Intro
Discover the crucial role of surfactant in the lungs and its impact on respiratory health. Learn about the functions, benefits, and deficiencies of lung surfactant, as well as its relationship to conditions like ARDS, RDS, and COPD. Understand how surfactant therapy can improve lung function and overall well-being.
The lungs are one of the most vital organs in the human body, responsible for taking in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide. However, the lungs are also susceptible to various diseases and conditions that can affect their function and overall health. One crucial component that plays a significant role in maintaining lung health is surfactant. In this article, we will delve into the world of surfactant, its importance in the lungs, and what you need to know about this vital substance.
Surfactant is a complex mixture of lipids and proteins that lines the alveoli, the tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs. It is produced by specialized cells in the lungs called type II pneumocytes and is secreted into the alveolar space. Surfactant's primary function is to reduce the surface tension of the water layer that lines the alveoli, allowing the lungs to expand and contract more easily during breathing. This is crucial, as it prevents the alveoli from collapsing and sticking together, which would make breathing difficult and inefficient.
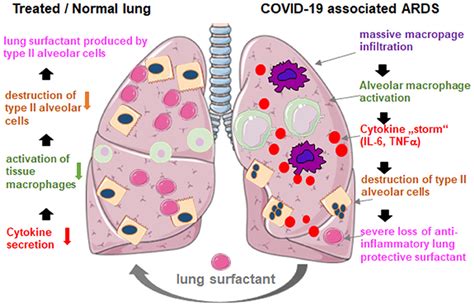
How Surfactant Works in the Lungs
Surfactant works by reducing the surface tension of the water layer that lines the alveoli. This is achieved through the interaction of surfactant's lipid and protein components. The lipid component, primarily composed of phospholipids, forms a monolayer at the air-liquid interface, reducing the surface tension and allowing the alveoli to expand and contract more easily. The protein component, on the other hand, helps to regulate the function of surfactant and ensures that it is properly distributed throughout the lungs.
Surfactant's role in the lungs is not limited to reducing surface tension. It also plays a critical role in immune function, helping to regulate the activity of immune cells and prevent inflammation in the lungs. Additionally, surfactant has been shown to have antimicrobial properties, helping to protect the lungs from infection.
Benefits of Surfactant in the Lungs
The benefits of surfactant in the lungs are numerous. Some of the most significant advantages include:
- Improved lung function: Surfactant helps to reduce the surface tension of the water layer that lines the alveoli, allowing the lungs to expand and contract more easily during breathing.
- Reduced risk of respiratory disease: Surfactant has been shown to have antimicrobial properties, helping to protect the lungs from infection and reduce the risk of respiratory disease.
- Improved immune function: Surfactant helps to regulate the activity of immune cells in the lungs, preventing inflammation and promoting immune function.
- Enhanced gas exchange: Surfactant helps to improve gas exchange in the lungs, allowing for more efficient oxygenation of the blood.
Surfactant Deficiency and Related Diseases
While surfactant is a vital component of lung health, deficiencies in surfactant can lead to a range of diseases and conditions. Some of the most common surfactant-related diseases include:
- Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS): A condition that affects premature infants, RDS is caused by a lack of surfactant in the lungs, leading to difficulty breathing and respiratory failure.
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): A condition that affects adults, ARDS is caused by a range of factors, including infection, trauma, and inflammation, leading to a deficiency in surfactant and respiratory failure.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): A condition that affects the airways, COPD is caused by a range of factors, including smoking and air pollution, leading to a deficiency in surfactant and respiratory symptoms.

Treatment Options for Surfactant Deficiency
Treatment options for surfactant deficiency vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some of the most common treatment options include:
- Surfactant replacement therapy: This involves the administration of exogenous surfactant to the lungs, either through inhalation or injection.
- Mechanical ventilation: This involves the use of a ventilator to support breathing and improve lung function.
- Medications: A range of medications, including bronchodilators and corticosteroids, may be used to help manage symptoms and improve lung function.
Preventing Surfactant Deficiency
While surfactant deficiency can be a serious condition, there are steps that can be taken to prevent it. Some of the most effective ways to prevent surfactant deficiency include:
- Quitting smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for surfactant deficiency, and quitting can help to reduce the risk of developing related diseases.
- Avoiding air pollution: Exposure to air pollution can increase the risk of surfactant deficiency, and avoiding polluted areas can help to reduce this risk.
- Getting regular exercise: Regular exercise can help to improve lung function and reduce the risk of surfactant deficiency.
- Eating a healthy diet: A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help to support lung health and reduce the risk of surfactant deficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, surfactant is a vital component of lung health, playing a critical role in reducing surface tension, regulating immune function, and preventing inflammation. While surfactant deficiency can lead to a range of diseases and conditions, there are steps that can be taken to prevent it. By quitting smoking, avoiding air pollution, getting regular exercise, and eating a healthy diet, individuals can help to support lung health and reduce the risk of surfactant deficiency.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of surfactant and its importance in the lungs. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
What is surfactant?
+Surfactant is a complex mixture of lipids and proteins that lines the alveoli, the tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs.
What is the function of surfactant in the lungs?
+Surfactant's primary function is to reduce the surface tension of the water layer that lines the alveoli, allowing the lungs to expand and contract more easily during breathing.
What are the benefits of surfactant in the lungs?
+The benefits of surfactant in the lungs include improved lung function, reduced risk of respiratory disease, improved immune function, and enhanced gas exchange.
