Intro
Discover the power of subjective data and its crucial role in research and decision-making. Learn how personal opinions, experiences, and emotions shape subjective data, and how it differs from objective data. Understand the importance of subjective data in various fields, including market research, social sciences, and customer feedback analysis.
Subjective data plays a crucial role in various fields, including healthcare, research, and social sciences. In this article, we will delve into the concept of subjective data, its characteristics, and its significance in different contexts.
What is Subjective Data?

Subjective data refers to information that is personal, emotional, and experiential in nature. It is based on individual perceptions, feelings, and opinions, which can vary greatly from person to person. Unlike objective data, which is factual and measurable, subjective data is often qualitative and interpretive. This type of data is typically collected through self-reported measures, such as surveys, interviews, and focus groups.
Characteristics of Subjective Data
Subjective data has several distinct characteristics that set it apart from objective data. Some of the key features of subjective data include:
- Personal and emotional: Subjective data is deeply rooted in individual experiences and emotions.
- Qualitative: Subjective data is often non-numerical and descriptive in nature.
- Interpretive: Subjective data requires interpretation and analysis to understand its meaning and significance.
- Variable: Subjective data can vary greatly from person to person, making it challenging to compare and analyze.
The Role of Subjective Data in Healthcare

In healthcare, subjective data plays a vital role in patient care and treatment. Healthcare professionals use subjective data to:
- Assess patient symptoms: Subjective data helps healthcare providers understand a patient's symptoms, pain levels, and overall well-being.
- Develop treatment plans: Subjective data informs treatment decisions and helps healthcare providers tailor care to individual patient needs.
- Evaluate treatment effectiveness: Subjective data is used to assess the effectiveness of treatments and make adjustments as needed.
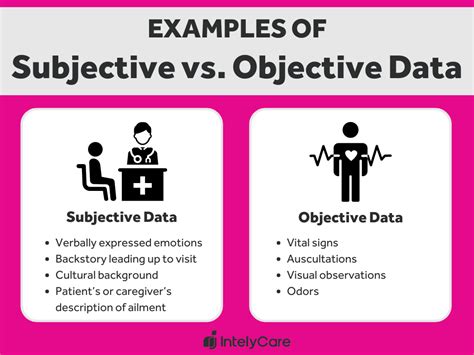
Examples of Subjective Data in Healthcare
Some examples of subjective data in healthcare include:
- Patient self-reported symptoms and pain levels
- Patient satisfaction surveys
- Clinician observations and impressions
- Family member or caregiver reports
The Role of Subjective Data in Research

In research, subjective data is used to:
- Explore complex phenomena: Subjective data helps researchers understand complex social and psychological phenomena.
- Develop theories and models: Subjective data informs the development of theories and models that explain human behavior and experiences.
- Evaluate program effectiveness: Subjective data is used to assess the effectiveness of programs and interventions.
Examples of Subjective Data in Research
Some examples of subjective data in research include:
- Survey responses
- Interview transcripts
- Focus group data
- Observational notes
Challenges and Limitations of Subjective Data
While subjective data provides valuable insights, it also has several challenges and limitations, including:
- Bias and subjectivity: Subjective data is prone to bias and subjectivity, which can impact its accuracy and reliability.
- Lack of generalizability: Subjective data may not be generalizable to larger populations or contexts.
- Difficulty in analysis: Subjective data can be challenging to analyze and interpret, requiring specialized skills and expertise.
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges
To overcome the challenges and limitations of subjective data, researchers and practitioners can use various strategies, including:
- Triangulation: Using multiple data sources and methods to validate findings.
- Member checking: Verifying findings with participants to ensure accuracy and validity.
- Coding and theme identification: Using systematic coding and theme identification techniques to analyze subjective data.
Conclusion
Subjective data plays a vital role in various fields, including healthcare and research. While it has several challenges and limitations, subjective data provides valuable insights into human experiences and behaviors. By understanding the characteristics and limitations of subjective data, researchers and practitioners can harness its power to inform practice, policy, and decision-making.
We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of subjective data and its role in different contexts. Share your thoughts and experiences with subjective data in the comments below!
What is subjective data?
+Subjective data refers to information that is personal, emotional, and experiential in nature. It is based on individual perceptions, feelings, and opinions.
What are some examples of subjective data in healthcare?
+Examples of subjective data in healthcare include patient self-reported symptoms and pain levels, patient satisfaction surveys, clinician observations and impressions, and family member or caregiver reports.
What are some challenges of working with subjective data?
+Some challenges of working with subjective data include bias and subjectivity, lack of generalizability, and difficulty in analysis.
