Intro
Discover the fascinating process of accommodation of the eye, a crucial aspect of human vision. Learn how the eye adapts to changing distances, and how the lens, ciliary muscles, and retina work together to focus light. Understand the science behind nearsightedness, farsightedness, and presbyopia, and explore the latest research on eye accommodation.
The human eye is a complex and fascinating organ, and one of its most impressive features is its ability to accommodate, or focus, on objects at varying distances. This process is crucial for our daily lives, enabling us to switch seamlessly between reading a book, watching TV, and driving a car. But have you ever wondered how the eye actually accomplishes this feat? In this article, we'll delve into the mechanics of accommodation, exploring how the eye works its magic to bring the world into sharp focus.
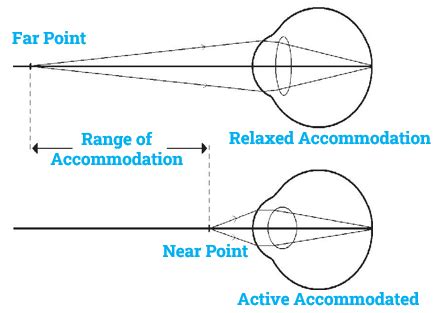
Accommodation is a complex process that involves the coordinated effort of multiple components within the eye. At its core, it's a matter of changing the shape of the lens to focus light properly on the retina. When we look at something close up, the lens becomes thicker and more curved, allowing us to focus on nearby objects. Conversely, when we gaze out at distant objects, the lens becomes thinner and less curved, enabling us to see clearly at a distance.
The Anatomy of Accommodation
To understand how accommodation works, it's essential to familiarize yourself with the key players involved. The eye's lens is the primary structure responsible for focusing light. It's a clear, flexible disc made of protein and water, located behind the iris and the pupil. The lens is attached to the ciliary muscles by zonular fibers, which are like tiny rubber bands that hold the lens in place.
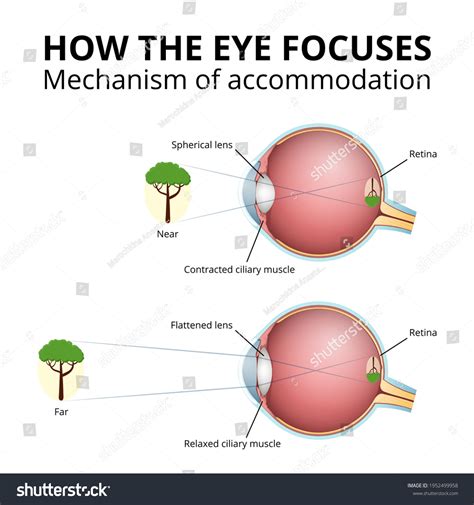
When we look at something close up, the ciliary muscles contract, releasing tension on the zonular fibers. This allows the lens to become thicker and more curved, increasing its refractive power. Conversely, when we gaze out at distant objects, the ciliary muscles relax, increasing tension on the zonular fibers and causing the lens to become thinner and less curved.
The Process of Accommodation
The process of accommodation is remarkably quick and precise, occurring in a matter of milliseconds. Here's a step-by-step breakdown of how it works:
- Detection of distance: The eye detects the distance of an object through a combination of visual cues, including binocular disparity (the difference between the images seen by each eye), convergence (the angle of the eyes), and blur.
- Signal transmission: The detected distance information is transmitted to the brain, which sends a signal to the ciliary muscles to adjust the lens accordingly.
- Ciliary muscle contraction or relaxation: Depending on the distance of the object, the ciliary muscles either contract or relax, changing the shape of the lens.
- Lens shape change: The lens becomes thicker and more curved for near vision or thinner and less curved for far vision.
- Focus achieved: The light is focused properly on the retina, allowing us to see the object clearly.

Types of Accommodation
There are two main types of accommodation: voluntary and involuntary. Voluntary accommodation occurs when we consciously focus on an object, such as when we look at a book or a screen. Involuntary accommodation, on the other hand, occurs automatically, without conscious effort, such as when we glance at something in our peripheral vision.
Factors Affecting Accommodation
Several factors can affect accommodation, including:
- Age: Accommodation declines with age, starting in the early to mid-40s. This is why many people start to experience presbyopia, a age-related decline in near vision.
- Eye health: Certain eye conditions, such as cataracts or glaucoma, can affect accommodation.
- Lighting: Insufficient lighting can make it harder for the eye to focus.
- Fatigue: Prolonged visual tasks can cause eye strain and affect accommodation.
Accommodation and Eye Health
Accommodation plays a crucial role in maintaining good eye health. When accommodation is impaired, it can lead to eye strain, headaches, and blurred vision. Regular eye exams can help detect any issues with accommodation, and corrective measures, such as glasses or contact lenses, can be taken to address any problems.
Conclusion
Accommodation is an incredible process that enables us to navigate the world with ease. By understanding how the eye works its magic, we can appreciate the intricate mechanisms that govern our vision. Whether you're reading a book, watching a movie, or simply enjoying the beauty of nature, remember the incredible process of accommodation that makes it all possible.

We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of accommodation and how it works. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
What is accommodation in the eye?
+Accommodation is the process by which the eye changes the shape of the lens to focus on objects at varying distances.
How does accommodation work?
+Accommodation works by changing the shape of the lens through the contraction or relaxation of the ciliary muscles.
What affects accommodation?
+Accommodation can be affected by age, eye health, lighting, and fatigue.
