Intro
Unlock the mysteries of the pulmonary circuit! Discover the 5 crucial steps of blood flow through the lungs, from deoxygenation to oxygenation. Learn about pulmonary circulation, gas exchange, and the vital role of the heart and lungs in this intricate process. Understand the pulmonary circuits importance in respiratory health and overall well-being.
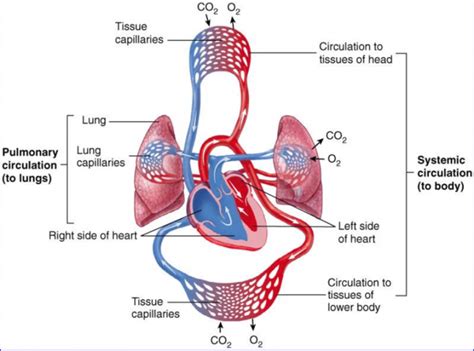
The pulmonary circuit, also known as the pulmonary circulation, is a vital part of the circulatory system. It is responsible for transporting deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide, and then returns the oxygen-rich blood back to the heart. In this article, we will explore the five steps of the pulmonary circuit in detail, highlighting the importance of each step and how they work together to maintain proper respiratory function.
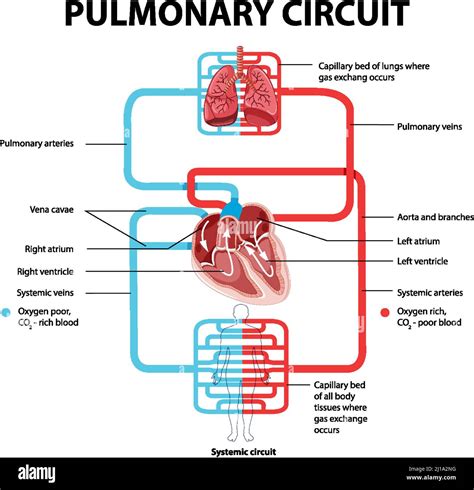
Step 1: Deoxygenated Blood Enters the Pulmonary Circuit
The pulmonary circuit begins when deoxygenated blood from the body enters the right atrium of the heart through the superior and inferior vena cava. From there, the blood flows into the right ventricle, which pumps it through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery is a large blood vessel that carries the deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
Step 2: Blood Travels to the Lungs
Once the deoxygenated blood enters the pulmonary artery, it travels to the lungs, where it will pick up oxygen and release carbon dioxide. The pulmonary artery branches into smaller and smaller arteries, eventually forming capillaries that surround the alveoli, the tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs.
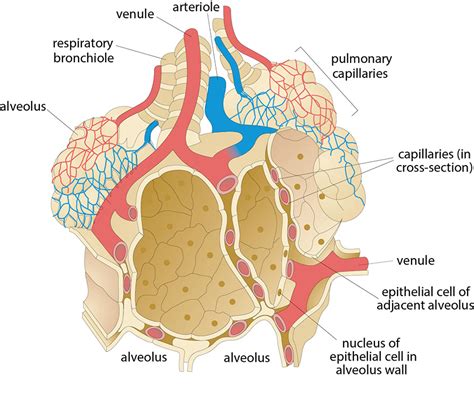
Step 3: Gas Exchange Occurs in the Alveoli
In the alveoli, oxygen from the inhaled air diffuses into the bloodstream, binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. At the same time, carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular metabolism, diffuses out of the bloodstream and into the alveoli, where it is exhaled out of the body. This process of gas exchange is essential for maintaining proper oxygen levels in the body.
Step 4: Oxygen-Rich Blood Returns to the Heart
After gas exchange occurs, the oxygen-rich blood flows back through the pulmonary capillaries and into the pulmonary veins. The pulmonary veins carry the oxygen-rich blood back to the left atrium of the heart, where it flows into the left ventricle.
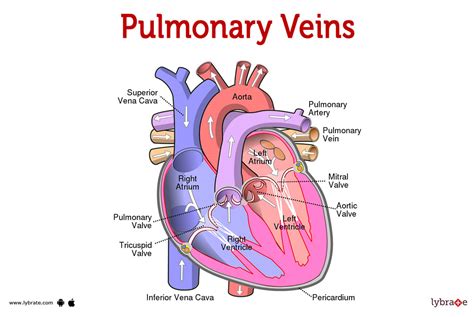
Step 5: Oxygen-Rich Blood is Pumped to the Body
Finally, the oxygen-rich blood is pumped from the left ventricle through the aortic valve into the aorta, the largest artery in the body. From there, the oxygen-rich blood is distributed to the rest of the body through a network of arteries, arterioles, and capillaries.
Importance of the Pulmonary Circuit
The pulmonary circuit is essential for maintaining proper respiratory function and overall health. Without it, the body would not be able to obtain the oxygen it needs to function properly. The pulmonary circuit is also closely linked to the systemic circuit, which carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
Common Disorders Affecting the Pulmonary Circuit
There are several common disorders that can affect the pulmonary circuit, including:
- Pulmonary hypertension: a condition in which the blood pressure in the pulmonary artery is too high
- Pulmonary embolism: a blockage of the pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary edema: a condition in which fluid accumulates in the lungs
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): a progressive lung disease that makes it difficult to breathe
Conclusion
In conclusion, the pulmonary circuit is a vital part of the circulatory system, responsible for transporting deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. The five steps of the pulmonary circuit work together to maintain proper respiratory function and overall health. Understanding the pulmonary circuit is essential for appreciating the importance of respiratory health and the impact of disorders that affect the lungs.
What is the main function of the pulmonary circuit?
+The main function of the pulmonary circuit is to transport deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide.
What is the difference between the pulmonary circuit and the systemic circuit?
+The pulmonary circuit carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, while the systemic circuit carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
What are some common disorders that affect the pulmonary circuit?
+Some common disorders that affect the pulmonary circuit include pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary edema, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the pulmonary circuit and its importance in maintaining proper respiratory function. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below!
