Intro
Discover the essential facts about Lisinopril 40 Mg, a widely prescribed medication for hypertension and heart failure. Learn about its uses, side effects, dosage, and interactions. Understand how Lisinopril 40 Mg works to improve cardiovascular health and explore its benefits and risks, including ACE inhibitor functions and blood pressure management.
Lisinopril, a medication commonly prescribed to treat high blood pressure and heart failure, is a well-known angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. One of the most frequently prescribed dosages of this medication is Lisinopril 40 mg. In this article, we will delve into the key facts about Lisinopril 40 mg, exploring its benefits, side effects, and usage guidelines.
High blood pressure is a significant health concern worldwide, affecting millions of people and increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. Lisinopril 40 mg is often prescribed to help manage blood pressure and reduce the risk of these complications.
What is Lisinopril 40 mg Used For?
Lisinopril 40 mg is primarily used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and heart failure. It works by relaxing blood vessels, making it easier for the heart to pump blood, and reducing the amount of fluid in the body. By doing so, it helps to lower blood pressure and alleviate symptoms associated with heart failure, such as shortness of breath and fatigue.
How Does Lisinopril 40 mg Work?
Lisinopril belongs to a class of medications known as ACE inhibitors. ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) is a naturally occurring enzyme in the body that converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor. Angiotensin II causes blood vessels to constrict, increasing blood pressure. Lisinopril works by blocking the action of ACE, reducing the production of angiotensin II, and resulting in the relaxation of blood vessels and a decrease in blood pressure.
Benefits of Lisinopril 40 mg
Lisinopril 40 mg offers several benefits, including:
- Effective blood pressure control: Lisinopril 40 mg has been shown to be effective in lowering blood pressure in patients with hypertension.
- Reduced risk of heart disease: By lowering blood pressure, Lisinopril 40 mg reduces the risk of heart disease, including heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease.
- Improved symptoms of heart failure: Lisinopril 40 mg can help alleviate symptoms associated with heart failure, such as shortness of breath and fatigue.
- Convenient dosing: Lisinopril 40 mg is typically taken once daily, making it a convenient option for patients.
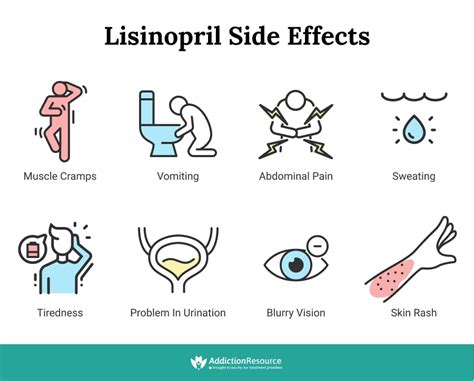
Common Side Effects of Lisinopril 40 mg
While generally well-tolerated, Lisinopril 40 mg can cause side effects, including:
- Cough: A dry, persistent cough is a common side effect of Lisinopril 40 mg, affecting up to 20% of patients.
- Dizziness: Lisinopril 40 mg can cause dizziness, especially when standing up quickly.
- Fatigue: Some patients may experience fatigue or weakness when taking Lisinopril 40 mg.
- Headache: Mild to moderate headaches can occur in some patients taking Lisinopril 40 mg.
Precautions and Contraindications
Before taking Lisinopril 40 mg, patients should be aware of the following precautions and contraindications:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Lisinopril 40 mg is contraindicated in pregnant women, especially during the second and third trimesters, as it can cause fetal harm.
- Kidney disease: Patients with kidney disease should use Lisinopril 40 mg with caution, as it can worsen kidney function.
- Allergic reactions: Patients who are allergic to ACE inhibitors or have a history of angioedema should not take Lisinopril 40 mg.
Interactions with Other Medications
Lisinopril 40 mg can interact with other medications, including:
- Diuretics: Patients taking diuretics may experience increased potassium levels when taking Lisinopril 40 mg.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs can reduce the effectiveness of Lisinopril 40 mg.
- Potassium supplements: Patients taking potassium supplements should use Lisinopril 40 mg with caution, as it can increase potassium levels.
Dosage and Administration
The typical dosage of Lisinopril 40 mg is one tablet taken once daily, with or without food. Patients should take the medication at the same time each day to maintain a consistent level of the medication in the body.
Missed Dose
If a patient misses a dose of Lisinopril 40 mg, they should take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, they should skip the missed dose and continue with their regular dosing schedule.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Lisinopril 40 mg is a commonly prescribed medication for the treatment of high blood pressure and heart failure. While generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, and patients should be aware of the precautions and contraindications associated with its use. By following the recommended dosage and administration guidelines, patients can effectively manage their blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable information about Lisinopril 40 mg. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to comment below. Share this article with your friends and family to help them understand the benefits and risks associated with this medication.
What is the typical dosage of Lisinopril 40 mg?
+The typical dosage of Lisinopril 40 mg is one tablet taken once daily, with or without food.
Can I take Lisinopril 40 mg with other medications?
+Lisinopril 40 mg can interact with other medications, including diuretics, NSAIDs, and potassium supplements. Patients should consult their doctor before taking Lisinopril 40 mg with other medications.
What are the common side effects of Lisinopril 40 mg?
+Common side effects of Lisinopril 40 mg include cough, dizziness, fatigue, and headache.

