Intro
Discover the complexities of mental health with our comprehensive guide to 10 common types of mental illnesses, including anxiety disorders, depressive disorders, personality disorders, and more. Learn about symptoms, causes, and treatment options for each condition, and gain a deeper understanding of mental health awareness and support.
Mental illnesses are a growing concern worldwide, affecting millions of people from all walks of life. Despite their prevalence, many mental health conditions remain shrouded in mystery and stigma, preventing individuals from seeking the help they need. It's essential to educate ourselves about the different types of mental illnesses to promote understanding, empathy, and support for those affected.
The importance of mental health awareness cannot be overstated. By acknowledging the complexities of mental illnesses, we can work towards creating a more inclusive and supportive environment for individuals struggling with their mental well-being. In this article, we will delve into 10 common types of mental illnesses, exploring their symptoms, causes, and treatment options.

1. Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
Major Depressive Disorder, also known as depression, is a mood disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include changes in appetite, sleep patterns, and energy levels.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Genetics
- Brain chemistry
- Traumatic events
- Chronic stress
Treatment Options:
- Medications (antidepressants)
- Psychotherapy (cognitive-behavioral therapy, interpersonal therapy)
- Lifestyle changes (exercise, healthy diet, social support)

2. Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by excessive and persistent fear, worry, or anxiety. The most common types of anxiety disorders include generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and phobias.
Symptoms:
- Restlessness and irritability
- Difficulty concentrating
- Sleep disturbances
- Physical symptoms (rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling)
Treatment Options:
- Medications (benzodiazepines, antidepressants)
- Psychotherapy (cognitive-behavioral therapy, exposure therapy)
- Relaxation techniques (deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation)
3. Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a mood disorder characterized by extreme mood swings, ranging from manic highs to depressive lows. Symptoms can vary in severity and may include changes in energy levels, activity, and sleep patterns.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Genetics
- Brain chemistry
- Traumatic events
- Substance abuse
Treatment Options:
- Medications (mood stabilizers, antipsychotics)
- Psychotherapy (cognitive-behavioral therapy, family therapy)
- Lifestyle changes (regular exercise, healthy diet, social support)

4. Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a chronic mental health disorder characterized by distorted thinking, perception, and behavior. Symptoms can include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking, and negative symptoms such as apathy and social withdrawal.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Genetics
- Brain chemistry
- Environmental factors (prenatal complications, substance abuse)
Treatment Options:
- Medications (antipsychotics)
- Psychotherapy (cognitive-behavioral therapy, family therapy)
- Social support (group therapy, rehabilitation programs)

5. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder is a mental health condition that develops after a person experiences a traumatic event, such as combat, abuse, or natural disasters. Symptoms can include flashbacks, nightmares, severe anxiety, and avoidance of triggers.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Traumatic events
- Genetics
- Brain chemistry
Treatment Options:
- Medications (antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications)
- Psychotherapy (cognitive-behavioral therapy, exposure therapy)
- Support groups (group therapy, peer support)

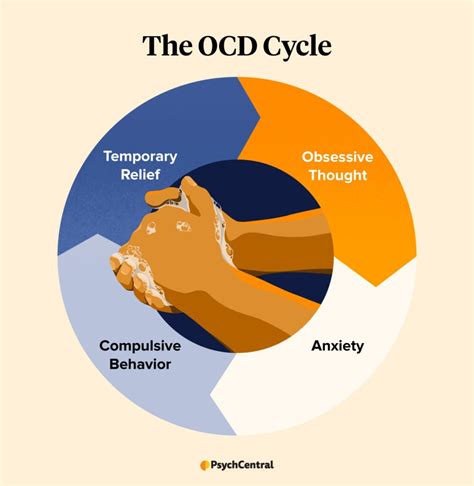
6. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder is a mental health condition characterized by recurring, intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions). Symptoms can include excessive cleaning, checking, or ordering.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Genetics
- Brain chemistry
- Environmental factors (stress, trauma)
Treatment Options:
- Medications (antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications)
- Psychotherapy (cognitive-behavioral therapy, exposure and response prevention)
- Lifestyle changes (regular exercise, healthy diet, relaxation techniques)
7. Eating Disorders
Eating disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by abnormal eating habits and body image concerns. The most common types of eating disorders include anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge eating disorder.
Symptoms:
- Restrictive eating
- Bingeing and purging
- Excessive exercise
- Body image distortion
Treatment Options:
- Medications (antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications)
- Psychotherapy (cognitive-behavioral therapy, family-based therapy)
- Nutrition counseling (meal planning, healthy eating habits)

8. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Symptoms can include difficulty paying attention, following instructions, and controlling impulses.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Genetics
- Brain chemistry
- Environmental factors (prenatal exposure to tobacco smoke, lead exposure)
Treatment Options:
- Medications (stimulants, non-stimulants)
- Psychotherapy (behavioral therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy)
- Lifestyle changes (regular exercise, healthy diet, sleep habits)

9. Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Autism Spectrum Disorder is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by symptoms of social communication, social interaction, and restricted and repetitive behaviors. Symptoms can include difficulty with verbal and nonverbal communication, social interactions, and repetitive behaviors.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Genetics
- Brain chemistry
- Environmental factors (prenatal exposure to air pollution, maternal infection)
Treatment Options:
- Behavioral therapies (applied behavior analysis, positive reinforcement)
- Medications (antipsychotics, antidepressants)
- Support services (speech therapy, occupational therapy)

10. Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
Borderline Personality Disorder is a mental health condition characterized by symptoms of emotional instability, impulsivity, and unstable relationships. Symptoms can include intense emotional dysregulation, impulsive behaviors, and unstable relationships.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Genetics
- Brain chemistry
- Environmental factors (trauma, neglect)
Treatment Options:
- Psychotherapy (dialectical behavior therapy, psychodynamic therapy)
- Medications (antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications)
- Support groups (group therapy, peer support)

In conclusion, mental illnesses are complex and multifaceted conditions that require compassion, understanding, and support. By educating ourselves about the different types of mental illnesses, we can work towards creating a more inclusive and supportive environment for individuals struggling with their mental well-being.
If you or someone you know is struggling with a mental illness, don't hesitate to reach out for help. Talk to a mental health professional, join a support group, or call a helpline. Remember, mental health matters, and seeking help is the first step towards recovery.
What is the most common mental illness?
+Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) is one of the most common mental illnesses, affecting over 300 million people worldwide.
Can mental illnesses be cured?
+While some mental illnesses can be managed with treatment, others may require ongoing therapy and support. Recovery is possible with the right treatment and support.
How can I support someone with a mental illness?
+Listen without judgment, offer emotional support, and encourage them to seek professional help. Educate yourself about their condition and be patient and understanding.
