Intro
Discover the best foods to eat on a low fiber diet plan. Learn how to manage digestive issues with a balanced diet rich in low-fiber fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Find out which foods to limit or avoid, and get expert tips on maintaining a healthy gut with a low fiber intake.
When following a low fiber diet plan, it's essential to focus on consuming foods that are gentle on the digestive system and minimize discomfort, bloating, and gas. A low fiber diet is often recommended for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn's disease, or ulcerative colitis, as well as those who have recently undergone gastrointestinal surgery.
In this article, we'll explore the best foods to eat on a low fiber diet plan, including fruits, vegetables, proteins, whole grains, and dairy products. We'll also provide some helpful tips for managing a low fiber diet and reducing symptoms.
Understanding Fiber and Its Effects on the Body
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy digestion, satiety, and blood sugar levels. However, for individuals with certain medical conditions or digestive issues, a high fiber diet can exacerbate symptoms and cause discomfort.
There are two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber dissolves in water and can help lower cholesterol levels and regulate blood sugar levels. Insoluble fiber, on the other hand, does not dissolve in water and helps add bulk to stool, promoting regular bowel movements.
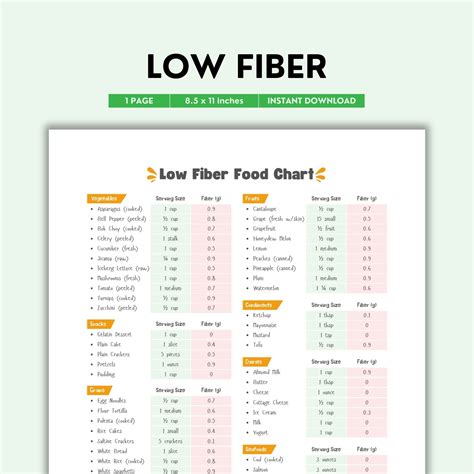
Foods to Eat on a Low Fiber Diet Plan
While it's essential to limit high fiber foods on a low fiber diet plan, there are still plenty of delicious and nutritious options to choose from. Here are some of the best foods to eat on a low fiber diet:
- Fresh fruits:
- Bananas (1 medium: 3 grams of fiber)
- Avocados (1 medium: 7 grams of fiber, but mostly healthy fats)
- Mangoes (1 cup sliced: 2.6 grams of fiber)
- Pears (1 medium: 4.4 grams of fiber)
- Vegetables:
- Bell peppers (1 cup sliced: 2.5 grams of fiber)
- Cucumbers (1 cup sliced: 0.5 grams of fiber)
- Carrots (1 cup cooked: 3.5 grams of fiber)
- Green beans (1 cup cooked: 3.8 grams of fiber)
- Proteins:
- Chicken breast (3 ounces cooked: 0 grams of fiber)
- Turkey breast (3 ounces cooked: 0 grams of fiber)
- Fish (salmon, tilapia, etc.) (3 ounces cooked: 0 grams of fiber)
- Eggs (1 large: 0 grams of fiber)
- Whole grains:
- White rice (1 cup cooked: 0.6 grams of fiber)
- White bread (1 slice: 0.6 grams of fiber)
- Pasta (1 cup cooked: 1.5 grams of fiber)
- Dairy products:
- Milk (1 cup: 0 grams of fiber)
- Yogurt (1 cup: 0 grams of fiber)
- Cheese (1 ounce: 0 grams of fiber)
Tips for Managing a Low Fiber Diet
While following a low fiber diet plan can be challenging, there are some helpful tips to keep in mind:
- Gradually introduce new foods: When adding new foods to your diet, start with small portions and gradually increase the serving size to allow your digestive system to adjust.
- Cook vegetables: Cooking vegetables can help break down some of the fiber, making them easier to digest.
- Choose low fiber fruits: Opt for fruits that are naturally low in fiber, such as bananas and avocados.
- Avoid high fiber foods: Limit or avoid foods that are high in fiber, such as beans, lentils, and whole grains.

Reducing Symptoms on a Low Fiber Diet
While a low fiber diet can help alleviate symptoms, there are some additional strategies to reduce discomfort:
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help soften stool and promote regular bowel movements.
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity can help stimulate bowel movements and improve digestion.
- Manage stress: Stress can exacerbate digestive issues; practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises.
Common Mistakes to Avoid on a Low Fiber Diet
When following a low fiber diet plan, it's essential to avoid common mistakes that can exacerbate symptoms:
- Not drinking enough water: Inadequate hydration can lead to constipation and worsen symptoms.
- Eating too many high fiber foods: While it may be tempting to indulge in high fiber foods, doing so can exacerbate symptoms and discomfort.
- Not introducing new foods gradually: Introducing new foods too quickly can cause digestive upset and worsen symptoms.
Conclusion
A low fiber diet plan can be an effective way to manage digestive issues and alleviate symptoms. By focusing on low fiber foods, managing stress, and staying hydrated, individuals can reduce discomfort and promote healthy digestion. Remember to introduce new foods gradually, avoid common mistakes, and consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
What is a low fiber diet, and who is it recommended for?
+A low fiber diet is a meal plan that restricts the intake of high fiber foods, which can exacerbate digestive issues. It is often recommended for individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, or those who have recently undergone gastrointestinal surgery.
How much fiber should I consume on a low fiber diet?
+The daily fiber intake on a low fiber diet varies depending on individual needs and medical conditions. Generally, it is recommended to consume 10-15 grams of fiber per day.
Can I still eat fruits and vegetables on a low fiber diet?
+Yes, you can still eat fruits and vegetables on a low fiber diet, but it's essential to choose low fiber options, such as bananas, avocados, and cooked vegetables.
