Intro
Discover the 5 essential steps of the nursing process, a systematic approach to patient care. Learn how to assess, diagnose, plan, implement, and evaluate care with precision. Mastering the nursing process is crucial for effective patient outcomes, improved quality of care, and enhanced nurse-patient relationships. Get the inside scoop on this fundamental nursing skill.
The nursing process is a systematic approach to providing patient care that has been widely adopted by nurses worldwide. It is a problem-solving approach that involves five essential steps: assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. These steps help nurses to identify patient problems, develop individualized care plans, and deliver high-quality care that meets the unique needs of each patient.
The nursing process is a critical component of nursing practice, and it is essential for nurses to understand and apply it in their daily work. By following the nursing process, nurses can ensure that their patients receive comprehensive, patient-centered care that addresses their physical, emotional, and spiritual needs. In this article, we will explore the five essential steps of the nursing process, and provide practical examples and tips for applying them in clinical practice.
Step 1: Assessment
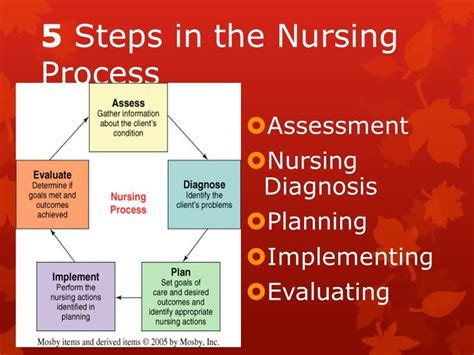
The first step of the nursing process is assessment. During this step, nurses gather data about the patient's physical, emotional, and spiritual status. This information is used to identify patient problems, and to develop a plan of care that addresses those problems. Assessment involves collecting data through various methods, including interviews, observations, and physical examinations.
Nurses use a variety of tools and techniques to collect data during the assessment phase. These may include:
- Clinical interviews: Nurses ask patients questions about their medical history, symptoms, and concerns.
- Physical examinations: Nurses perform physical examinations to assess the patient's physical status.
- Laboratory tests: Nurses order laboratory tests to gather additional data about the patient's condition.
- Observations: Nurses observe the patient's behavior, and note any changes or abnormalities.
Types of Assessment
There are several types of assessment that nurses may use, including:
- Initial assessment: This is the first assessment that is done when the patient is admitted to the hospital or clinic.
- Ongoing assessment: This is an ongoing process of collecting data and evaluating the patient's condition.
- Focused assessment: This is a targeted assessment that is done to gather specific information about the patient's condition.
Step 2: Diagnosis
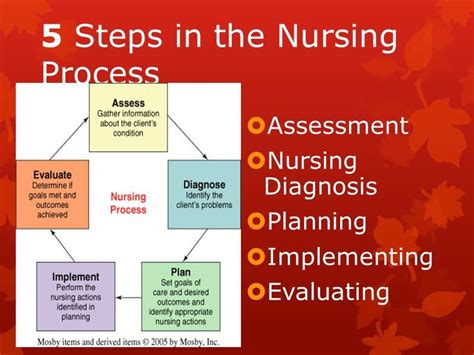
The second step of the nursing process is diagnosis. During this step, nurses analyze the data that was collected during the assessment phase, and identify patient problems. These problems may be physical, emotional, or spiritual in nature, and may include conditions such as pain, anxiety, or respiratory distress.
Nurses use a variety of techniques to identify patient problems, including:
- Pattern recognition: Nurses recognize patterns in the data that was collected during the assessment phase.
- Critical thinking: Nurses use critical thinking skills to analyze the data and identify patient problems.
- Decision-making: Nurses make decisions about the patient's condition, and identify the most likely diagnosis.
Types of Diagnoses
There are several types of diagnoses that nurses may use, including:
- Medical diagnosis: This is a diagnosis that is made by a physician, and is used to identify a specific medical condition.
- Nursing diagnosis: This is a diagnosis that is made by a nurse, and is used to identify a specific patient problem.
- Collaborative diagnosis: This is a diagnosis that is made by a team of healthcare professionals, including nurses, physicians, and other healthcare providers.
Step 3: Planning

The third step of the nursing process is planning. During this step, nurses develop a plan of care that addresses the patient's unique needs and problems. This plan is based on the data that was collected during the assessment phase, and the diagnosis that was made during the diagnosis phase.
Nurses use a variety of techniques to develop a plan of care, including:
- Goal setting: Nurses set specific goals for the patient's care, and develop a plan to achieve those goals.
- Intervention planning: Nurses plan specific interventions that will be used to address the patient's problems.
- Outcome measurement: Nurses identify specific outcomes that will be used to measure the effectiveness of the plan.
Types of Plans
There are several types of plans that nurses may use, including:
- Individualized care plan: This is a plan that is tailored to the patient's unique needs and problems.
- Standardized care plan: This is a plan that is used for patients with similar needs and problems.
- Collaborative care plan: This is a plan that is developed by a team of healthcare professionals, including nurses, physicians, and other healthcare providers.
Step 4: Implementation

The fourth step of the nursing process is implementation. During this step, nurses put the plan of care into action, and deliver care to the patient. This may involve administering medications, performing procedures, and providing education and support to the patient and their family.
Nurses use a variety of techniques to implement the plan of care, including:
- Medication administration: Nurses administer medications to the patient as prescribed by the physician.
- Procedure performance: Nurses perform procedures such as wound care, and respiratory therapy.
- Education and support: Nurses provide education and support to the patient and their family, and help them to understand the plan of care.
Types of Implementation
There are several types of implementation that nurses may use, including:
- Direct care: This is care that is provided directly to the patient, such as administering medications and performing procedures.
- Indirect care: This is care that is provided indirectly, such as providing education and support to the patient and their family.
- Delegated care: This is care that is delegated to other healthcare professionals, such as nursing assistants and medical technicians.
Step 5: Evaluation
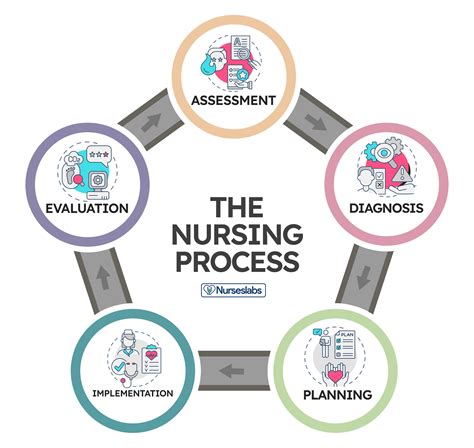
The fifth and final step of the nursing process is evaluation. During this step, nurses evaluate the effectiveness of the plan of care, and determine whether the patient's needs have been met. This may involve assessing the patient's condition, and evaluating the outcomes of the plan.
Nurses use a variety of techniques to evaluate the plan of care, including:
- Outcome measurement: Nurses measure the outcomes of the plan, and determine whether the patient's needs have been met.
- Patient feedback: Nurses solicit feedback from the patient, and use this information to evaluate the plan.
- Peer review: Nurses review the plan with their peers, and use this information to evaluate its effectiveness.
Types of Evaluation
There are several types of evaluation that nurses may use, including:
- Formative evaluation: This is an ongoing evaluation that is used to monitor the patient's progress, and make adjustments to the plan as needed.
- Summative evaluation: This is a final evaluation that is used to determine the effectiveness of the plan, and make decisions about future care.
- Peer evaluation: This is an evaluation that is conducted by a team of healthcare professionals, including nurses, physicians, and other healthcare providers.
What is the nursing process?
+The nursing process is a systematic approach to providing patient care that involves five essential steps: assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation.
Why is the nursing process important?
+The nursing process is important because it helps nurses to provide comprehensive, patient-centered care that addresses the unique needs of each patient. It also helps to ensure that patients receive high-quality care that is tailored to their individual needs.
How do nurses use the nursing process in clinical practice?
+Nurses use the nursing process in clinical practice by following the five essential steps: assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. They use a variety of techniques, including clinical interviews, physical examinations, and laboratory tests, to gather data and develop a plan of care that addresses the patient's unique needs.
In conclusion, the nursing process is a critical component of nursing practice that helps nurses to provide comprehensive, patient-centered care. By following the five essential steps of the nursing process, nurses can ensure that their patients receive high-quality care that addresses their unique needs and problems. We hope that this article has provided you with a better understanding of the nursing process, and how it is used in clinical practice. Thank you for reading!
