Intro
Discover what a normal troponin level is and why it matters for your heart health. Learn about the troponin test, its significance, and the factors that influence troponin levels. Get the facts on troponin ranges, elevated troponin levels, and how to interpret your test results. Understand the connection between troponin and cardiac health, including myocardial infarction and cardiac biomarkers.
Troponin is a protein found in cardiac muscle cells, and its levels in the blood can indicate the presence of heart damage or disease. Understanding what constitutes a normal troponin level is essential for diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular conditions. In this article, we will delve into the facts about troponin levels, including what is considered normal, how troponin tests work, and what elevated levels might signify.
What is Troponin?
Troponin is a complex of three proteins (troponin C, troponin I, and troponin T) that play a crucial role in the contraction of cardiac muscle cells. When cardiac cells are damaged, troponin is released into the bloodstream, making it a valuable biomarker for diagnosing cardiac conditions.
How are Troponin Levels Measured?
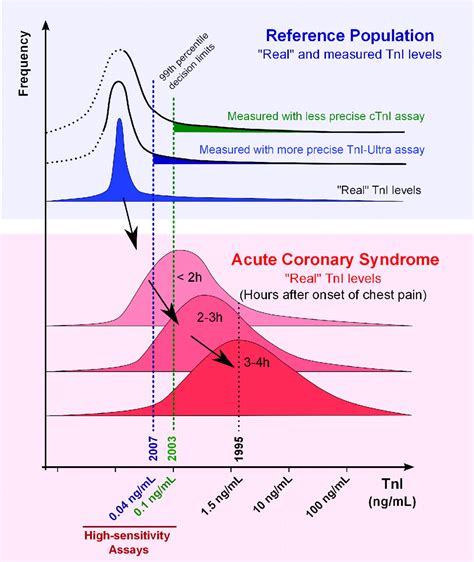
Troponin levels are measured using a blood test, typically a high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) assay. This test detects the presence of troponin T or troponin I in the blood. The results are usually reported in units of nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL) or picograms per milliliter (pg/mL).
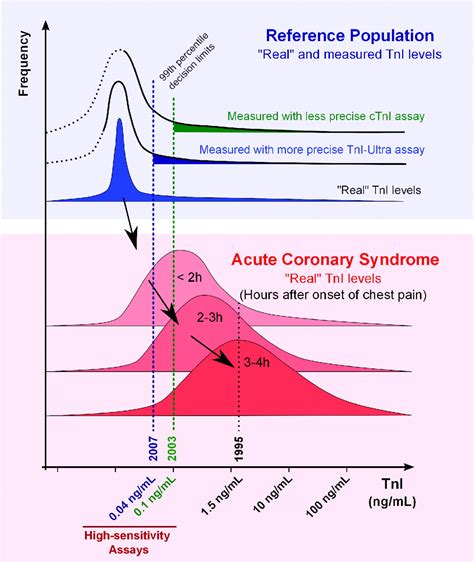
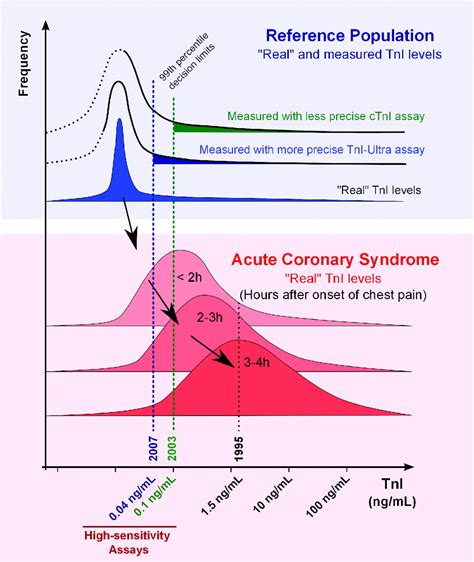
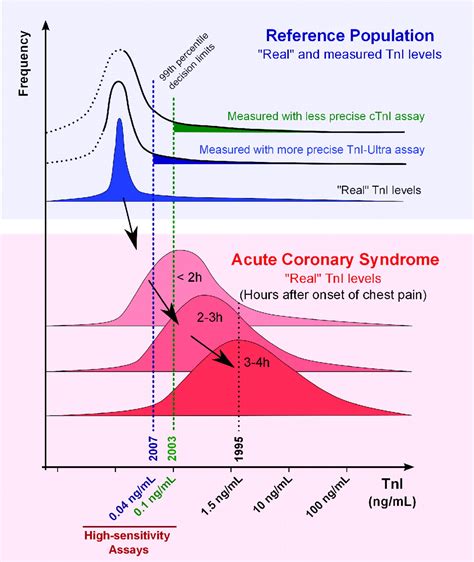
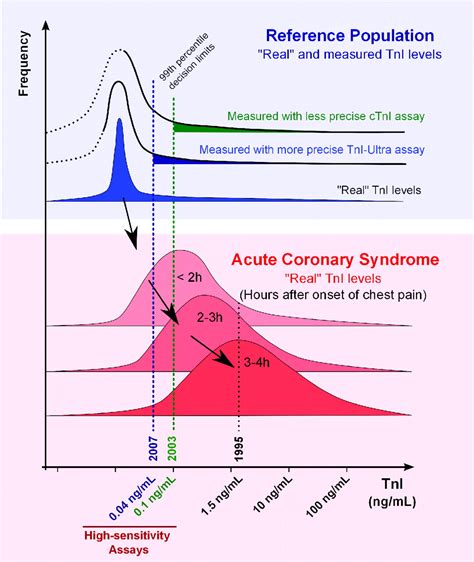
What is a Normal Troponin Level?
A normal troponin level is typically considered to be below 0.01 ng/mL or 10 pg/mL. However, the exact cutoff value may vary depending on the laboratory and the specific assay used. Some studies suggest that even slightly elevated troponin levels, such as 0.01-0.05 ng/mL, may be associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events.
Factors that Can Affect Troponin Levels
Several factors can influence troponin levels, including:
- Age: Troponin levels may be higher in older adults due to age-related cardiac changes.
- Sex: Women tend to have lower troponin levels than men.
- Kidney function: Impaired kidney function can lead to elevated troponin levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as heparin and fibrinolytics, can affect troponin levels.
Elevated Troponin Levels: What Do They Mean?
Elevated troponin levels can indicate cardiac damage or disease, such as:
- Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
- Unstable angina
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Cardiomyopathy
- Heart failure
However, elevated troponin levels can also occur in non-cardiac conditions, such as:
- Pulmonary embolism
- Sepsis
- Trauma
- Kidney disease
Interpreting Troponin Test Results
When interpreting troponin test results, healthcare providers consider the following:
- The absolute value of the troponin level
- The change in troponin levels over time
- The presence of other biomarkers, such as creatine kinase (CK) and myoglobin
- Clinical symptoms and medical history
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Troponin Levels
Understanding what constitutes a normal troponin level is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular conditions. By recognizing the factors that can affect troponin levels and interpreting test results in the context of clinical symptoms and medical history, healthcare providers can make informed decisions about patient care.
Takeaway Points
- A normal troponin level is typically below 0.01 ng/mL or 10 pg/mL.
- Elevated troponin levels can indicate cardiac damage or disease, but can also occur in non-cardiac conditions.
- Factors such as age, sex, kidney function, and medications can influence troponin levels.
- Accurate interpretation of troponin test results requires consideration of clinical symptoms, medical history, and other biomarkers.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of troponin levels and their significance in diagnosing cardiovascular conditions. If you have any questions or concerns, please feel free to comment below.
What is a normal troponin level?
+A normal troponin level is typically below 0.01 ng/mL or 10 pg/mL.
What can cause elevated troponin levels?
+Elevated troponin levels can be caused by cardiac damage or disease, as well as non-cardiac conditions such as pulmonary embolism, sepsis, trauma, and kidney disease.
How are troponin levels measured?
+Troponin levels are measured using a blood test, typically a high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) assay.
