Intro
Discover the significance of a Sed Rate Blood Test, a crucial diagnostic tool measuring inflammation levels in the body. Learn what a Sed Rate test is, how its performed, and what the results mean for your health, including indications of conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and infections.
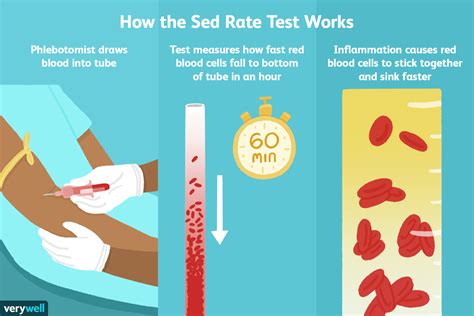
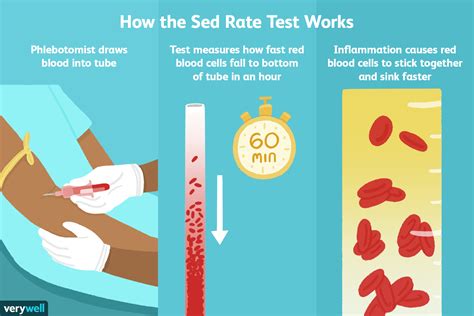
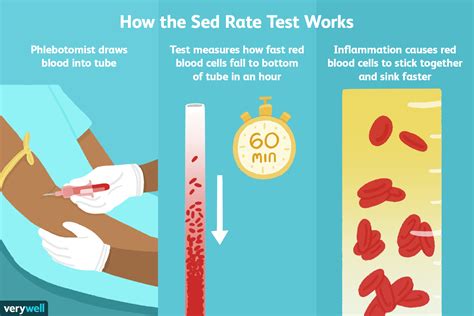
The sed rate blood test, also known as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test, is a simple yet informative diagnostic tool used to measure the rate at which red blood cells settle to the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. This test is often ordered by doctors to help diagnose and monitor various conditions, including inflammatory diseases, infections, and cancers.
In this article, we will delve into the details of the sed rate blood test, its purpose, procedure, and what the results mean.
What is the purpose of a sed rate blood test?
The primary purpose of a sed rate blood test is to detect the presence of inflammation in the body. When inflammation occurs, the body produces abnormal proteins that cause red blood cells to clump together and settle more quickly than normal. By measuring the rate at which red blood cells settle, doctors can determine the level of inflammation in the body.
The sed rate blood test is often used to:
- Diagnose inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and vasculitis
- Monitor the effectiveness of treatment for inflammatory conditions
- Detect infections such as tuberculosis and pneumonia
- Diagnose certain types of cancer, such as lymphoma and leukemia
- Monitor the progression of diseases such as multiple myeloma and Waldenström's macroglobulinemia
How is a sed rate blood test performed?
The sed rate blood test is a relatively simple procedure that involves the following steps:
- A healthcare professional will collect a blood sample from a vein in your arm using a sterile needle and syringe.
- The blood sample is then placed in a test tube containing a substance that prevents the blood from clotting.
- The test tube is left standing upright for a period of time, usually one hour.
- The rate at which the red blood cells settle to the bottom of the test tube is measured and recorded.
What do the results of a sed rate blood test mean?
The results of a sed rate blood test are measured in millimeters per hour (mm/h). A normal sed rate varies depending on age, sex, and other factors, but generally falls within the following ranges:
- Newborns: 0-2 mm/h
- Children: 0-10 mm/h
- Adults: 0-20 mm/h
- Elderly: 0-30 mm/h
A high sed rate indicates the presence of inflammation in the body, while a low sed rate suggests the absence of inflammation. However, it's essential to note that a high sed rate can also be caused by other factors such as:
- Anemia
- Pregnancy
- Menstruation
- Certain medications
What are the limitations of a sed rate blood test?
While the sed rate blood test is a useful diagnostic tool, it has some limitations. These include:
- A high sed rate can be caused by various factors, making it difficult to determine the underlying cause of inflammation.
- A low sed rate does not necessarily rule out the presence of inflammation.
- The test is not specific to any particular disease or condition.
- The test results can be influenced by various factors such as age, sex, and certain medications.
What are the risks and complications of a sed rate blood test?
The sed rate blood test is a relatively safe procedure, but as with any blood test, there are some risks and complications to be aware of. These include:
- Pain or discomfort at the needle site
- Bleeding or bruising at the needle site
- Infection at the needle site
- Fainting or dizziness due to blood loss
What are the alternatives to a sed rate blood test?
There are several alternative tests that can be used to diagnose and monitor inflammatory conditions. These include:
- C-reactive protein (CRP) test
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test using a different method
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Blood chemistry tests
Conclusion
In conclusion, the sed rate blood test is a useful diagnostic tool that can help doctors detect the presence of inflammation in the body. While it has some limitations, it remains a valuable test for diagnosing and monitoring various conditions. If you have any concerns or questions about the sed rate blood test, be sure to discuss them with your healthcare professional.
What is the normal range for a sed rate blood test?
+The normal range for a sed rate blood test varies depending on age, sex, and other factors. Generally, a normal sed rate falls within the following ranges: newborns: 0-2 mm/h, children: 0-10 mm/h, adults: 0-20 mm/h, and elderly: 0-30 mm/h.
What does a high sed rate indicate?
+A high sed rate indicates the presence of inflammation in the body. However, it can also be caused by other factors such as anemia, pregnancy, menstruation, and certain medications.
What are the risks and complications of a sed rate blood test?
+The sed rate blood test is a relatively safe procedure, but there are some risks and complications to be aware of, including pain or discomfort at the needle site, bleeding or bruising at the needle site, infection at the needle site, and fainting or dizziness due to blood loss.
