Intro
Discover the essential facts about lymph node biopsy, a diagnostic procedure for cancer and other diseases. Learn about the types of biopsies, preparation, risks, and what to expect during and after the procedure. Understand the importance of lymph node evaluation and how it informs treatment decisions for conditions like lymphoma, breast cancer, and more.
A lymph node biopsy is a medical procedure that involves removing a lymph node from the body to examine it for abnormal cell growth, infection, or cancer. Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped organs that are part of the body's immune system, and they play a crucial role in fighting infection and disease. If a lymph node becomes swollen or enlarged, it may be a sign of an underlying medical condition, and a biopsy may be necessary to determine the cause. Here are five things to know about lymph node biopsies:
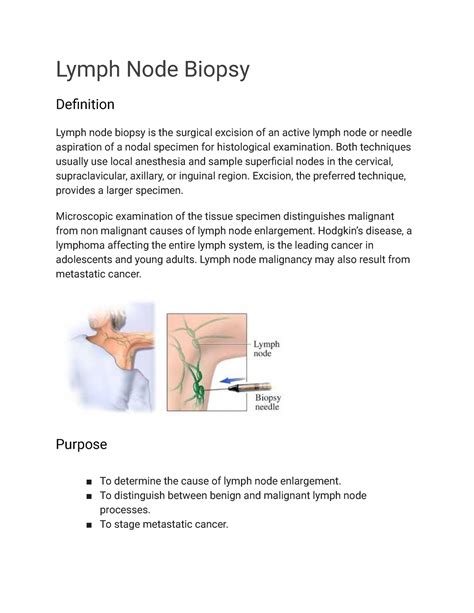
What is a Lymph Node Biopsy?
A lymph node biopsy is a surgical procedure that involves removing a lymph node from the body to examine it for abnormal cell growth, infection, or cancer. There are several types of lymph node biopsies, including:
- Fine-needle aspiration biopsy: This is a minimally invasive procedure that involves using a thin needle to remove a small sample of cells from the lymph node.
- Core needle biopsy: This is a slightly more invasive procedure that involves using a thicker needle to remove a larger sample of cells from the lymph node.
- Surgical biopsy: This is a more invasive procedure that involves making an incision in the skin to remove the entire lymph node.
Why is a Lymph Node Biopsy Performed?
A lymph node biopsy is performed to diagnose and treat a variety of medical conditions, including:
- Cancer: A lymph node biopsy can help diagnose cancer and determine the stage of the disease.
- Infection: A lymph node biopsy can help diagnose infections such as lymphadenitis, which is an infection of the lymph nodes.
- Autoimmune disorders: A lymph node biopsy can help diagnose autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis.
- Lymphoma: A lymph node biopsy can help diagnose lymphoma, which is a type of cancer that affects the immune system.
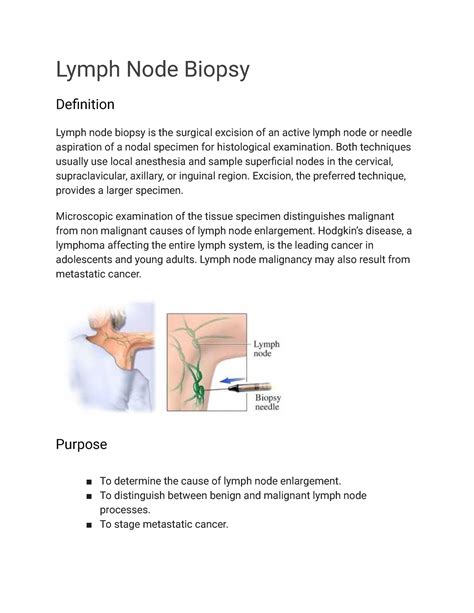
How is a Lymph Node Biopsy Performed?
The procedure for a lymph node biopsy varies depending on the type of biopsy being performed. Here are the general steps involved in a lymph node biopsy:
- Preparation: The patient is given a local anesthetic to numb the area where the biopsy will be performed.
- Biopsy: The doctor uses a needle or makes an incision in the skin to remove the lymph node.
- Removal of the lymph node: The lymph node is removed and sent to a laboratory for examination.
- Recovery: The patient is taken to a recovery room to rest and recover from the procedure.
Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks and complications associated with a lymph node biopsy. These include:
- Bleeding: There is a risk of bleeding or bruising at the site of the biopsy.
- Infection: There is a risk of infection at the site of the biopsy.
- Nerve damage: There is a risk of nerve damage or numbness at the site of the biopsy.
- Allergic reaction: There is a risk of an allergic reaction to the anesthetic or other medications used during the procedure.

What to Expect After a Lymph Node Biopsy
After a lymph node biopsy, the patient can expect to experience some discomfort or pain at the site of the biopsy. This can be managed with pain medication and rest. The patient may also experience some bruising or swelling at the site of the biopsy.
Results
The results of a lymph node biopsy can take several days to several weeks to become available. The doctor will discuss the results with the patient and explain what they mean. If the results indicate cancer or another medical condition, the doctor will discuss treatment options with the patient.

Conclusion
A lymph node biopsy is a medical procedure that involves removing a lymph node from the body to examine it for abnormal cell growth, infection, or cancer. While the procedure can be uncomfortable and carries some risks, it is an important diagnostic tool that can help doctors diagnose and treat a variety of medical conditions. If you have any questions or concerns about a lymph node biopsy, be sure to discuss them with your doctor.
What is a lymph node biopsy?
+A lymph node biopsy is a medical procedure that involves removing a lymph node from the body to examine it for abnormal cell growth, infection, or cancer.
Why is a lymph node biopsy performed?
+A lymph node biopsy is performed to diagnose and treat a variety of medical conditions, including cancer, infection, autoimmune disorders, and lymphoma.
What are the risks and complications of a lymph node biopsy?
+The risks and complications of a lymph node biopsy include bleeding, infection, nerve damage, and allergic reaction.
What can I expect after a lymph node biopsy?
+After a lymph node biopsy, you can expect to experience some discomfort or pain at the site of the biopsy, as well as bruising or swelling.
How long do the results of a lymph node biopsy take to become available?
+The results of a lymph node biopsy can take several days to several weeks to become available.
