Intro
Discover the vital role of a case manager in healthcare and social services. Learn about the responsibilities, skills, and qualifications required to become a successful case manager. Understand how case managers coordinate care, advocate for patients, and connect them with essential resources, improving health outcomes and quality of life.
The role of a case manager is often misunderstood, yet it is a vital profession that plays a significant part in the healthcare and social services industries. Case managers are highly trained professionals who work with patients, families, and healthcare providers to ensure that individuals receive the necessary care and support to achieve their health and wellness goals. In this article, we will delve into the world of case management, exploring the role, responsibilities, and benefits of this helping profession.
What is a Case Manager?

A case manager is a healthcare professional who coordinates and manages patient care, ensuring that individuals receive the necessary medical, social, and emotional support to achieve optimal health outcomes. Case managers work with patients, families, and healthcare providers to develop personalized care plans that address the patient's unique needs and circumstances. They act as advocates, navigators, and educators, helping patients to access the resources and services they need to manage their health conditions effectively.
Responsibilities of a Case Manager
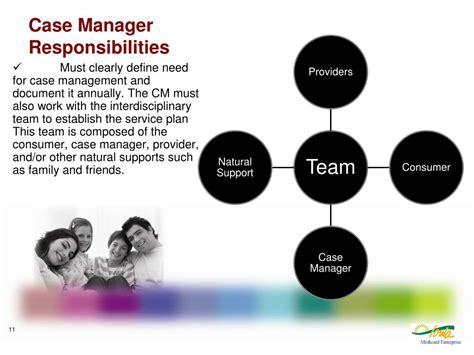
Case managers have a wide range of responsibilities, including:
- Conducting patient assessments to identify needs and develop care plans
- Coordinating medical and social services, such as doctor's appointments, therapy sessions, and home care
- Communicating with patients, families, and healthcare providers to ensure that everyone is informed and on the same page
- Advocating for patients' needs and rights
- Educating patients and families about their health conditions, treatment options, and self-care strategies
- Monitoring patient progress and adjusting care plans as needed
- Collaborating with healthcare providers to ensure that patients receive comprehensive and coordinated care
Types of Case Managers
There are several types of case managers, each with their own specialized focus and expertise. Some of the most common types of case managers include:
- Medical Case Managers: Work with patients who have complex medical conditions, such as chronic illnesses or injuries.
- Psychiatric Case Managers: Work with patients who have mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety, or substance abuse.
- Social Case Managers: Work with patients who have social and emotional needs, such as housing, employment, or family support.
- Geriatric Case Managers: Work with older adults who have age-related health and social needs.
Benefits of Case Management
Case management offers numerous benefits to patients, families, and healthcare providers. Some of the most significant advantages of case management include:
- Improved Health Outcomes: Case managers help patients to receive the necessary care and support to manage their health conditions effectively.
- Increased Patient Satisfaction: Case managers act as advocates and navigators, helping patients to access the resources and services they need.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: Case managers help to reduce healthcare costs by coordinating care, reducing hospitalizations, and preventing complications.
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: Case managers educate patients and families about their health conditions, treatment options, and self-care strategies.
How to Become a Case Manager

To become a case manager, you typically need to have a bachelor's degree in a healthcare-related field, such as nursing, social work, or healthcare administration. Many case managers also have specialized certifications, such as the Certified Case Manager (CCM) or the Certified Professional in Healthcare Management (CPHM). Some of the key skills and qualities required to be a successful case manager include:
- Communication and Interpersonal Skills: Case managers must be able to communicate effectively with patients, families, and healthcare providers.
- Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking Skills: Case managers must be able to analyze complex situations and develop creative solutions.
- Empathy and Compassion: Case managers must be able to empathize with patients and families, providing emotional support and guidance.
- Organizational and Time Management Skills: Case managers must be able to prioritize tasks, manage time effectively, and maintain accurate records.
Conclusion
Case managers play a vital role in the healthcare and social services industries, working with patients, families, and healthcare providers to ensure that individuals receive the necessary care and support to achieve their health and wellness goals. By understanding the role, responsibilities, and benefits of case management, we can appreciate the importance of this helping profession and the positive impact it has on patients' lives.
What is the primary role of a case manager?
+The primary role of a case manager is to coordinate and manage patient care, ensuring that individuals receive the necessary medical, social, and emotional support to achieve optimal health outcomes.
What are the benefits of case management?
+Case management offers numerous benefits, including improved health outcomes, increased patient satisfaction, reduced healthcare costs, and enhanced patient engagement.
How do I become a case manager?
+To become a case manager, you typically need to have a bachelor's degree in a healthcare-related field, such as nursing, social work, or healthcare administration. Many case managers also have specialized certifications, such as the Certified Case Manager (CCM) or the Certified Professional in Healthcare Management (CPHM).
