises, and flexibility exercises, to improve muscle strength and mobility.
- Assistive devices: Provide assistive devices, such as canes, walkers, or wheelchairs, to facilitate mobility and reduce the risk of falls.
- Transfer techniques: Teach the patient and caregivers proper transfer techniques to prevent injury and promote safe mobility.
- Pressure ulcer prevention: Implement pressure ulcer prevention strategies, such as turning and repositioning, to prevent skin breakdown.
- Pain management: Manage pain effectively to promote mobility and reduce discomfort.
- Education and support: Educate the patient and caregivers on mobility techniques, safety precautions, and the importance of regular exercise to promote optimal mobility.
Interventions for Specific Mobility Issues

Nurses can implement specific interventions to address various mobility issues, including:
- Difficulty walking: Use assistive devices, such as canes or walkers, to facilitate walking and reduce the risk of falls.
- Difficulty standing: Use stand-up lifts or transfer boards to assist the patient with standing and transferring.
- Difficulty transferring: Use transfer boards or slide boards to facilitate safe transfers and reduce the risk of injury.
Collaboration with Interdisciplinary Team

Effective care for impaired mobility requires collaboration with an interdisciplinary team, including:
- Physical therapists: To develop and implement mobility exercises and interventions.
- Occupational therapists: To promote independence and safety in daily activities.
- Speech therapists: To address communication and swallowing issues related to impaired mobility.
- Nutritionists: To ensure adequate nutrition and hydration to promote healing and mobility.
Conclusion and Future Directions
Impaired mobility is a significant concern that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Nurses play a critical role in diagnosing and managing impaired mobility, and it is essential to develop effective care strategies to promote optimal recovery. By implementing a comprehensive and individualized approach to care, nurses can address the physical, emotional, and social needs of patients with impaired mobility. Future directions in mobility care include the development of innovative technologies, such as robotic exoskeletons, and the implementation of evidence-based practices to promote optimal mobility outcomes.
What is impaired mobility?
+Impaired mobility, also known as limited mobility or mobility impairment, refers to the inability to move freely and easily, which can be caused by various factors such as injury, illness, or disability.
What are the consequences of impaired mobility?
+Impaired mobility can lead to secondary complications, such as pressure ulcers, contractures, and respiratory problems, and can also affect an individual's quality of life, social interactions, and overall independence.
What are the care strategies for impaired mobility?
+Effective care strategies for impaired mobility involve a comprehensive and individualized approach that addresses the patient's physical, emotional, and social needs, including mobility exercises, assistive devices, transfer techniques, pressure ulcer prevention, pain management, and education and support.
