Intro
Discover the significance of Sed Rate, a crucial blood test that measures inflammation levels in the body. Learn how ESR (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate) works, its normal ranges, and what abnormal results indicate. Understand the relationship between Sed Rate and conditions like anemia, arthritis, and infections, and how it aids in diagnosis and monitoring.
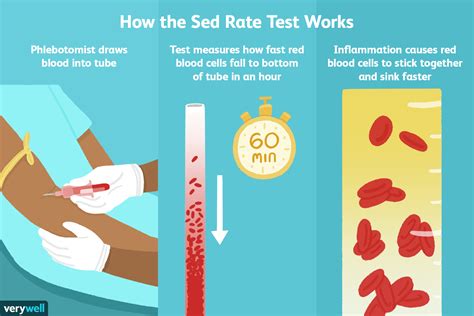
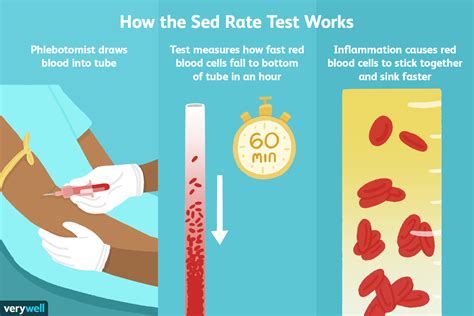
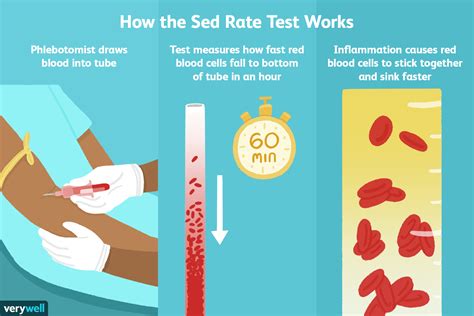
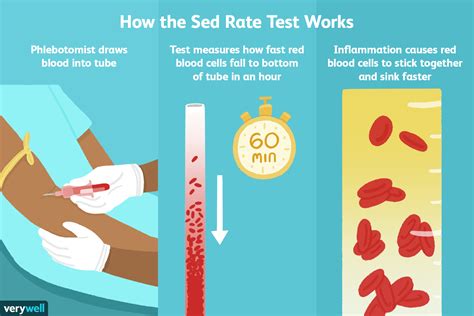
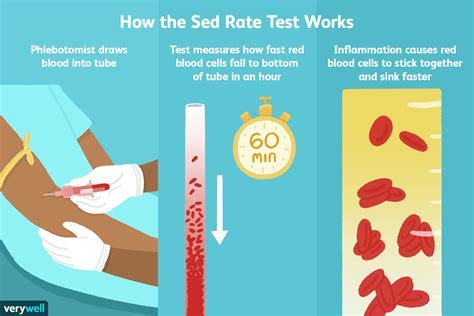
The sedimentation rate, also known as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle in a test tube containing a blood sample. It's a simple, inexpensive, and widely used test that can help doctors diagnose and monitor a range of health conditions.
The ESR test is often used to detect inflammation in the body, which can be a sign of various medical conditions, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancer. In this article, we'll delve into the details of the ESR test, including what it measures, how it's performed, and what the results can indicate.
What Does the Sed Rate Measure?
The sedimentation rate measures the rate at which red blood cells settle to the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. When a blood sample is placed in a test tube, the red blood cells will eventually settle to the bottom, while the plasma (the liquid portion of the blood) and white blood cells remain at the top. The rate at which the red blood cells settle is influenced by several factors, including the presence of inflammation, infection, or other medical conditions.
In a healthy individual, the red blood cells will settle slowly, resulting in a low sedimentation rate. However, in the presence of inflammation or infection, the red blood cells will settle more quickly, resulting in a higher sedimentation rate.
How Is the Sed Rate Test Performed?
The ESR test is a relatively simple procedure that involves the following steps:
- A healthcare professional will collect a blood sample from a vein in your arm using a sterile needle and syringe.
- The blood sample is then placed in a test tube containing an anticoagulant to prevent clotting.
- The test tube is then placed in a rack and left to stand for a specified period, usually 60 minutes.
- After the specified period, the test tube is removed from the rack, and the level of the red blood cells is measured.
- The sedimentation rate is then calculated based on the level of the red blood cells.
What Do the Results Mean?
The results of the ESR test are usually reported in millimeters per hour (mm/h). A normal sedimentation rate varies depending on age, sex, and other factors, but generally, a rate of 0-20 mm/h is considered normal.
A high sedimentation rate can indicate the presence of inflammation or infection in the body. Some common conditions that can cause a high sedimentation rate include:
- Infections, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis
- Autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus
- Cancer, such as lymphoma or leukemia
- Inflammatory bowel disease, such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis
On the other hand, a low sedimentation rate can indicate a lack of inflammation or infection in the body.
Interpreting Sed Rate Results
Interpreting the results of the ESR test requires careful consideration of various factors, including the patient's medical history, symptoms, and physical examination. A high sedimentation rate can indicate the presence of inflammation or infection, but it's not a specific test for any particular condition.
To determine the underlying cause of a high sedimentation rate, doctors may order additional tests, such as a complete blood count (CBC), blood cultures, or imaging studies.
Limitations of the Sed Rate Test
While the ESR test is a useful tool for detecting inflammation and monitoring disease activity, it has several limitations. Some of the limitations of the ESR test include:
- Non-specificity: The ESR test is not specific for any particular condition and can be elevated in a range of diseases.
- Sensitivity: The ESR test may not detect mild inflammation or infection.
- Variability: The ESR test can be influenced by various factors, including age, sex, and medication use.
Conclusion
The sedimentation rate test is a simple, inexpensive, and widely used test that can help doctors diagnose and monitor a range of health conditions. While it has several limitations, the ESR test remains a useful tool in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory and infectious diseases. By understanding the principles of the ESR test and its limitations, healthcare professionals can use this test to provide better care for their patients.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the sedimentation rate test. If you have any questions or concerns about the ESR test, please don't hesitate to ask your doctor or healthcare professional.
What is the normal range for the sedimentation rate test?
+A normal sedimentation rate varies depending on age, sex, and other factors, but generally, a rate of 0-20 mm/h is considered normal.
What can cause a high sedimentation rate?
+A high sedimentation rate can indicate the presence of inflammation or infection in the body. Some common conditions that can cause a high sedimentation rate include infections, autoimmune disorders, cancer, and inflammatory bowel disease.
How is the sedimentation rate test performed?
+The ESR test involves collecting a blood sample from a vein in your arm using a sterile needle and syringe. The blood sample is then placed in a test tube containing an anticoagulant to prevent clotting. The test tube is then placed in a rack and left to stand for a specified period, usually 60 minutes.
