Intro
Discover the ins and outs of negative feedback loops, a crucial concept in systems thinking. Learn how this self-reinforcing cycle can lead to instability and unwanted outcomes. Explore real-life examples and understand how to break the cycle. Get insights into the definition, causes, and effects of negative feedback loops and how to manage them effectively.
The concept of negative feedback loops is a fundamental aspect of various fields, including biology, psychology, economics, and engineering. Despite its importance, many people are unfamiliar with the concept, its mechanisms, and its impact on our daily lives. In this article, we will delve into the world of negative feedback loops, exploring their definition, examples, and significance.
Negative feedback loops are an essential part of maintaining balance and stability in complex systems. They play a crucial role in regulating various processes, from the simplest biological mechanisms to complex economic systems. By understanding how negative feedback loops work, we can better appreciate the intricate dynamics of the world around us.
What is a Negative Feedback Loop?
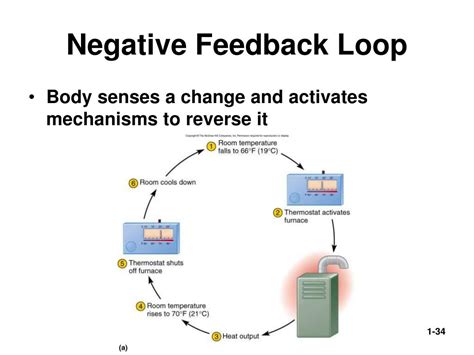
A negative feedback loop is a process where a system responds to a change by reversing the direction of the change. In other words, when a system detects a deviation from its equilibrium state, it triggers a response that counteracts the deviation, restoring balance to the system. This self-regulatory mechanism is essential for maintaining stability and preventing extreme fluctuations.
Key Components of a Negative Feedback Loop
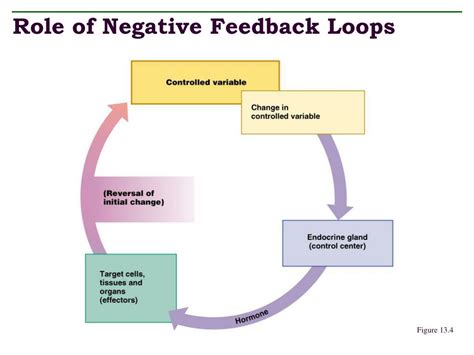
A negative feedback loop consists of three primary components:
- Sensor: The sensor detects changes in the system and sends a signal to the control center.
- Control Center: The control center interprets the signal and determines the necessary response.
- Effector: The effector carries out the response, which counteracts the initial change.
Examples of Negative Feedback Loops
Negative feedback loops are ubiquitous in various domains. Here are a few examples:
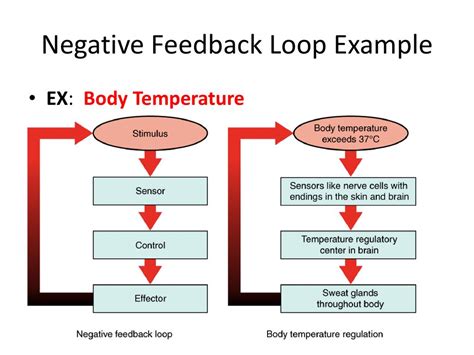
- Thermoregulation: The human body maintains a stable temperature through a negative feedback loop. When the body temperature rises, the hypothalamus (sensor) sends a signal to the sweat glands (effector), which release sweat to cool the body down.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: The pancreas (sensor) detects changes in blood sugar levels and releases insulin (effector) to lower blood sugar levels when they rise.
- Economic Systems: The Federal Reserve (sensor) monitors inflation rates and adjusts interest rates (effector) to control inflation and maintain economic stability.
- Population Growth: The availability of food and resources (sensor) affects population growth. As resources become scarce, population growth slows down, and the population size (effector) adjusts to maintain a balance.
Benefits of Negative Feedback Loops
Negative feedback loops offer several benefits, including:
- Stability: Negative feedback loops maintain stability in complex systems by counteracting changes that deviate from the equilibrium state.
- Adaptability: These loops enable systems to adapt to changing conditions by responding to signals and adjusting their behavior.
- Efficiency: Negative feedback loops optimize system performance by minimizing waste and maximizing resource utilization.
Challenges and Limitations of Negative Feedback Loops
While negative feedback loops are essential for maintaining balance, they also face challenges and limitations:
- Time Delays: Delays in the feedback loop can lead to oscillations and instability.
- Non-Linear Dynamics: Complex systems often exhibit non-linear dynamics, making it challenging to predict the behavior of negative feedback loops.
- Multiple Feedback Loops: Interacting feedback loops can lead to unintended consequences and make it difficult to control the system.
Real-World Applications of Negative Feedback Loops
Negative feedback loops have numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Control Systems: Negative feedback loops are used in control systems to regulate temperature, pressure, and flow rates.
- Biology: Negative feedback loops play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis in living organisms.
- Economics: Central banks use negative feedback loops to regulate interest rates and maintain economic stability.
Conclusion: The Power of Negative Feedback Loops
Negative feedback loops are a fundamental aspect of complex systems, enabling them to maintain balance and stability. By understanding the mechanisms and examples of negative feedback loops, we can appreciate the intricate dynamics of the world around us. As we continue to navigate the complexities of our world, recognizing the power of negative feedback loops can help us make informed decisions and develop more effective solutions.
What is the primary function of a negative feedback loop?
+The primary function of a negative feedback loop is to maintain balance and stability in a system by counteracting changes that deviate from the equilibrium state.
Can you provide an example of a negative feedback loop in biology?
+Yes, thermoregulation is an example of a negative feedback loop in biology. The human body maintains a stable temperature through a negative feedback loop, where the hypothalamus detects changes in body temperature and sends a signal to the sweat glands to cool the body down.
What are the benefits of negative feedback loops?
+Negative feedback loops offer several benefits, including stability, adaptability, and efficiency. They enable systems to maintain balance, adapt to changing conditions, and optimize performance.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of negative feedback loops. Share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below, and don't forget to share this article with others who may find it informative.
