Intro
Develop a proactive approach to infection prevention with a personalized care plan. Learn 7 effective strategies to minimize the risk of infection, including proper wound care, hygiene practices, and medication management. Discover how to create a tailored plan that incorporates your unique needs and promotes optimal health outcomes.
The importance of infection prevention cannot be overstated, particularly for individuals with compromised immune systems or those undergoing medical procedures. A well-structured care plan is essential in preventing infections and promoting overall health and well-being. In this article, we will delve into the significance of infection prevention, explore the key components of a care plan, and provide seven effective ways to prevent infections.

Understanding Infection Prevention
Infection prevention is a critical aspect of healthcare that involves taking proactive measures to prevent the spread of infections. This can include practices such as hand hygiene, proper wound care, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Infections can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, and can have serious consequences if left untreated.
The Role of a Care Plan in Infection Prevention
A care plan is a comprehensive document that outlines an individual's specific healthcare needs and goals. In the context of infection prevention, a care plan can help identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them. A well-structured care plan should include the following components:
- Identification of potential infection risks
- Development of infection prevention strategies
- Monitoring and evaluation of infection prevention efforts
- Education and training for healthcare providers and caregivers
7 Ways to Prevent Infection with a Care Plan
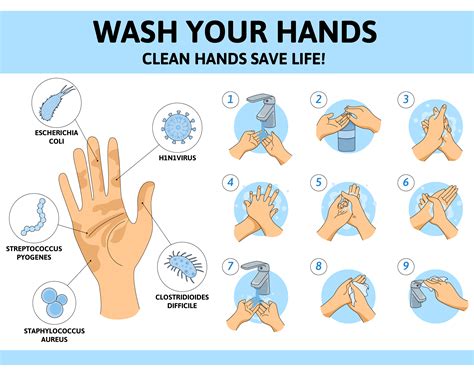
1. Hand Hygiene
Hand hygiene is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of infections. A care plan should emphasize the importance of hand hygiene and provide guidance on proper handwashing techniques. This can include:
- Washing hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds
- Using hand sanitizer when soap and water are not available
- Avoiding touching eyes, nose, and mouth
2. Proper Wound Care
Proper wound care is essential in preventing infections. A care plan should provide guidance on wound cleaning, dressing, and monitoring. This can include:
- Cleaning wounds with sterile saline solution
- Applying topical antibiotics to prevent infection
- Monitoring wounds for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or increased pain
3. Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
PPE is an essential component of infection prevention. A care plan should emphasize the importance of using PPE, such as gloves, masks, and eye protection, when interacting with individuals who are at risk of infection. This can include:
- Wearing gloves when handling bodily fluids or contaminated materials
- Wearing masks when interacting with individuals who have respiratory infections
- Wearing eye protection when interacting with individuals who have conjunctivitis

4. Vaccination
Vaccination is an effective way to prevent infections. A care plan should emphasize the importance of vaccination and provide guidance on recommended vaccinations. This can include:
- Influenza vaccination for individuals with compromised immune systems
- Pneumococcal vaccination for individuals with respiratory infections
- Hepatitis B vaccination for individuals with liver disease
5. Environmental Cleaning
Environmental cleaning is an essential component of infection prevention. A care plan should emphasize the importance of cleaning and disinfecting high-touch surfaces, such as doorknobs, light switches, and countertops. This can include:
- Using disinfectant wipes to clean high-touch surfaces
- Vacuuming carpets and upholstered furniture to reduce dust and allergens
- Cleaning and disinfecting bathrooms and kitchens regularly

6. Education and Training
Education and training are critical components of infection prevention. A care plan should provide guidance on educating healthcare providers, caregivers, and individuals on infection prevention strategies. This can include:
- Providing educational materials on infection prevention
- Conducting training sessions on infection prevention strategies
- Encouraging individuals to ask questions and seek guidance on infection prevention
7. Monitoring and Evaluation
Monitoring and evaluation are essential components of infection prevention. A care plan should provide guidance on monitoring and evaluating infection prevention efforts. This can include:
- Tracking infection rates and trends
- Conducting regular audits to ensure compliance with infection prevention strategies
- Evaluating the effectiveness of infection prevention efforts and making adjustments as needed

By incorporating these seven strategies into a care plan, individuals can reduce their risk of infection and promote overall health and well-being. Remember, infection prevention is a team effort that requires the collaboration of healthcare providers, caregivers, and individuals.
Take Action
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences on infection prevention in the comments section below. What strategies have you found to be effective in preventing infections? How have you incorporated infection prevention into your care plan? By sharing your insights, you can help others prevent infections and promote overall health and well-being.
What is the most effective way to prevent infections?
+Hand hygiene is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of infections. Washing hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
What is the role of a care plan in infection prevention?
+A care plan plays a critical role in infection prevention by identifying potential risks, developing strategies to mitigate them, and monitoring and evaluating infection prevention efforts.
What are some common infection prevention strategies?
+Common infection prevention strategies include hand hygiene, proper wound care, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), vaccination, environmental cleaning, education and training, and monitoring and evaluation.
