Intro
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test, also known as the sed rate test, is a simple yet informative blood test that helps diagnose and monitor various medical conditions. It's a crucial tool in the medical field, and understanding its working mechanism can provide valuable insights into the world of healthcare.
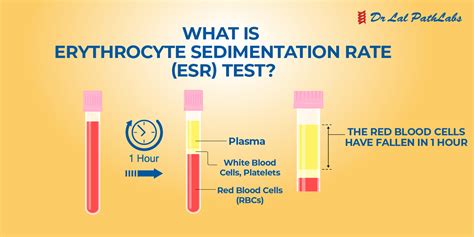
The ESR test measures the rate at which red blood cells (erythrocytes) settle in a test tube containing a blood sample. This rate is affected by the presence of inflammation, infection, or other conditions that alter the blood's composition. In this article, we'll delve into the details of the ESR test, its working mechanism, and its significance in medical diagnosis.
What is the purpose of the ESR test?
The primary purpose of the ESR test is to detect the presence of inflammation or infection in the body. When an inflammatory response occurs, the liver produces proteins that make red blood cells clump together, causing them to settle faster in a test tube. By measuring the rate of settlement, healthcare providers can identify potential health issues.
How does the ESR test work?
The ESR test involves a simple process:
- A blood sample is collected from a vein in the arm or finger.
- The blood sample is placed in a test tube containing an anticoagulant to prevent clotting.
- The test tube is left to stand upright for a specified period, usually one hour.
- During this time, the red blood cells settle at the bottom of the tube, leaving a clear liquid (plasma) on top.
- The rate at which the red blood cells settle is measured in millimeters per hour (mm/h).
What do ESR test results mean?
The ESR test results are interpreted based on the rate of settlement. A normal ESR rate varies depending on age, sex, and other factors, but generally falls within the following ranges:
- Normal: 0-20 mm/h (men), 0-30 mm/h (women)
- Mild inflammation: 20-40 mm/h
- Moderate inflammation: 40-60 mm/h
- Severe inflammation: 60-100 mm/h or higher
An elevated ESR rate indicates the presence of inflammation or infection, which can be caused by various conditions, such as:
- Infections (bacterial, viral, or fungal)
- Autoimmune disorders (rheumatoid arthritis, lupus)
- Cancer
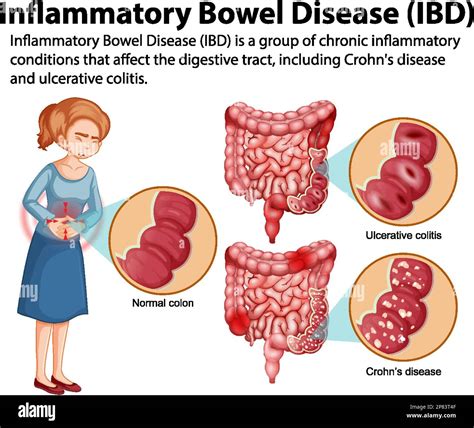
- Inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis)
What are the benefits of the ESR test?
The ESR test offers several benefits:
- Non-invasive: The test is simple and doesn't require any surgical procedures.
- Quick results: The test can be performed in a matter of hours, providing rapid diagnosis and treatment.
- Cost-effective: The ESR test is relatively inexpensive compared to other diagnostic tests.
- Monitoring: The test can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and track changes in inflammation levels.
What are the limitations of the ESR test?
While the ESR test is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has some limitations:
- Non-specific: The test doesn't identify the underlying cause of inflammation.
- Variable results: Results can be influenced by factors such as age, sex, and medications.
- Not a definitive diagnosis: The test should be used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and medical evaluations.
Image:
How is the ESR test used in medical diagnosis?
The ESR test is used in various medical settings to diagnose and monitor conditions such as:
- Rheumatoid arthritis: The test helps diagnose and monitor the progression of the disease.
- Lupus: The test is used to diagnose and monitor the activity of the disease.
- Cancer: The test can help diagnose and monitor the progression of certain types of cancer.
- Infections: The test is used to diagnose and monitor the severity of infections.
Image:

What are some common conditions diagnosed using the ESR test?
Some common conditions diagnosed using the ESR test include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Lupus
- Cancer (e.g., lymphoma, leukemia)
- Infections (e.g., pneumonia, tuberculosis)
- Inflammatory bowel disease (e.g., Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis)
Image:
FAQs:
What is the normal range for an ESR test?
+The normal range for an ESR test varies depending on age, sex, and other factors, but generally falls within the following ranges: 0-20 mm/h (men), 0-30 mm/h (women).
What does an elevated ESR rate indicate?
+An elevated ESR rate indicates the presence of inflammation or infection, which can be caused by various conditions, such as infections, autoimmune disorders, cancer, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Is the ESR test a definitive diagnosis?
+No, the ESR test is not a definitive diagnosis. It should be used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and medical evaluations to determine the underlying cause of inflammation.
Conclusion:
The ESR test is a valuable diagnostic tool that helps healthcare providers detect and monitor inflammation and infection. While it has its limitations, the test is widely used in various medical settings to diagnose and manage conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, cancer, and infections. By understanding the working mechanism and benefits of the ESR test, patients and healthcare providers can work together to achieve accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
