Intro
Unlock the secrets of relative age with our 5 simple explanations. Understand how relative age differs from absolute age, and learn how geologists use relative dating methods like law of superposition, fossil succession, and cross-cutting relationships to reconstruct Earths history. Discover how relative age helps us grasp the timeline of geological events and Earths evolution.
As humans, we have an inherent desire to understand our place in the world and how we fit into the grand scheme of things. One way to gain insight into this is by understanding relative age, a concept that can help us appreciate the vastness of time and our position within it. In this article, we will explore five simple ways to comprehend relative age, making it easier to grasp this complex idea.
Relative age is a fundamental concept in geology, astronomy, and other fields that deal with the study of time and its passage. It refers to the age of an object, event, or process relative to others, rather than its absolute age in years. By understanding relative age, we can reconstruct the history of our planet, universe, and even our own lives.

1. The Layer Cake Analogy
Imagine a layer cake with multiple tiers, each representing a different period in Earth's history. The bottom layer represents the oldest rocks, while the top layer represents the most recent deposits. By analyzing the layers, we can determine the relative age of each layer based on its position in the sequence. This analogy helps us visualize how relative age works, with each layer building upon the previous one, creating a timeline of events.
For example, if we find a layer of sedimentary rock containing fossils of ancient creatures, we can infer that this layer is older than the layer above it, which contains fossils of more modern species. By correlating the layers, we can reconstruct the sequence of events that shaped our planet.
Key Takeaway:
- Relative age is determined by the position of an object or event within a sequence.
- The layer cake analogy helps us visualize how relative age works, with each layer building upon the previous one.
2. The Rock Record
The rock record is a fundamental concept in geology that provides a tangible representation of Earth's history. By studying the types of rocks, their composition, and their sequence, we can reconstruct the relative age of different geological events. For example, if we find a layer of volcanic rock on top of a layer of sedimentary rock, we can infer that the volcanic activity occurred after the sedimentation process.

- Igneous rocks, such as granite, are formed from magma and are typically older than sedimentary rocks, which are formed from compressed sediments.
- Metamorphic rocks, such as marble, are formed when existing rocks are transformed by heat and pressure, and are often younger than the rocks they originated from.
Key Takeaway:
- The rock record provides a tangible representation of Earth's history.
- By studying the types of rocks and their sequence, we can reconstruct the relative age of different geological events.
3. Fossil Succession
Fossils are the remains or imprints of ancient organisms that provide valuable information about the history of life on Earth. By studying the types of fossils found in different rocks, we can determine the relative age of the rocks and reconstruct the sequence of events that led to the evolution of life.
For example, if we find a layer of rock containing fossils of trilobites, we can infer that this layer is from the Cambrian period, which dates back to around 541 million years ago. Similarly, if we find a layer of rock containing fossils of dinosaurs, we can infer that this layer is from the Mesozoic era, which spanned from around 252 million to 66 million years ago.
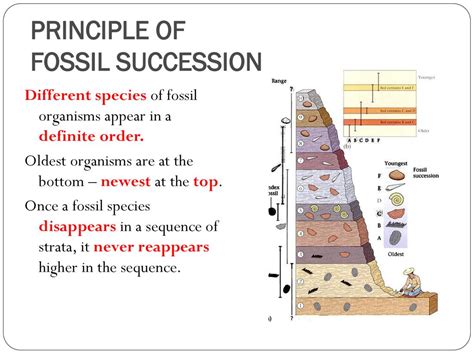
- Fossils provide a chronological record of the evolution of life on Earth.
- By studying the types of fossils found in different rocks, we can reconstruct the sequence of events that led to the evolution of life.
Key Takeaway:
- Fossil succession provides a chronological record of the evolution of life on Earth.
- By studying the types of fossils found in different rocks, we can reconstruct the sequence of events that led to the evolution of life.
4. Relative Dating Methods
Relative dating methods are used to determine the age of rocks and fossils relative to others. These methods include:
- Stratigraphy: the study of the sequence of rock layers.
- Biostratigraphy: the study of the sequence of fossils.
- Paleomagnetism: the study of the Earth's magnetic field as recorded in rocks.
These methods allow us to reconstruct the relative age of different rocks and fossils, providing a framework for understanding the history of our planet.

- Relative dating methods provide a framework for understanding the history of our planet.
- By combining multiple relative dating methods, we can reconstruct a more accurate timeline of events.
Key Takeaway:
- Relative dating methods provide a framework for understanding the history of our planet.
- By combining multiple relative dating methods, we can reconstruct a more accurate timeline of events.
5. Cosmic Context
Finally, understanding relative age requires considering the cosmic context of our planet and universe. By studying the ages of stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects, we can gain insight into the vastness of time and our position within it.
For example, the universe is estimated to be around 13.8 billion years old, while the Earth is estimated to be around 4.5 billion years old. By considering these ages, we can appreciate the relative youth of our planet and the brevity of human existence.

- The universe is estimated to be around 13.8 billion years old.
- The Earth is estimated to be around 4.5 billion years old.
Key Takeaway:
- Understanding relative age requires considering the cosmic context of our planet and universe.
- By studying the ages of stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects, we can gain insight into the vastness of time and our position within it.
In conclusion, understanding relative age is essential for grasping the complexity of time and our position within it. By using analogies, studying the rock record, fossil succession, relative dating methods, and considering the cosmic context, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the vastness of time and the history of our planet.
What is relative age?
+Relative age is the age of an object, event, or process relative to others, rather than its absolute age in years.
How is relative age determined?
+Relative age is determined by the position of an object or event within a sequence, such as the layer cake analogy or the rock record.
What is the difference between relative and absolute age?
+Relative age is the age of an object or event relative to others, while absolute age is the age of an object or event in years.
We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of relative age and its significance in understanding the complexity of time. Share your thoughts and comments below!
