Intro
The International Normalized Ratio (INR) blood test is a crucial diagnostic tool used to measure the time it takes for blood to clot. This test is essential for individuals taking anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin, to ensure their blood is not too thin or too thick. In this article, we will delve into the world of INR blood tests, exploring what they entail, how they work, and what the results mean.
The INR blood test is a vital tool for monitoring patients on anticoagulant therapy, as it helps prevent complications such as bleeding or stroke. With the rise of anticoagulant medications, the importance of INR blood tests has grown significantly. According to the American Heart Association, over 2 million people in the United States are on anticoagulant therapy, highlighting the need for accurate and reliable INR testing.
What is an INR Blood Test?
An INR blood test measures the time it takes for blood to clot by evaluating the prothrombin time (PT). Prothrombin time is the time it takes for blood to clot in the absence of anticoagulants. The INR test is a standardized version of the PT test, allowing for accurate comparisons between laboratories. The INR test is usually performed on a blood sample taken from a vein in the arm.
How Does an INR Blood Test Work?
During an INR blood test, a healthcare professional will draw a blood sample from a vein in the arm using a needle. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. In the laboratory, the blood sample is mixed with a substance that triggers clotting. The time it takes for the blood to clot is then measured using a specialized device. The results are calculated using a complex formula that takes into account the patient's age, sex, and other factors.
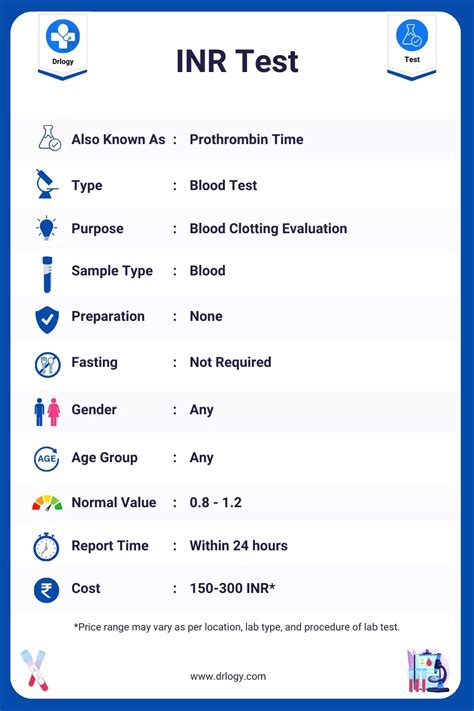
What Do INR Blood Test Results Mean?
INR blood test results are expressed as a ratio, with a normal range of 0.9 to 1.1. Patients on anticoagulant therapy typically have an INR range of 2.0 to 3.0. Results outside of this range may indicate that the patient's blood is too thin or too thick, increasing the risk of bleeding or stroke.
- An INR result below 2.0 may indicate that the patient's blood is too thick, increasing the risk of stroke.
- An INR result above 3.0 may indicate that the patient's blood is too thin, increasing the risk of bleeding.
What Factors Can Affect INR Blood Test Results?
Several factors can affect INR blood test results, including:
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antibiotics and antifungals, can interact with anticoagulants and affect INR results.
- Diet: Foods high in vitamin K, such as leafy greens, can affect INR results.
- Age: Older adults may require more frequent INR testing due to age-related changes in blood clotting.
- Kidney function: Patients with kidney disease may require more frequent INR testing due to changes in blood clotting.
How Often Should INR Blood Tests Be Performed?
The frequency of INR blood tests depends on several factors, including the patient's medical history, medication regimen, and kidney function. Typically, patients on anticoagulant therapy require regular INR testing, usually every 2 to 4 weeks.
What Are the Risks and Complications of INR Blood Tests?
INR blood tests are generally safe and well-tolerated. However, some patients may experience minor side effects, such as bruising or bleeding at the needle site. In rare cases, patients may experience more serious complications, such as infection or nerve damage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, INR blood tests play a vital role in monitoring patients on anticoagulant therapy. By understanding what INR blood tests entail, how they work, and what the results mean, patients can take an active role in managing their care.
We encourage you to share your experiences with INR blood tests in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to ask.
What is the normal range for INR blood test results?
+The normal range for INR blood test results is 0.9 to 1.1. Patients on anticoagulant therapy typically have an INR range of 2.0 to 3.0.
How often should INR blood tests be performed?
+The frequency of INR blood tests depends on several factors, including the patient's medical history, medication regimen, and kidney function. Typically, patients on anticoagulant therapy require regular INR testing, usually every 2 to 4 weeks.
What are the risks and complications of INR blood tests?
+INR blood tests are generally safe and well-tolerated. However, some patients may experience minor side effects, such as bruising or bleeding at the needle site. In rare cases, patients may experience more serious complications, such as infection or nerve damage.
Can I eat before an INR blood test?
+Yes, you can eat before an INR blood test. However, it is recommended to avoid foods high in vitamin K, such as leafy greens, as they can affect INR results.
Can I take my medications before an INR blood test?
+Yes, you can take your medications as prescribed before an INR blood test. However, it is recommended to inform your healthcare provider of any medications you are taking, as some may interact with anticoagulants and affect INR results.
