Intro
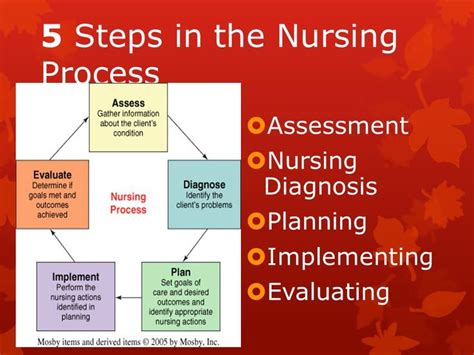
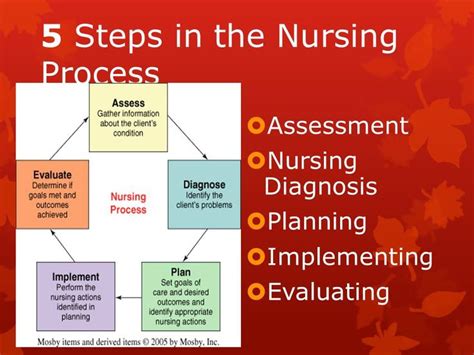
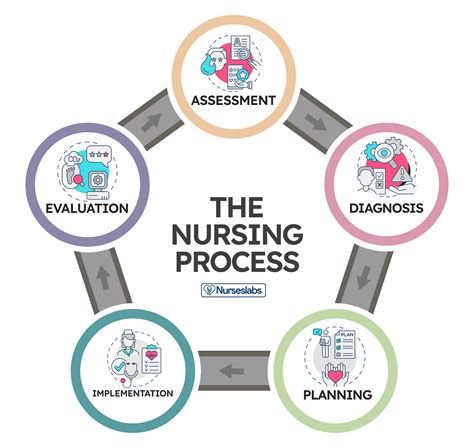
Discover the nursing process explained simply and effectively. Learn the 5 stages of the nursing process: assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. Understand how nurses use critical thinking and problem-solving skills to deliver patient-centered care, improve health outcomes, and enhance the overall nursing experience.
The nursing process is a systematic approach to providing care to patients, and it's a crucial part of the nursing profession. It's a framework that guides nurses in assessing, planning, implementing, and evaluating patient care. In this article, we'll break down the nursing process into simple, easy-to-understand terms, so you can grasp the concept and its importance in nursing practice.
The nursing process is a problem-solving approach that helps nurses identify patient needs, develop plans to meet those needs, and evaluate the effectiveness of their care. It's a cyclical process that involves continuous assessment, planning, implementation, and evaluation. The nursing process is essential in ensuring that patients receive high-quality, individualized care that addresses their unique needs and promotes optimal health outcomes.
Assessment: The First Step in the Nursing Process
The assessment phase is the first step in the nursing process. During this phase, nurses collect data about the patient's physical, emotional, and social status. This includes gathering information about the patient's medical history, current health status, and lifestyle habits. Nurses use this information to identify potential health problems and develop a plan to address them.
There are two types of assessments: subjective and objective. Subjective assessments involve gathering information from the patient's perspective, such as their symptoms, feelings, and concerns. Objective assessments involve gathering data through observations, measurements, and laboratory tests.
Types of Assessments
- Initial assessment: This is the first assessment done when the patient is admitted to the hospital or clinic.
- Focused assessment: This type of assessment is done to gather information about a specific problem or issue.
- Ongoing assessment: This is a continuous process of gathering data to monitor the patient's progress and adjust the care plan as needed.
Diagnosis: Identifying Patient Problems
After collecting data during the assessment phase, nurses analyze the information to identify patient problems or needs. This is known as the diagnosis phase. Nurses use their critical thinking skills to identify patterns and relationships between the data and develop a list of potential diagnoses.
Nursing diagnoses are different from medical diagnoses. Nursing diagnoses focus on the patient's response to their condition, while medical diagnoses focus on the disease or condition itself. Nursing diagnoses are used to develop a plan to address the patient's needs and promote optimal health outcomes.
Types of Nursing Diagnoses
- Actual diagnosis: This type of diagnosis is based on the presence of a specific problem or condition.
- Risk diagnosis: This type of diagnosis is based on the potential for a problem or condition to develop.
- Health promotion diagnosis: This type of diagnosis is based on the patient's need for health promotion and disease prevention.
Planning: Developing a Care Plan

The planning phase involves developing a care plan to address the patient's needs and problems. Nurses use the data collected during the assessment phase and the nursing diagnoses to develop a plan that outlines the patient's goals, outcomes, and interventions.
The care plan should be individualized to meet the patient's unique needs and should be developed in collaboration with the patient and their family. The plan should also be flexible and subject to change as the patient's needs and condition change.
Components of a Care Plan
- Goals: These are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives that the patient and nurse want to achieve.
- Outcomes: These are specific, measurable results that the patient and nurse want to achieve.
- Interventions: These are specific actions that the nurse will take to help the patient achieve the goals and outcomes.
Implementation: Putting the Care Plan into Action

The implementation phase involves putting the care plan into action. Nurses use the care plan to guide their actions and interventions. This phase involves administering medications, performing treatments and procedures, and providing education and support to the patient and their family.
Nurses should also document their actions and interventions in the patient's medical record. This helps to ensure that the patient receives consistent care and that the care plan is adjusted as needed.
Types of Interventions
- Independent interventions: These are actions that the nurse can perform independently, such as administering medications.
- Dependent interventions: These are actions that the nurse must perform in collaboration with other healthcare professionals, such as surgeons or therapists.
- Interdependent interventions: These are actions that the nurse must perform in collaboration with other healthcare professionals, such as consulting with a doctor to adjust the patient's medication.
Evaluation: Measuring the Effectiveness of Care
The evaluation phase involves measuring the effectiveness of the care plan. Nurses collect data to determine if the patient has achieved the goals and outcomes outlined in the care plan.
Nurses use this data to adjust the care plan as needed and to identify areas for improvement. The evaluation phase is an ongoing process that continues throughout the patient's care.
Types of Evaluation
- Formative evaluation: This type of evaluation is done during the care process to monitor the patient's progress and adjust the care plan as needed.
- Summative evaluation: This type of evaluation is done at the end of the care process to determine the overall effectiveness of the care plan.
Conclusion
The nursing process is a systematic approach to providing care to patients. It involves assessing, diagnosing, planning, implementing, and evaluating patient care. By following the nursing process, nurses can ensure that patients receive high-quality, individualized care that addresses their unique needs and promotes optimal health outcomes.
We hope this article has helped you understand the nursing process and its importance in nursing practice. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us.
What is the nursing process?
+The nursing process is a systematic approach to providing care to patients. It involves assessing, diagnosing, planning, implementing, and evaluating patient care.
What are the five steps of the nursing process?
+The five steps of the nursing process are assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation.
Why is the nursing process important?
+The nursing process is important because it helps nurses provide high-quality, individualized care to patients. It ensures that patients receive care that addresses their unique needs and promotes optimal health outcomes.
