Intro
Discover the uses and benefits of Bactrim antibiotic. Learn what Bactrim treats, its dosage, and potential side effects. Understand how this sulfa-based medication combats bacterial infections, including UTIs, bronchitis, and pneumonia. Get informed about Bactrims mechanism of action, interactions, and contraindications.
The Bactrim antibiotic, also known as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, is a widely used medication that treats various bacterial infections. In this article, we will delve into the world of Bactrim, exploring its uses, benefits, and potential side effects.
What is Bactrim Used For?
Bactrim is a combination antibiotic that contains two active ingredients: trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole. This powerful duo works together to combat bacterial infections by inhibiting the growth of bacteria and preventing them from multiplying.
Bactrim is commonly used to treat a range of infections, including:
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Respiratory tract infections, such as bronchitis and pneumonia
- Skin and soft tissue infections, such as cellulitis and abscesses
- Gastrointestinal infections, such as traveler's diarrhea
- Ear infections, such as otitis media
How Does Bactrim Work?
Bactrim works by targeting the bacterial cell's ability to produce folic acid, a crucial nutrient for bacterial growth and survival. Trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole inhibit the production of folic acid, ultimately leading to the death of the bacterial cells.
This mechanism of action allows Bactrim to effectively combat a wide range of bacterial infections, including those caused by:
- Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus
- Gram-negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli)
- Anaerobic bacteria, such as Bacteroides fragilis
Benefits of Using Bactrim
Bactrim offers several benefits, including:
- Broad-spectrum coverage: Bactrim is effective against a wide range of bacterial infections, making it a versatile treatment option.
- Easy to administer: Bactrim is available in oral and intravenous forms, making it easy to administer in various settings.
- Cost-effective: Bactrim is generally less expensive than other antibiotics, making it a cost-effective treatment option.
Side Effects and Precautions
While Bactrim is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
- Dizziness
In rare cases, Bactrim can cause more serious side effects, such as:
- Allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis
- Blood disorders, such as thrombocytopenia
- Liver damage
It is essential to discuss any concerns or pre-existing medical conditions with your healthcare provider before taking Bactrim.
Precautions and Contraindications
Bactrim is contraindicated in individuals with:
- Known hypersensitivity to trimethoprim or sulfamethoxazole
- Severe liver or kidney disease
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding
Additionally, Bactrim should be used with caution in individuals with:
- G6PD deficiency
- Porphyria
- Folate deficiency
Interactions with Other Medications
Bactrim can interact with other medications, including:
- Warfarin (Coumadin)
- Phenylbutazone (Butazolidin)
- Cyclosporine (Sandimmune)
It is essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking before starting Bactrim.
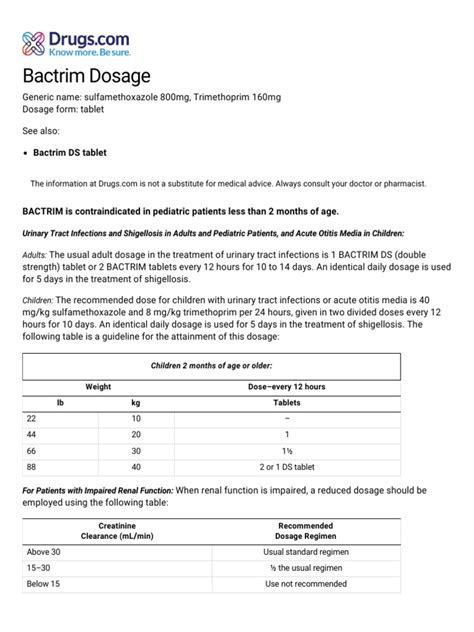
Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of Bactrim vary depending on the type and severity of the infection. The typical adult dosage is:
- 160mg/800mg (trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole) orally every 12 hours for 10-14 days
The pediatric dosage is:
- 8mg/kg/day (trimethoprim) + 40mg/kg/day (sulfamethoxazole) orally every 12 hours for 10-14 days
Resistance and Alternatives
The rise of antibiotic resistance has led to concerns about the effectiveness of Bactrim. In cases where Bactrim is not effective, alternative antibiotics may be prescribed, such as:
- Ciprofloxacin (Cipro)
- Amoxicillin-clavulanate (Augmentin)
- Levofloxacin (Levaquin)
Conclusion: Bactrim Antibiotic - A Powerful Tool in the Fight Against Bacterial Infections
Bactrim is a widely used and effective antibiotic that treats a range of bacterial infections. While it is generally well-tolerated, it is essential to be aware of potential side effects and interactions with other medications. By understanding the benefits and risks of Bactrim, healthcare providers can make informed decisions about its use in various clinical settings.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Bactrim in the comments section below. Have you taken Bactrim for a bacterial infection? What were your experiences with the medication?
What is Bactrim used for?
+Bactrim is used to treat a range of bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections, respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, gastrointestinal infections, and ear infections.
How does Bactrim work?
+Bactrim works by targeting the bacterial cell's ability to produce folic acid, ultimately leading to the death of the bacterial cells.
What are the common side effects of Bactrim?
+Common side effects of Bactrim include nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headache, and dizziness.
Can Bactrim be used in pregnant or breastfeeding women?
+No, Bactrim is contraindicated in pregnant or breastfeeding women due to the risk of fetal harm or neonatal hyperbilirubinemia.
What are the alternatives to Bactrim?
+Alternatives to Bactrim include ciprofloxacin (Cipro), amoxicillin-clavulanate (Augmentin), and levofloxacin (Levaquin).
