Intro
Learn about scaphoid bone fracture, a common wrist injury. Discover its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Understand how this fracture affects the wrists anatomy and function. Get insights into diagnosis, non-surgical, and surgical treatments, including cast immobilization, physical therapy, and recovery times. Manage your scaphoid fracture effectively.
Scaphoid bone fractures are a common type of wrist injury that can be painful and debilitating. The scaphoid bone is one of the eight small bones in the wrist, and it plays a crucial role in the movement and flexibility of the wrist joint. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for scaphoid bone fractures.
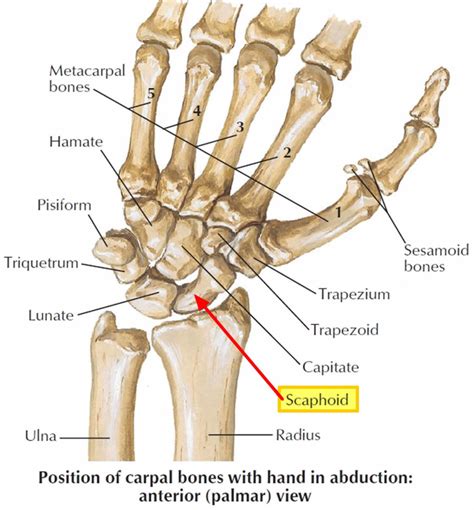
Understanding the Scaphoid Bone
The scaphoid bone is a small, boat-shaped bone located in the wrist, near the base of the thumb. It is one of the most commonly fractured bones in the wrist, accounting for approximately 60-70% of all wrist fractures. The scaphoid bone is responsible for allowing the wrist to move in multiple directions, including flexion, extension, and rotation.
Causes of Scaphoid Bone Fractures
Scaphoid bone fractures are typically caused by a fall onto an outstretched hand or a direct blow to the wrist. They can also occur as a result of a sudden twisting motion or a bending force applied to the wrist. Common activities that can lead to scaphoid bone fractures include:
- Sports, such as football, basketball, or tennis
- Falling onto an outstretched hand
- Direct blows to the wrist, such as in a car accident
- Repetitive strain or overuse of the wrist joint
Symptoms of Scaphoid Bone Fractures
The symptoms of a scaphoid bone fracture can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Common symptoms include:
- Pain and tenderness in the wrist, particularly in the area near the base of the thumb
- Swelling and bruising around the wrist
- Limited mobility or stiffness in the wrist joint
- Difficulty gripping or holding objects
- A feeling of instability or weakness in the wrist
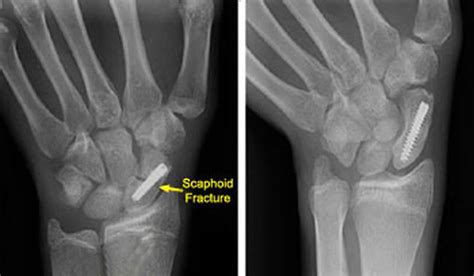
Diagnosing Scaphoid Bone Fractures
Diagnosing a scaphoid bone fracture typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests. A healthcare provider may perform the following tests:
- Physical examination: A thorough examination of the wrist and hand to assess pain, tenderness, and range of motion.
- X-rays: X-rays may be taken to confirm the presence of a fracture and to determine the severity of the injury.
- Computed Tomography (CT) scan: A CT scan may be ordered to provide a more detailed image of the wrist joint and to assess the extent of the fracture.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan: An MRI scan may be ordered to assess the surrounding soft tissues and to determine if there are any other injuries to the wrist joint.
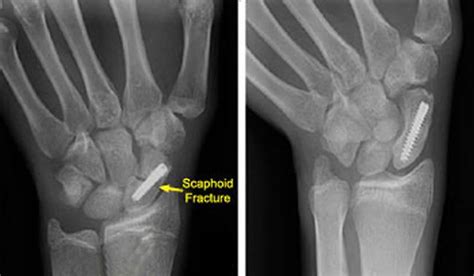
Treatment Options for Scaphoid Bone Fractures
Treatment for scaphoid bone fractures depends on the severity of the injury and the individual's overall health. The following are some common treatment options:
- Immobilization: A cast or splint may be applied to immobilize the wrist and allow the fracture to heal.
- Pain management: Pain medication may be prescribed to manage pain and discomfort.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy may be recommended to improve range of motion and strength in the wrist joint.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to realign and stabilize the fracture.
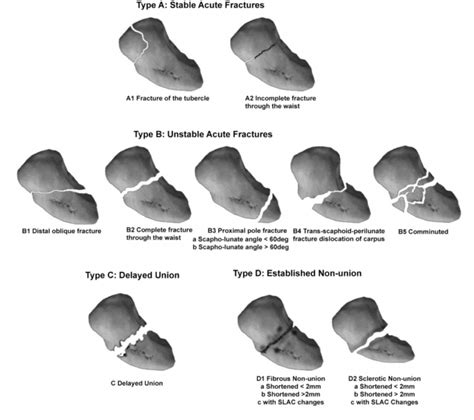
Types of Scaphoid Bone Fractures
There are several types of scaphoid bone fractures, including:
- Nondisplaced fracture: A fracture in which the bone remains in its normal position.
- Displaced fracture: A fracture in which the bone is out of place.
- Comminuted fracture: A fracture in which the bone is broken into multiple pieces.
- Avulsion fracture: A fracture in which a small piece of bone is pulled away from the main bone.
Complications of Scaphoid Bone Fractures
Scaphoid bone fractures can lead to several complications, including:
- Arthritis: Scaphoid bone fractures can increase the risk of developing arthritis in the wrist joint.
- Chronic pain: Scaphoid bone fractures can lead to chronic pain and stiffness in the wrist joint.
- Limited mobility: Scaphoid bone fractures can result in limited mobility and stiffness in the wrist joint.
- Nerve damage: Scaphoid bone fractures can cause nerve damage, leading to numbness or tingling in the hand or fingers.
Preventing Scaphoid Bone Fractures
Preventing scaphoid bone fractures involves taking steps to reduce the risk of injury. The following are some tips to prevent scaphoid bone fractures:
- Wear protective gear: Wear protective gear, such as wrist guards or gloves, when participating in sports or activities that involve high-impact movements.
- Use proper technique: Use proper technique when performing activities that involve bending or twisting the wrist.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of injury to the wrist joint.
- Stay active: Regular exercise can help to maintain strength and flexibility in the wrist joint.
Conclusion
Scaphoid bone fractures are a common type of wrist injury that can be painful and debilitating. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for scaphoid bone fractures can help individuals to seek prompt medical attention and prevent long-term complications. By taking steps to prevent scaphoid bone fractures and seeking medical attention if an injury occurs, individuals can reduce the risk of long-term damage to the wrist joint.
FAQs
What is the most common cause of scaphoid bone fractures?
+The most common cause of scaphoid bone fractures is a fall onto an outstretched hand or a direct blow to the wrist.
What are the symptoms of a scaphoid bone fracture?
+The symptoms of a scaphoid bone fracture include pain and tenderness in the wrist, swelling and bruising, limited mobility, and difficulty gripping or holding objects.
How is a scaphoid bone fracture diagnosed?
+A scaphoid bone fracture is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests, such as X-rays or CT scans.
