Intro
Pregnancy is a complex and multifaceted journey, filled with numerous tests, scans, and check-ups. One of the most crucial tests during the early stages of pregnancy is the Nuchal Fold Translucency (NT) test. This non-invasive test is a vital tool for assessing the health of the developing fetus and detecting potential risks. As an expectant mother, understanding the ins and outs of the NT test can help alleviate anxiety and provide valuable insights into the well-being of your unborn child.
The NT test is typically performed between 11 and 14 weeks of gestation, a critical period in fetal development. During this time, the fetus is growing rapidly, and the risk of chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome, is higher. The NT test provides a preliminary assessment of the risk of these abnormalities, allowing for informed decision-making and further testing if necessary.
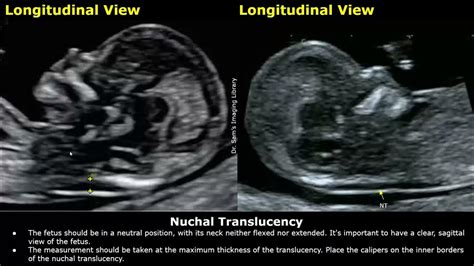
What is the Nuchal Fold Translucency Test?
The Nuchal Fold Translucency test is an ultrasound scan that measures the thickness of the nuchal fold, a fluid-filled space at the back of the fetus's neck. This measurement is used to assess the risk of chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome, trisomy 18, and trisomy 13. The test is usually performed in conjunction with a blood test, known as the combined test, which measures the levels of certain proteins and hormones in the mother's blood.
How is the NT Test Performed?
The NT test is a non-invasive procedure that typically takes around 30 minutes to an hour to complete. During the test:
- A trained sonographer will apply a gel to the mother's abdomen and use a transducer to capture images of the fetus.
- The sonographer will measure the thickness of the nuchal fold, usually between 2-8 mm.
- The measurement is then used to calculate the risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
What Do the Results Mean?
The results of the NT test are usually expressed as a ratio of the measured nuchal fold thickness to the expected thickness for the gestational age. A higher ratio indicates a higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities. The results are usually classified into three categories:
- Low risk: The risk of chromosomal abnormalities is less than 1 in 300.
- Intermediate risk: The risk of chromosomal abnormalities is between 1 in 300 and 1 in 50.
- High risk: The risk of chromosomal abnormalities is greater than 1 in 50.
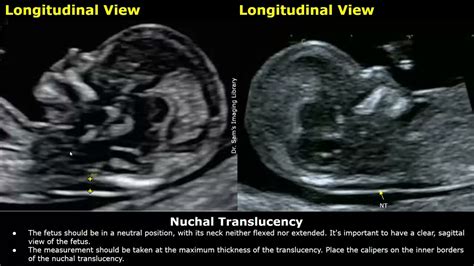
What Happens Next?
If the results indicate a high risk of chromosomal abnormalities, the mother may be offered further testing, such as:
- Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT): A blood test that analyzes the DNA of the fetus.
- Amniocentesis: A procedure that involves removing a sample of amniotic fluid for testing.
- Chorionic villus sampling (CVS): A procedure that involves removing a sample of placental tissue for testing.
Benefits and Limitations of the NT Test
The NT test has several benefits, including:
- Early detection of chromosomal abnormalities
- Non-invasive and painless procedure
- Can be performed in conjunction with other tests to increase accuracy
However, the test also has some limitations:
- Not 100% accurate
- May produce false positive or false negative results
- Cannot detect all chromosomal abnormalities
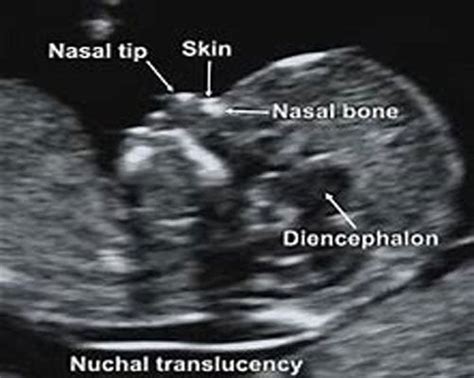
Preparing for the NT Test
To prepare for the NT test, the mother should:
- Arrive with a full bladder
- Wear comfortable clothing
- Bring any relevant medical records or test results
- Ask questions and discuss concerns with the healthcare provider
Conclusion
The Nuchal Fold Translucency test is a valuable tool for assessing the health of the developing fetus and detecting potential risks. While the test has its limitations, it provides a preliminary assessment of the risk of chromosomal abnormalities, allowing for informed decision-making and further testing if necessary. By understanding the ins and outs of the NT test, expectant mothers can feel more empowered and prepared for the journey ahead.
What is the accuracy of the Nuchal Fold Translucency test?
+The accuracy of the NT test varies depending on the gestational age and the risk of chromosomal abnormalities. However, studies have shown that the test can detect around 80-90% of cases of Down syndrome.
Can the NT test detect other chromosomal abnormalities?
+Yes, the NT test can detect other chromosomal abnormalities, such as trisomy 18 and trisomy 13. However, the test is most effective in detecting Down syndrome.
Is the NT test painful?
+No, the NT test is a non-invasive and painless procedure. The mother may experience some discomfort or pressure during the ultrasound, but this is usually mild and temporary.
