Intro
Master the building blocks of language with our comprehensive guide to understanding parts of speech. Learn the definitions, functions, and examples of nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Improve your grammar, writing, and communication skills with our easy-to-follow explanations and interactive exercises.
Mastering the parts of speech is a fundamental step in understanding the structure and nuances of language. Whether you're a student, a writer, or simply someone looking to improve your communication skills, grasping the basics of parts of speech can make a significant difference in how effectively you express yourself. In this article, we'll delve into the world of parts of speech, breaking down each category into easily digestible chunks, and providing examples to illustrate their usage.
What are the Parts of Speech?
The parts of speech are the basic categories of words in a language, based on their grammatical function. There are nine parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, interjections, and articles. Understanding these categories can help you identify the role of each word in a sentence, making it easier to construct coherent and meaningful expressions.
Nouns: The Building Blocks of Language
Nouns are words that refer to people, places, things, and ideas. They can be common (cat) or proper (John), concrete (book) or abstract (happiness). Nouns can also be classified as countable (one book, two books) or uncountable (water, air).
- Examples:
- Common noun: dog
- Proper noun: London
- Concrete noun: chair
- Abstract noun: love

Pronouns: Replacing Nouns
Pronouns are words that replace nouns in a sentence, making it easier to refer to them without repeating the noun. There are several types of pronouns, including personal pronouns (I, you, he), possessive pronouns (my, your, his), reflexive pronouns (myself, yourself, himself), and demonstrative pronouns (this, that, these).
- Examples:
- Personal pronoun: I
- Possessive pronoun: mine
- Reflexive pronoun: myself
- Demonstrative pronoun: this

Verbs: The Action Words
Verbs are words that express action, occurrence, or state of being. They can be action verbs (run, jump, read), linking verbs (be, seem, appear), or helping verbs (will, would, shall). Verbs can also be classified as transitive (taking an object) or intransitive (not taking an object).
- Examples:
- Action verb: write
- Linking verb: be
- Helping verb: will
- Transitive verb: eat (I eat an apple)
- Intransitive verb: sleep (I sleep)

Adjectives: Describing Words
Adjectives are words that modify or describe nouns or pronouns. They can tell us about size (big, small), shape (round, square), color (red, blue), or other characteristics (happy, sad). Adjectives can also be used to compare things (bigger, smaller).
- Examples:
- Descriptive adjective: happy
- Quantitative adjective: three
- Demonstrative adjective: this
- Comparative adjective: bigger
Adverbs: Modifying Verbs, Adjectives, and Other Adverbs
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They can tell us about manner (quickly, loudly), time (yesterday, soon), place (here, there), or frequency (often, rarely).
- Examples:
- Manner adverb: quickly
- Time adverb: yesterday
- Place adverb: here
- Frequency adverb: often
Prepositions: Showing Relationships
Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. They can indicate location (in, on, under), direction (to, from, up), or time (at, during, before).
- Examples:
- Location preposition: in
- Direction preposition: to
- Time preposition: at
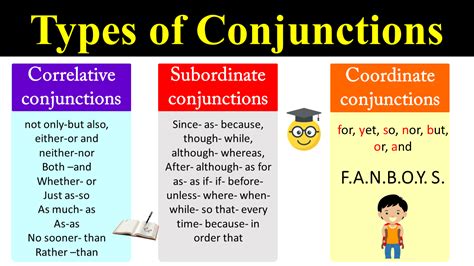
Conjunctions: Connecting Words
Conjunctions are words that connect words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence. They can be coordinating (and, but, or) or subordinating (because, although, if).
- Examples:
- Coordinating conjunction: and
- Subordinating conjunction: because
Interjections: Expressing Emotion
Interjections are words that express emotion or feeling. They can be used to convey strong emotions like joy (oh, wow), anger (ouch, darn), or surprise (ah, oh).
- Examples:
- Joy interjection: wow
- Anger interjection: ouch
- Surprise interjection: ah

Articles: Modifying Nouns
Articles are words that modify nouns and indicate whether they are specific or general. There are two types of articles: definite (the) and indefinite (a, an).
- Examples:
- Definite article: the
- Indefinite article: a

In conclusion, mastering the parts of speech is a crucial step in understanding the intricacies of language. By familiarizing yourself with the different categories of words, you'll be able to construct more effective sentences, communicate more clearly, and express yourself with confidence.
We hope this article has helped you understand the parts of speech and how they work together to create meaningful language. If you have any questions or would like to share your thoughts, please leave a comment below.
What are the nine parts of speech in English?
+The nine parts of speech in English are nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, interjections, and articles.
What is the difference between a noun and a pronoun?
+A noun refers to a specific person, place, thing, or idea, while a pronoun replaces a noun in a sentence.
What is the function of an adverb?
+An adverb modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb, telling us more about the manner, time, place, or frequency of an action.
