Intro
Discover the ins and outs of umbilical hernia surgery, a common procedure to repair a hernia near the belly button. Learn about symptoms, causes, treatment options, and recovery time. Our comprehensive guide covers laparoscopic and open surgery methods, hernia repair techniques, and post-operative care to help you make informed decisions about your health.
An umbilical hernia is a protrusion that occurs when part of the intestine bulges through an opening in the abdominal muscles near the navel. This type of hernia is relatively common, especially in infants and young children, but can also occur in adults. While some umbilical hernias may not cause symptoms, others can lead to discomfort, pain, and potentially serious complications. In many cases, surgery is the most effective treatment option for umbilical hernias.
Umbilical hernia surgery is a relatively common procedure, with thousands of operations performed every year. The surgery is typically done on an outpatient basis, meaning the patient can go home the same day. However, the decision to undergo surgery should be made after careful consideration and consultation with a qualified healthcare professional.
Understanding Umbilical Hernias
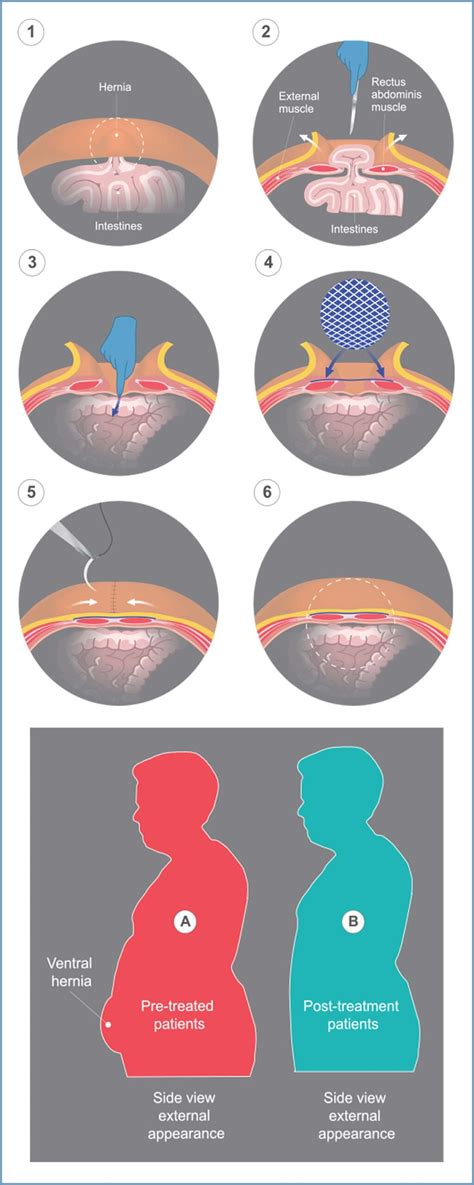
An umbilical hernia occurs when there is a weak spot in the abdominal wall near the navel. This weak spot can be present at birth or develop later in life due to various factors, such as obesity, pregnancy, or chronic coughing. When the weak spot is large enough, part of the intestine can bulge through the opening, creating a hernia.
Causes and Risk Factors
Umbilical hernias can occur in anyone, but some people are more likely to develop them. Risk factors include:
- Age: Infants and young children are more prone to umbilical hernias.
- Family history: Having a family history of umbilical hernias increases the risk.
- Obesity: Excess weight can put additional strain on the abdominal muscles, leading to a hernia.
- Pregnancy: The increased pressure on the abdominal muscles during pregnancy can cause a hernia.
- Chronic coughing: Coughing can put additional strain on the abdominal muscles, leading to a hernia.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options

Diagnosing an umbilical hernia typically involves a physical examination and medical history. The doctor may also order imaging tests, such as an ultrasound or CT scan, to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment options for umbilical hernias depend on the size and severity of the hernia, as well as the individual's overall health. In some cases, the doctor may recommend watchful waiting, especially if the hernia is small and not causing symptoms. However, surgery is often the most effective treatment option, especially if the hernia is large or causing discomfort.
Surgical Options
There are two main surgical options for umbilical hernia repair:
- Open hernia repair: This involves making a single incision in the abdomen to repair the hernia.
- Laparoscopic hernia repair: This involves making several small incisions in the abdomen to repair the hernia using a laparoscope.
Both surgical options are effective, but laparoscopic hernia repair is often preferred because it is less invasive and results in less scarring.
Preparing for Surgery
Preparing for umbilical hernia surgery involves several steps, including:
- Stopping certain medications: The doctor may advise stopping certain medications, such as blood thinners, before surgery.
- Fasting: The patient will need to fast for several hours before surgery.
- Arranging for transportation: The patient will need to arrange for someone to drive them home after surgery.
What to Expect During Surgery
During surgery, the patient will be given general anesthesia to ensure they are comfortable and pain-free. The surgeon will then make the necessary incisions to repair the hernia. The surgery typically takes about 30-60 minutes to complete.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovering from umbilical hernia surgery typically takes several days to a week. During this time, the patient will need to:
- Rest: The patient will need to rest and avoid heavy lifting, bending, or straining.
- Manage pain: The patient will be given pain medication to manage any discomfort or pain.
- Follow a diet: The patient will need to follow a diet that is easy to digest, such as bland foods.
Complications and Risks
As with any surgery, there are risks and complications associated with umbilical hernia surgery. These include:
- Infection: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection with umbilical hernia surgery.
- Adhesions: Adhesions can form in the abdomen after surgery, which can lead to bowel obstruction.
- Hernia recurrence: There is a risk of the hernia recurring after surgery.
Conclusion
Umbilical hernia surgery is a common and effective treatment option for umbilical hernias. While the surgery is typically straightforward, it's essential to carefully consider the risks and benefits before making a decision. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for umbilical hernias, individuals can make informed decisions about their care.
What is an umbilical hernia?
+An umbilical hernia is a protrusion that occurs when part of the intestine bulges through an opening in the abdominal muscles near the navel.
What are the symptoms of an umbilical hernia?
+Symptoms of an umbilical hernia may include a visible bulge near the navel, discomfort or pain, and potentially serious complications if left untreated.
Is umbilical hernia surgery painful?
+No, umbilical hernia surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia, which ensures the patient is comfortable and pain-free during the procedure.
