Intro
Unlock the fundamentals of project success with the 7 Key Concepts of Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK). Discover how to initiate, plan, execute, monitor, and control projects with precision, using tools like scope management, schedule development, budgeting, risk assessment, and resource allocation to drive results and achieve strategic objectives.
Effective project management is crucial for the success of any organization, and the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) provides a framework for project managers to follow. The PMBOK is a comprehensive guide that outlines the best practices, terminologies, and techniques for managing projects. In this article, we will delve into the 7 key concepts of the PMBOK, exploring each concept in detail and providing practical examples to illustrate their application.

Integration Management
Integration Management
Integration management is the first key concept of the PMBOK, and it involves coordinating all aspects of a project to ensure that it is completed successfully. This concept encompasses the development of the project charter, scope statement, and management plan, as well as the execution, monitoring, and control of the project. Effective integration management requires the project manager to have a holistic view of the project, ensuring that all stakeholders are informed and engaged throughout the project lifecycle.
Key Activities in Integration Management
- Developing the project charter and scope statement
- Creating the project management plan
- Executing the project plan
- Monitoring and controlling the project
- Closing the project
Scope Management
Scope Management
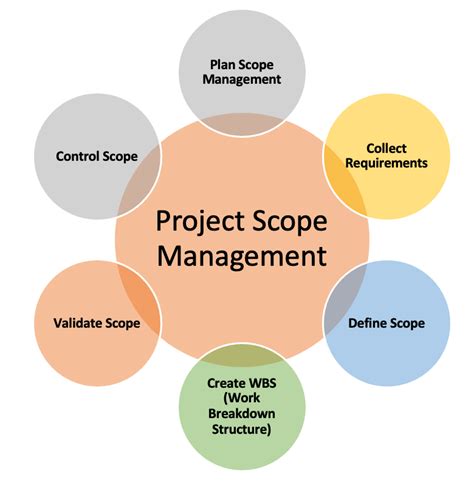
Scope management is the process of defining and managing the scope of a project. It involves identifying the specific goals, deliverables, and boundaries of the project, as well as ensuring that all stakeholders are aware of and agree on the scope. Effective scope management is critical to preventing scope creep, which can lead to delays, cost overruns, and decreased quality.
Key Activities in Scope Management
- Defining the project scope
- Creating the work breakdown structure (WBS)
- Identifying and documenting scope changes
- Obtaining scope change approvals
- Ensuring scope compliance
Time Management
Time Management
Time management is the process of planning, organizing, and controlling the project schedule. It involves defining the project timeline, identifying dependencies, and allocating resources to ensure that the project is completed on time. Effective time management requires the project manager to have a thorough understanding of the project scope, resources, and risks.
Key Activities in Time Management
- Defining the project schedule
- Creating the project timeline
- Identifying dependencies and critical path activities
- Allocating resources to tasks
- Monitoring and controlling the project schedule
Cost Management
Cost Management
Cost management is the process of planning, organizing, and controlling the project budget. It involves estimating costs, establishing a budget, and ensuring that expenses are tracked and controlled throughout the project lifecycle. Effective cost management requires the project manager to have a thorough understanding of the project scope, resources, and risks.
Key Activities in Cost Management
- Estimating costs
- Establishing a budget
- Identifying and documenting cost changes
- Obtaining cost change approvals
- Ensuring cost compliance

Quality Management
Quality Management
Quality management is the process of planning, organizing, and controlling the quality of the project deliverables. It involves defining quality standards, identifying quality risks, and implementing quality control measures to ensure that the project meets the required standards. Effective quality management requires the project manager to have a thorough understanding of the project scope, resources, and risks.
Key Activities in Quality Management
- Defining quality standards
- Identifying quality risks
- Implementing quality control measures
- Monitoring and controlling quality
- Ensuring quality compliance
Resource Management
Resource Management
Resource management is the process of planning, organizing, and controlling the resources required to complete the project. It involves identifying, allocating, and managing resources, including team members, equipment, and materials. Effective resource management requires the project manager to have a thorough understanding of the project scope, resources, and risks.
Key Activities in Resource Management
- Identifying resource requirements
- Allocating resources to tasks
- Managing resource utilization
- Monitoring and controlling resource usage
- Ensuring resource compliance

Communications Management
Communications Management
Communications management is the process of planning, organizing, and controlling the flow of information throughout the project lifecycle. It involves identifying stakeholders, defining communication requirements, and implementing communication plans to ensure that all stakeholders are informed and engaged. Effective communications management requires the project manager to have a thorough understanding of the project scope, resources, and risks.
Key Activities in Communications Management
- Identifying stakeholders
- Defining communication requirements
- Implementing communication plans
- Monitoring and controlling communication
- Ensuring communication compliance

Risk Management
Risk Management
Risk management is the process of identifying, analyzing, and responding to risks throughout the project lifecycle. It involves identifying potential risks, assessing their likelihood and impact, and implementing risk mitigation strategies to minimize their effects. Effective risk management requires the project manager to have a thorough understanding of the project scope, resources, and risks.
Key Activities in Risk Management
- Identifying potential risks
- Assessing risk likelihood and impact
- Implementing risk mitigation strategies
- Monitoring and controlling risk
- Ensuring risk compliance

In conclusion, the 7 key concepts of the PMBOK provide a comprehensive framework for project managers to follow. By understanding and applying these concepts, project managers can ensure that their projects are completed successfully, on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards. We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences on project management in the comments section below.
What is the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK)?
+The PMBOK is a comprehensive guide that outlines the best practices, terminologies, and techniques for managing projects.
What are the 7 key concepts of the PMBOK?
+The 7 key concepts of the PMBOK are integration management, scope management, time management, cost management, quality management, resource management, communications management, and risk management.
Why is project management important?
+Project management is important because it ensures that projects are completed successfully, on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.
