Intro
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, nurse practitioners (NPs) are playing an increasingly vital role in delivering high-quality patient care. However, despite the numerous benefits of NPs, there are also some concerns that need to be addressed. In this article, we will explore five key concerns with nurse practitioners and discuss the implications for patients, healthcare systems, and the nursing profession as a whole.

Concern 1: Scope of Practice Limitations
One of the primary concerns with nurse practitioners is the limitations on their scope of practice. In many states, NPs are restricted from practicing to the full extent of their education and training, which can lead to frustration and burnout. These limitations can also impact patient care, as NPs may not be able to provide the level of care that they are capable of providing.
For example, in some states, NPs are not allowed to prescribe certain medications or order diagnostic tests without the supervision of a physician. This can lead to delays in care and increased costs, as patients may need to see a physician for services that an NP could provide.
Potential Solutions
To address this concern, many organizations are advocating for the removal of scope of practice limitations on NPs. This would allow NPs to practice to the full extent of their education and training, which would improve patient care and increase access to healthcare services.

Concern 2: Education and Training
Another concern with nurse practitioners is the variation in education and training programs. While NPs are required to have a master's degree in nursing, the curriculum and clinical training can vary significantly between programs.
This can lead to inconsistencies in the quality of care provided by NPs, as some may not have received the same level of education and training as others. Additionally, the lack of standardization in NP education and training can make it difficult for employers to evaluate the qualifications of NP candidates.
Potential Solutions
To address this concern, many organizations are advocating for the development of standardized education and training programs for NPs. This would ensure that all NPs receive the same level of education and training, which would improve the quality of care and increase consistency in NP practice.

Concern 3: Autonomy and Collaboration
Nurse practitioners often work in collaborative environments with physicians and other healthcare professionals. However, there can be concerns about autonomy and collaboration, particularly when it comes to decision-making and patient care.
In some cases, NPs may feel that they are not being utilized to their full potential, or that their input is not being valued by physicians and other healthcare professionals. This can lead to frustration and burnout, as well as decreased job satisfaction.
Potential Solutions
To address this concern, many organizations are advocating for the development of collaborative practice models that promote autonomy and teamwork. This would ensure that NPs are able to work to the full extent of their education and training, while also promoting effective communication and collaboration with other healthcare professionals.
Concern 4: Patient Safety and Quality of Care
Patient safety and quality of care are top priorities in healthcare, and NPs play a critical role in ensuring that patients receive high-quality care. However, there can be concerns about patient safety and quality of care, particularly when it comes to the use of NPs in certain settings.
For example, some studies have suggested that NPs may not be as effective as physicians in certain areas, such as diagnosing and managing complex medical conditions. However, other studies have shown that NPs can provide high-quality care that is comparable to that of physicians.
Potential Solutions
To address this concern, many organizations are advocating for the development of evidence-based guidelines for NP practice. This would ensure that NPs are using the best available evidence to inform their practice, which would improve patient safety and quality of care.

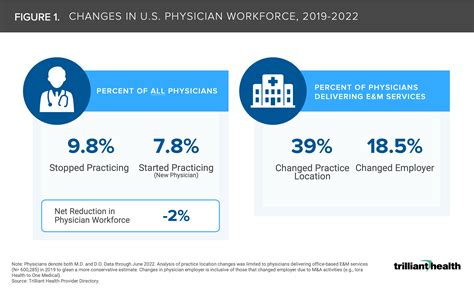
Concern 5: Workforce Shortages and Burnout
Finally, there can be concerns about workforce shortages and burnout among NPs. The demand for NPs is high, and many organizations are struggling to recruit and retain qualified NPs.
This can lead to burnout and decreased job satisfaction, as NPs may feel overwhelmed by heavy workloads and lack of support. Additionally, workforce shortages can impact patient care, as organizations may not have enough NPs to meet patient needs.
Potential Solutions
To address this concern, many organizations are advocating for the development of strategies to support NP recruitment and retention. This could include offering competitive salaries and benefits, providing opportunities for professional development and advancement, and promoting a positive work environment.
In conclusion, while there are several concerns with nurse practitioners, there are also many potential solutions. By addressing these concerns and promoting the development of evidence-based guidelines, collaborative practice models, and strategies to support NP recruitment and retention, we can improve patient care and increase access to healthcare services.
What is the role of nurse practitioners in healthcare?
+Nurse practitioners play a critical role in delivering high-quality patient care. They provide primary and specialty care to patients, including diagnosing and managing medical conditions, prescribing medications, and ordering diagnostic tests.
What are the benefits of using nurse practitioners in healthcare?
+The benefits of using nurse practitioners in healthcare include improved patient outcomes, increased access to healthcare services, and reduced healthcare costs. NPs can also provide high-quality care that is comparable to that of physicians.
What are the concerns about nurse practitioners in healthcare?
+Some of the concerns about nurse practitioners in healthcare include scope of practice limitations, education and training variations, autonomy and collaboration issues, patient safety and quality of care concerns, and workforce shortages and burnout.
