Intro
Discover the Systems Approach to Social Work, a holistic method that integrates individual, family, and community needs. Learn how this comprehensive framework addresses social problems, promotes collaboration, and fosters sustainable change. Explore the benefits of a systems thinking approach in social work practice, policy, and research.
The social work profession has long been dedicated to improving the lives of individuals, families, and communities. However, the complexities of modern social issues have led to a growing recognition of the need for a more comprehensive approach to social work practice. A systems approach to social work offers a holistic method for addressing the intricate relationships between individuals, families, communities, and societal systems.
Social work has traditionally focused on the individual or family unit, with interventions aimed at addressing specific problems or needs. However, this narrow focus can overlook the broader social and environmental factors that contribute to these issues. A systems approach, on the other hand, recognizes that individuals and families are part of larger systems, including communities, organizations, and societal structures. By examining the interactions and interdependencies within and between these systems, social workers can develop more effective and sustainable solutions.
Understanding Systems Theory
A systems approach to social work is grounded in systems theory, which posits that systems are composed of interconnected components that interact and influence one another. Systems can be open or closed, with open systems exchanging resources and information with their environment, and closed systems operating independently. Social workers must consider the type of system they are working with, as well as the boundaries, relationships, and power dynamics within and between systems.
In social work, systems theory is applied through the use of various models, such as the ecological systems model, the family systems model, and the structural-functional model. These models provide a framework for understanding the complex interactions within and between systems, and for identifying potential points of intervention.
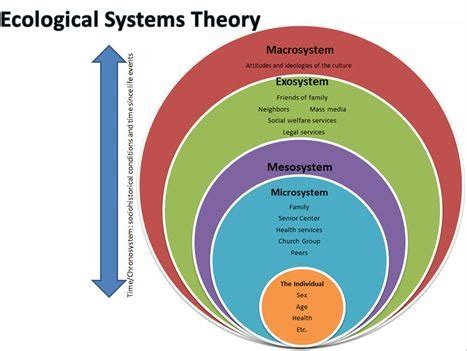
Ecological Systems Model
The ecological systems model, developed by Urie Bronfenbrenner, views the individual as part of a series of nested systems, including the microsystem, mesosystem, exosystem, and macrosystem. The microsystem consists of the individual's immediate environment, such as family and peers. The mesosystem refers to the relationships between the individual's microsystems, such as the connection between family and school. The exosystem includes external factors that influence the individual's life, such as parental work schedules or community resources. The macrosystem is the broader societal context, encompassing cultural norms, policies, and institutions.
Applying a Systems Approach in Social Work Practice
A systems approach to social work involves several key steps:
- Assessment: Identify the individual's or family's strengths, needs, and goals, as well as the relevant systems and relationships involved.
- Analysis: Examine the interactions and interdependencies within and between systems, including power dynamics, boundaries, and communication patterns.
- Intervention: Develop a plan that addresses the individual's or family's needs, taking into account the broader systems context.
- Evaluation: Monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the intervention, making adjustments as needed.

Case Example: Working with a Family in Crisis
A social worker is working with a family who has experienced a recent crisis, such as a parent's job loss or a child's serious illness. The social worker uses a systems approach to assess the family's strengths, needs, and goals, as well as the relevant systems and relationships involved.
- Assessment: The social worker identifies the family's strengths, such as their resilience and support network, as well as their needs, including financial assistance and emotional support.
- Analysis: The social worker examines the interactions and interdependencies within and between systems, including the family's relationships with their employer, healthcare providers, and community resources.
- Intervention: The social worker develops a plan that addresses the family's needs, including connecting them with financial assistance programs, providing emotional support, and facilitating communication between the family and their employer.
- Evaluation: The social worker monitors and evaluates the effectiveness of the intervention, making adjustments as needed to ensure the family's continued well-being.
Benefits of a Systems Approach to Social Work
A systems approach to social work offers several benefits, including:
- Holistic understanding: A systems approach provides a comprehensive understanding of the individual's or family's situation, taking into account the broader social and environmental factors that contribute to their needs.
- Effective interventions: By addressing the interactions and interdependencies within and between systems, social workers can develop more effective and sustainable solutions.
- Improved outcomes: A systems approach can lead to improved outcomes, as social workers are better equipped to address the complex needs of individuals and families.
- Increased efficiency: By considering the broader systems context, social workers can reduce duplication of services and improve communication between agencies and organizations.

Challenges and Limitations of a Systems Approach
While a systems approach to social work offers many benefits, it also presents several challenges and limitations, including:
- Complexity: A systems approach can be complex and time-consuming, requiring social workers to consider multiple systems and relationships.
- Power dynamics: Social workers must be aware of the power dynamics within and between systems, including issues of privilege, oppression, and social justice.
- Limited resources: Social workers may face limited resources, including funding, personnel, and organizational support.
- Resistance to change: Social workers may encounter resistance to change from individuals, families, or organizations, requiring them to navigate complex power dynamics and communication patterns.
Future Directions for a Systems Approach to Social Work
As the social work profession continues to evolve, a systems approach will remain a critical component of effective practice. Future directions for a systems approach to social work include:
- Integration with technology: Social workers must be prepared to integrate technology into their practice, including the use of electronic health records, social media, and other digital tools.
- Increased focus on prevention: A systems approach can help social workers focus on prevention, rather than solely on intervention, by addressing the broader social and environmental factors that contribute to individual and family needs.
- Greater emphasis on social justice: Social workers must prioritize social justice, recognizing the ways in which systems and relationships can perpetuate inequality and oppression.

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with a systems approach to social work. How have you used a systems approach in your practice? What benefits and challenges have you encountered? Share your insights in the comments below.
What is a systems approach to social work?
+A systems approach to social work is a holistic method that recognizes the individual or family as part of larger systems, including communities, organizations, and societal structures.
What are the benefits of a systems approach to social work?
+The benefits of a systems approach to social work include a holistic understanding of the individual's or family's situation, effective interventions, improved outcomes, and increased efficiency.
What are the challenges and limitations of a systems approach to social work?
+The challenges and limitations of a systems approach to social work include complexity, power dynamics, limited resources, and resistance to change.

