Intro
The importance of rapid response teams in hospitals cannot be overstated. These teams are designed to quickly respond to emergencies and provide life-saving interventions to patients who are deteriorating or at risk of cardiac arrest. In this article, we will explore the concept of rapid response teams, their benefits, and how they work to save lives in hospitals.

Rapid response teams, also known as Medical Emergency Teams (MET), are composed of a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and other specialists. They are trained to quickly respond to emergencies and provide timely interventions to prevent cardiac arrest, respiratory failure, and other life-threatening conditions.
Benefits of Rapid Response Teams
The benefits of rapid response teams are numerous. Studies have shown that these teams can significantly reduce the incidence of cardiac arrest, hospital mortality, and morbidity. They can also improve patient outcomes, reduce length of stay, and enhance patient safety.

Improved Patient Outcomes
Rapid response teams can improve patient outcomes by providing timely interventions and preventing complications. Studies have shown that these teams can reduce the incidence of cardiac arrest by up to 50% and hospital mortality by up to 30%.
Enhanced Patient Safety
Rapid response teams can enhance patient safety by identifying potential problems early and taking prompt action to prevent them. They can also improve communication among healthcare professionals and reduce errors.
Reduced Length of Stay
Rapid response teams can reduce length of stay by preventing complications and improving patient outcomes. Studies have shown that these teams can reduce length of stay by up to 30%.
How Rapid Response Teams Work
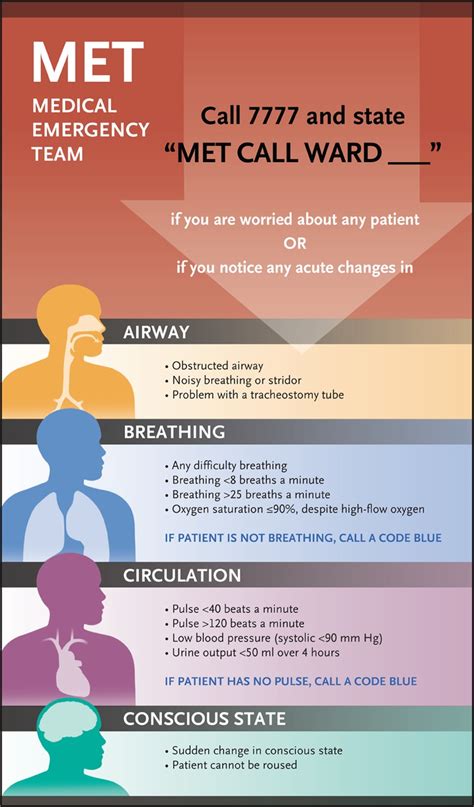
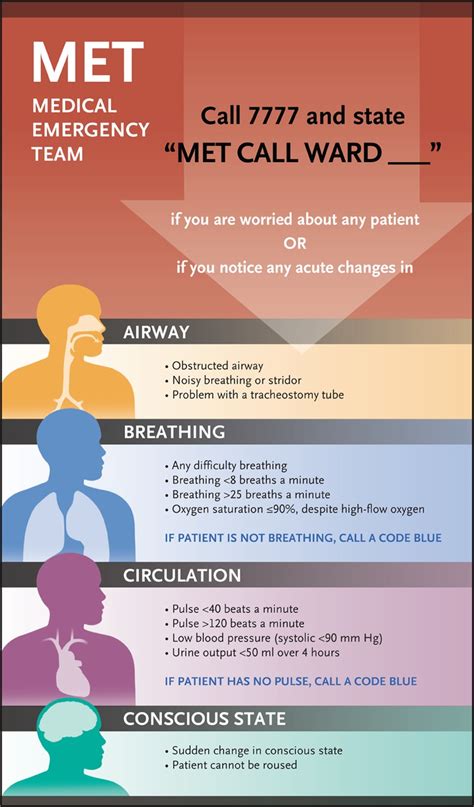
Rapid response teams work by quickly responding to emergencies and providing timely interventions. They are typically activated by a call to a designated phone number or by a bedside alarm.

Activation Criteria
Rapid response teams are typically activated by specific criteria, such as:
- Sudden deterioration in a patient's condition
- Cardiac arrest or near-arrest
- Respiratory failure or distress
- Severe hypotension or hypertension
- Severe pain or discomfort
Team Composition
Rapid response teams are composed of a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including:
- Doctors (e.g., intensivists, hospitalists)
- Nurses (e.g., critical care nurses, nurse practitioners)
- Respiratory therapists
- Other specialists (e.g., cardiologists, anesthesiologists)
Implementation and Training
Implementing a rapid response team requires careful planning and training. Hospitals must establish clear policies and procedures for activating and responding to emergencies.
Training Programs
Training programs for rapid response teams should include:
- Simulation training
- Didactic lectures
- Case-based discussions
- Interdisciplinary training
Quality Improvement
Hospitals should regularly review and evaluate the effectiveness of their rapid response teams. This can include:
- Reviewing activation criteria and team composition
- Analyzing patient outcomes and length of stay
- Conducting regular drills and simulations
Challenges and Limitations
While rapid response teams can be highly effective, there are also challenges and limitations to consider.
Resource Constraints
Rapid response teams require significant resources, including personnel, equipment, and training. Hospitals with limited resources may struggle to implement and maintain these teams.
Communication Breakdowns
Communication breakdowns can occur when rapid response teams are activated, particularly if team members are not familiar with each other or the patient's condition.
Activation Criteria
Activating rapid response teams can be challenging, particularly if the criteria for activation are unclear or if team members are unsure of when to call for help.
Future Directions
The future of rapid response teams is exciting, with ongoing research and innovation aimed at improving patient outcomes and reducing hospital mortality.
Technology Integration
The integration of technology, such as electronic health records and bedside monitoring systems, can enhance the effectiveness of rapid response teams.
Personalized Medicine
The use of personalized medicine, such as genetic testing and precision therapy, can improve patient outcomes and reduce hospital mortality.
Global Collaboration
Global collaboration and knowledge sharing can help to improve the effectiveness of rapid response teams and reduce hospital mortality worldwide.
What is a rapid response team?
+A rapid response team is a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals that quickly responds to emergencies and provides life-saving interventions to patients who are deteriorating or at risk of cardiac arrest.
What are the benefits of rapid response teams?
+The benefits of rapid response teams include improved patient outcomes, enhanced patient safety, and reduced length of stay.
How do rapid response teams work?
+Rapid response teams work by quickly responding to emergencies and providing timely interventions. They are typically activated by a call to a designated phone number or by a bedside alarm.
In conclusion, rapid response teams are a critical component of hospital care, providing life-saving interventions to patients who are deteriorating or at risk of cardiac arrest. By understanding the benefits, working mechanisms, and challenges of these teams, hospitals can improve patient outcomes, enhance patient safety, and reduce hospital mortality. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with rapid response teams in the comments below.
