Intro
Discover who must comply with HIPAA Security Rule regulations, including covered entities and business associates. Learn about the HIPAA Security Rule requirements, compliance guidelines, and enforcement actions. Ensure your organization meets the standards for protecting electronic protected health information (ePHI) and avoid costly HIPAA security breaches and penalties.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Security Rule regulations are a set of federal standards that outline the security measures that must be taken to protect electronic protected health information (ePHI). The regulations are designed to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of ePHI, and they apply to a wide range of individuals and organizations.

The HIPAA Security Rule regulations apply to two main categories of individuals and organizations: covered entities and business associates.
Covered Entities
Covered entities are defined as health care providers, health plans, and health care clearinghouses that transmit or maintain ePHI. Examples of covered entities include:
- Hospitals and health systems
- Physician practices and clinics
- Nursing homes and assisted living facilities
- Health insurance companies and health maintenance organizations (HMOs)
- Health care clearinghouses, such as billing services and claims processing companies
These organizations must comply with the HIPAA Security Rule regulations to ensure the security and integrity of ePHI.
Business Associates
Business associates are individuals or organizations that perform functions or activities on behalf of a covered entity that involve the use or disclosure of ePHI. Examples of business associates include:
- Billing and coding companies
- Claims processing companies
- Medical transcription services
- Data storage and hosting companies
- IT vendors and consultants
Business associates must also comply with the HIPAA Security Rule regulations to ensure the security and integrity of ePHI.
What is ePHI?
ePHI is any individually identifiable health information that is created, received, maintained, or transmitted electronically. This includes:
- Medical records and billing information
- Insurance claims and payment information
- Laboratory results and test reports
- Medication lists and allergy information
- Demographic information, such as names, addresses, and dates of birth
Any organization or individual that creates, receives, maintains, or transmits ePHI must comply with the HIPAA Security Rule regulations.
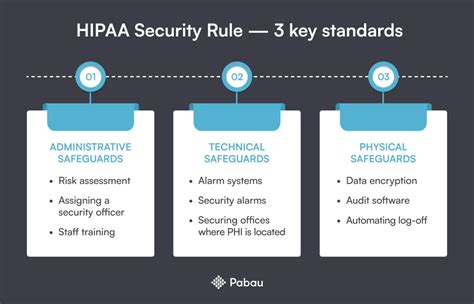
Key Components of the HIPAA Security Rule
The HIPAA Security Rule regulations consist of three main components:
- Administrative Safeguards: These are policies and procedures that must be implemented to ensure the security of ePHI. Examples include:
- Conducting a risk analysis to identify potential security threats
- Implementing policies and procedures for authorizing access to ePHI
- Providing training and awareness programs for workforce members
- Technical Safeguards: These are technology-based measures that must be implemented to protect ePHI. Examples include:
- Implementing encryption and decryption technologies
- Using secure authentication and authorization protocols
- Implementing audit controls and monitoring systems
- Physical Safeguards: These are measures that must be implemented to protect ePHI from physical damage or theft. Examples include:
- Implementing access controls and security cameras
- Using secure storage and disposal methods for ePHI
- Implementing policies and procedures for responding to security incidents
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with the HIPAA Security Rule regulations can result in significant penalties, including:
- Fines ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation
- Imprisonment for up to 10 years
- Civil monetary penalties
- Corrective action plans and monitoring
Conclusion
The HIPAA Security Rule regulations are an essential part of protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of ePHI. Covered entities and business associates must comply with these regulations to ensure the security and integrity of ePHI. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties and reputational damage.
We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on HIPAA Security Rule regulations and how they impact your organization.
Understanding HIPAA Security Rule Requirements
The HIPAA Security Rule requires covered entities and business associates to implement specific security measures to protect ePHI.
Risk Analysis
A risk analysis is a critical component of the HIPAA Security Rule. It involves identifying potential security threats and vulnerabilities to ePHI.
- Identify potential security threats and vulnerabilities
- Assess the likelihood and potential impact of each threat
- Implement measures to mitigate or manage each threat
Security Management Process
A security management process is a set of policies and procedures that must be implemented to ensure the security of ePHI.
- Implement policies and procedures for authorizing access to ePHI
- Provide training and awareness programs for workforce members
- Conduct regular security audits and risk analyses
Assigned Security Responsibility
Assigned security responsibility refers to the designation of a single individual or entity to oversee the implementation of the HIPAA Security Rule.
- Designate a single individual or entity to oversee security
- Ensure that the designated individual or entity has the necessary authority and resources
Workforce Security
Workforce security refers to the measures that must be implemented to ensure that workforce members are aware of and comply with the HIPAA Security Rule.
- Provide training and awareness programs for workforce members
- Implement policies and procedures for authorizing access to ePHI
- Conduct regular security audits and risk analyses
Information Access Management
Information access management refers to the measures that must be implemented to control access to ePHI.
- Implement policies and procedures for authorizing access to ePHI
- Use secure authentication and authorization protocols
- Implement audit controls and monitoring systems
Security Incident Procedures
Security incident procedures refer to the measures that must be implemented to respond to security incidents.
- Implement policies and procedures for responding to security incidents
- Conduct regular security audits and risk analyses
- Provide training and awareness programs for workforce members
Business Associate Contracts
Business associate contracts refer to the agreements that must be entered into with business associates to ensure compliance with the HIPAA Security Rule.
- Enter into contracts with business associates that require compliance with the HIPAA Security Rule
- Ensure that business associates implement the necessary security measures
- Conduct regular security audits and risk analyses
FAQs
Who must comply with the HIPAA Security Rule?
+Covered entities and business associates must comply with the HIPAA Security Rule.
What is ePHI?
+ePHI is any individually identifiable health information that is created, received, maintained, or transmitted electronically.
What are the key components of the HIPAA Security Rule?
+The key components of the HIPAA Security Rule are administrative safeguards, technical safeguards, and physical safeguards.
